Learn to Astronomy: Discover the fascinating world of Saturn’s extensive moon system. Dive into the question: why does Saturn have so many moons? Explore the captivating theories behind this celestial phenomenon and unravel the secrets of this magnificent ringed planet. Join us on an astronomical adventure as we unlock the mysteries of Saturn’s mesmerizing lunar collection.
The Fascinating Mystery of Saturn’s Abundance of Moons
The Fascinating Mystery of Saturn’s Abundance of Moons
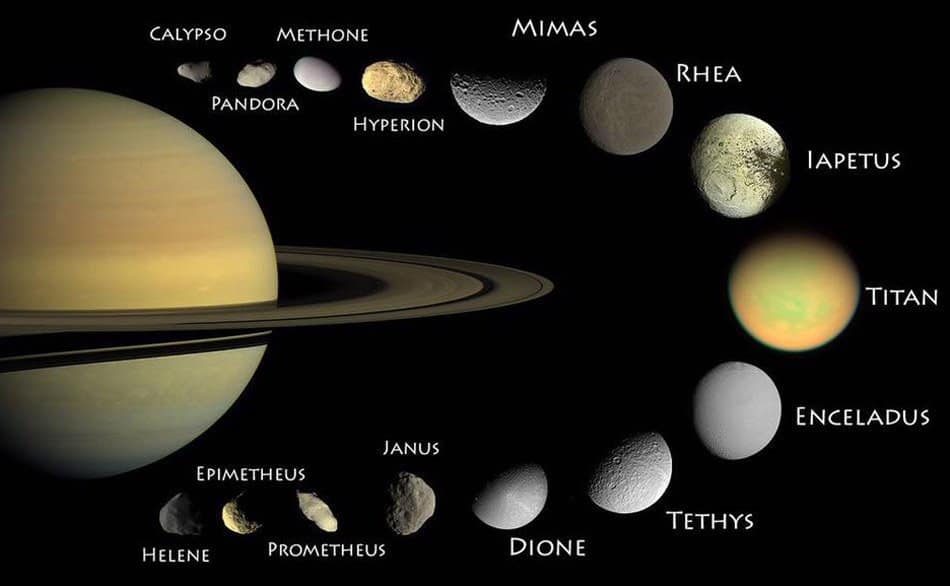
Saturn, the sixth planet from the Sun, has always captured the fascination of astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. One of the most intriguing aspects of this gas giant is its incredible abundance of moons. With a current count of 82 confirmed moons, surpassing even Jupiter’s 79, Saturn stands as the undisputed champion of moon-rich planets in our solar system.
One might wonder, how did Saturn acquire so many moons? The answer lies in its massive gravitational influence and its unique formation history. Primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, Saturn boasts a mass nearly 100 times that of Earth. This immense gravitational force, combined with its large size, enables Saturn to capture passing objects into its orbit.
The majority of Saturn’s moons are relatively small, composed mostly of ice and rock. They range in size from less than a kilometer to several hundred kilometers in diameter. While some of these moons orbit close to Saturn, others reside in more distant regions, forming intricate and complex systems.
One of Saturn’s most famous moons is Titan, the second-largest moon in our solar system and the only moon to have a substantial atmosphere. Scientists believe that Titan’s atmosphere may resemble the early Earth’s, making it an essential target for exploration in the search for extraterrestrial life.
Interestingly, not all of Saturn’s moons are permanent residents in its orbit. Some moons are transient, moving in and out of Saturn’s sphere of influence over time. These transient moons are thought to have originated from outside the Saturnian system and were captured during close encounters.
Despite extensive research and observations, there are still mysteries surrounding Saturn’s moon abundance. Scientists continue to study the origins and formation processes of these moons, seeking to unravel the secrets hidden within their composition and behavior.
In conclusion, Saturn’s vast collection of moons is a testament to the planet’s gravitational power and unique history. Unlocking the mysteries of these moons not only deepens our understanding of Saturn but also provides valuable insights into the formation and dynamics of moons in our solar system and beyond.
What If You Jumped Into Saturn’s Rings?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/8SgtXNftOEM”/]
Why Can’t You Walk On Saturn?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/p2JdLhHAmkY”/]
Frequent questions
Why does Saturn have such a large number of moons compared to other planets in our solar system?
Saturn has such a large number of moons compared to other planets in our solar system due to several factors.
One reason is that Saturn’s large size and strong gravitational pull allow it to capture and retain more moons than smaller planets. The planet’s powerful gravity can capture passing objects like asteroids or comets and make them orbit around it as moons.
Another factor is the presence of several “shepherd” moons, which help to maintain the stability of Saturn’s rings. These shepherd moons generate gravitational forces that shape and confine the particles within the rings, preventing them from dispersing or colliding with each other.
Additionally, Saturn’s distance from the Sun allows for more stable moon orbits. The outer regions of the solar system have a higher concentration of icy bodies, providing more opportunities for moon formation.
Lastly, Saturn’s dynamic environment, which includes its rings and strong magnetic field, creates conditions favorable for moon formation. The interactions between the rings, moons, and the planet itself can result in the fragmentation and accretion of materials, leading to the formation of new moons.
Overall, Saturn’s large size, strong gravitational pull, the presence of shepherd moons, its distance from the Sun, and its dynamic environment all contribute to the planet having a larger number of moons compared to other planets in our solar system.
How do the gravitational forces from Saturn’s massive size contribute to the formation and retention of numerous moons?
The gravitational forces from Saturn’s massive size play a crucial role in the formation and retention of numerous moons.
Saturn’s gravitational pull is incredibly strong due to its large mass, which creates a powerful gravitational field around the planet. This gravitational force attracts nearby objects, including smaller celestial bodies like asteroids and comets. Over time, these objects can be captured by Saturn’s gravity and become moons.
The process of moon formation around Saturn begins with the capture of a small object within its gravitational influence. Once captured, these objects are pulled into elongated orbits around the planet. As they orbit Saturn, they may collide or merge with other captured objects, gradually growing larger in size.
Saturn’s strong gravity also helps retain its moons. The gravitational force between Saturn and its moons keeps them in stable orbits around the planet. If the gravitational force were weaker, the moons could drift away or be easily perturbed by other celestial bodies. However, thanks to Saturn’s massive size, it exerts a significant gravitational pull that keeps its moons intact.
Moreover, some of Saturn’s moons are locked in resonances called orbital resonances. These resonances occur when the orbital periods of two celestial bodies are related by a ratio of small integers. For example, one moon might complete three orbits around Saturn for every two orbits completed by another moon. These resonances help stabilize the moons’ orbits and prevent them from colliding or escaping Saturn’s gravitational pull.
In summary, the massive size of Saturn contributes to the formation and retention of numerous moons through its strong gravitational forces. This gravitational pull captures small objects and allows them to grow into moons, while also keeping them in stable orbits around the planet. The phenomenon of orbital resonances further enhances the stability of Saturn’s moon system.
What are the possible mechanisms behind the ongoing formation of new moons around Saturn, and how does this process differ from that of other planets?
One possible mechanism behind the ongoing formation of new moons around Saturn is through the process of accretion from a protoplanetary disk. This occurs when the material in the disk gradually comes together and forms larger bodies, such as planets or moons. In the case of Saturn, these moons are thought to have formed from the remnants of the original gas and dust disk that surrounded the planet during its early stages of formation.
Another mechanism that may contribute to moon formation around Saturn is capture. This occurs when an object, such as a passing asteroid or comet, is gravitationally pulled into orbit around the planet. These captured objects can then become moons if they remain stable in their orbit over long periods of time.
It is important to note that the process of moon formation around Saturn is not unique to this planet. Similar mechanisms are believed to be responsible for the formation of moons around other gas giant planets in our solar system, such as Jupiter and Uranus. However, there are some differences in the specifics of moon formation between these planets.
One notable difference is the size and diversity of the moon populations. Saturn has a large number of moons, with over 80 confirmed to date. Some of these moons are relatively small, while others, such as Titan and Enceladus, are substantial in size and exhibit complex geological activity. In contrast, Jupiter has over 70 moons, with four large moons known as the Galilean moons. Uranus, on the other hand, has a smaller number of moons, with only 27 confirmed so far.
Another difference lies in the dominant mechanisms of moon formation. While both accretion and capture are believed to contribute to moon formation around Saturn, it is thought that accretion played a more significant role in shaping its diverse moon population. In contrast, the moons around Jupiter and Uranus are believed to have mainly formed through capture events.
In conclusion, the ongoing formation of new moons around Saturn is likely a result of accretion from a protoplanetary disk and capture of passing objects. This process shares similarities with moon formation around other gas giant planets but also exhibits some distinct differences in terms of moon populations and dominant formation mechanisms.
In conclusion, Saturn’s extensive collection of moons serves as a captivating reminder of the wonders of our solar system. Through ongoing exploration and advancements in technology, scientists have been able to identify and study these intriguing celestial bodies, bringing us closer to understanding the complexities of Saturn’s vast domain.
The reason behind Saturn’s abundant moon population can be attributed to several factors. The planet’s strong gravitational pull, coupled with its vast rings, creates an environment conducive to moon formation. Furthermore, planetary resonances and interactions among the moons themselves have played a significant role in shaping their numbers and orbits.
Each of Saturn’s moons possesses unique characteristics, ranging from icy surfaces to subsurface oceans that potentially harbor signs of life. These moons offer scientists valuable insights into the processes that govern the formation and evolution of celestial bodies, making Saturn a crucial laboratory for studying planetary systems beyond our own.
As our understanding of Saturn’s moons continues to evolve, future missions and scientific endeavors will undoubtedly unearth even more fascinating findings. The intricate dance of gravity, tidal forces, and orbital dynamics will continue to shape and reshape Saturn’s moon system, captivating astronomers and enthusiasts alike for generations to come.
Saturn’s plethora of moons is a testament to the vast diversity and complexity of the cosmos, reminding us of the infinite possibilities that exist beyond our home planet. Exploring these celestial bodies and unraveling their mysteries serves not only to satisfy our innate curiosity but also to expand our knowledge of the universe and our place within it.