Introduction: Have you ever wondered about the origins of all matter in the universe? In this article, we delve into the fascinating question of where does all matter come from, exploring the theories and discoveries that shed light on the cosmic processes responsible for the creation of everything we see around us. Join us on a journey to unravel the mysteries of our existence in the vastness of space.
The Origins of Matter: Exploring the Cosmic Sources in Astronomy
The Origins of Matter: Exploring the Cosmic Sources in Astronomy
The study of astronomy allows us to delve into the origins of matter and understand the cosmic sources from which it is derived. Matter, the fundamental building block of the universe, is intricately connected to the processes that occur in space. By examining the various celestial objects and phenomena, astronomers can piece together the story of how matter came to be.
One of the primary cosmic sources of matter is stellar nucleosynthesis, which takes place within stars. Through the fusion of lighter elements like hydrogen and helium, heavier elements such as carbon, oxygen, and iron are synthesized. These elements are then released into space through processes like stellar winds or during stellar explosions, such as supernovae.
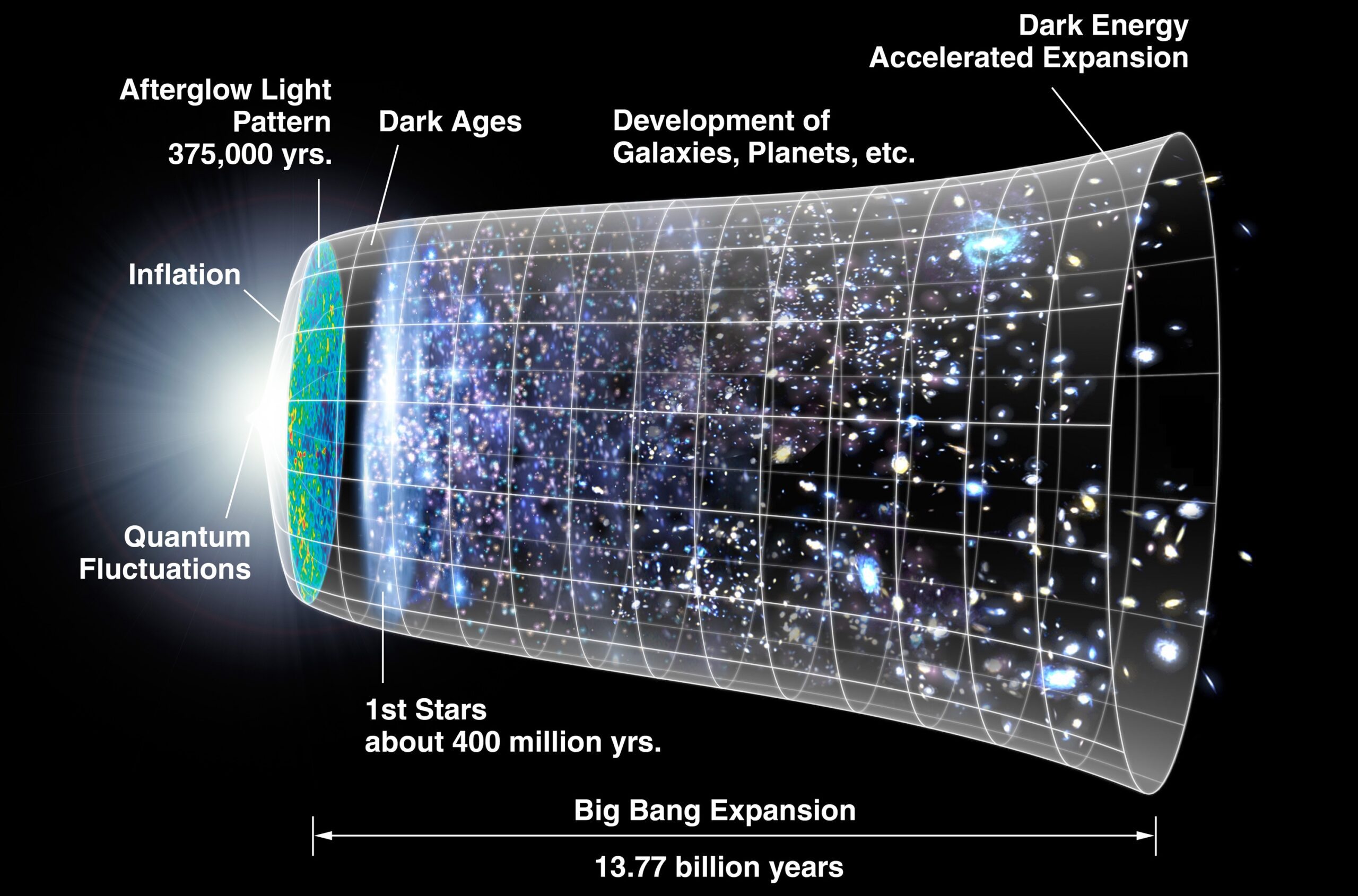
Another significant source of matter in the universe is the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). The CMB is the remnant energy from the early stages of the universe, often referred to as the “afterglow” of the Big Bang. By studying the CMB, astronomers can gain insights into the composition and distribution of matter at its infancy.
Additionally, the study of galaxies provides crucial information about the origins of matter. Galaxies are vast systems composed of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter. The interplay between these components shapes the evolution of galaxies and influences the formation of new stars. Galaxies also serve as reservoirs for various elements, and interactions between galaxies can lead to the mixing and exchange of matter.
Furthermore, exploring the properties of cosmic rays gives us valuable clues about the sources and nature of matter in the universe. Cosmic rays are high-energy particles that originate from astrophysical phenomena such as supernovae or active galactic nuclei. By analyzing their composition and energy spectra, scientists can gain insights into the processes that generate these particles and the matter they carry.
In conclusion, astronomy provides a window into the origins of matter by studying various cosmic sources such as stellar nucleosynthesis, cosmic microwave background radiation, galaxies, and cosmic rays. By understanding how different elements are created and distributed throughout the universe, we can gain a deeper understanding of our cosmic origins.
Why Did Time Start Going Forward?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/x9m0sz2sUfU”/]
Jordan Matter FORGOT To Stop Recording.. (Salish & Nidal MAD)
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/FSdkh6Rireg”/]
Preguntas Frecuentes
What is the origin of all matter in the universe according to current astronomical theories?
According to current astronomical theories, the origin of all matter in the universe is believed to be the result of a process called cosmic inflation. Cosmic inflation posits that in the very early stages of the universe, it underwent a rapid and exponential expansion, during which tiny quantum fluctuations were amplified and stretched across vast distances.
These fluctuations eventually led to the formation of galaxies, stars, and ultimately, all matter as we know it.
Another important concept in understanding the origin of matter is the Big Bang theory. The Big Bang theory suggests that the universe originated from a singularity, an extremely hot and dense state, approximately 13.8 billion years ago. As the universe expanded and cooled down, elementary particles such as protons, neutrons, and electrons formed.
Through various processes like nuclear fusion in the cores of stars, these elementary particles eventually combined to form atoms and more complex structures.
It is important to note that our current understanding of the origin of matter is based on theoretical models, experimental observations, and ongoing research. While these concepts provide a framework for explaining the development of the universe, there is still much to learn and discover about the fundamental nature of matter and its origins.
How do astronomers believe that the Big Bang gave rise to all matter in the universe?
Astronomers believe that the Big Bang gave rise to all matter in the universe through a process known as nucleosynthesis. During the early moments of the Big Bang, the universe was extremely hot and dense. As it expanded and cooled, subatomic particles such as protons and neutrons began to form.
Within the first few minutes after the Big Bang, the conditions were perfect for nuclear reactions to occur. Protons and neutrons collided and combined to form atomic nuclei, a process called nucleosynthesis. These nuclei consisted mainly of hydrogen and helium, with trace amounts of lithium and beryllium.
However, the amount of helium and other elements produced during nucleosynthesis was not sufficient to account for the observed abundances of these elements in the universe today. This led astronomers to propose that there must have been additional processes at work to explain the origin of heavier elements like carbon, oxygen, and iron.
These additional processes include stellar nucleosynthesis, which occurs within the cores of stars. Through nuclear fusion reactions, stars convert hydrogen into helium and then continue to fuse helium into heavier elements. During supernova explosions, these synthesized elements are scattered back into the surrounding space, enriching the interstellar medium with heavier elements.
Over billions of years, as stars formed and died, this cycle of nucleosynthesis and enrichment continued, contributing to the vast array of elements present in the universe today. Thus, astronomers believe that the Big Bang set the stage for the formation of the basic building blocks of matter, and subsequent stellar processes shaped the composition of the elements we observe.
Can the formation of matter from energy be explained in the context of astrophysics?
Astrophysics can indeed provide valuable insights into the formation of matter from energy.
According to the Big Bang theory, the universe began as an infinitely small and dense singularity, where all matter and energy were concentrated. As the universe expanded and cooled, this primordial energy started to convert into matter.
In the first few minutes after the Big Bang, the conditions were so incredibly hot and energetic that only the lightest elements like hydrogen and helium could form through a process called nucleosynthesis. However, the formation of heavier elements required the extreme conditions found within stars.
Inside stars, immense gravitational pressure and temperatures cause nuclear fusion reactions, which convert lighter elements into heavier ones. Through these processes, stars create elements like carbon, oxygen, and iron. When massive stars eventually explode as supernovae, they release this enriched matter back into space.
It is through these stellar processes that matter in the universe is created from energy. The expelled matter then becomes part of the interstellar medium, where new star-forming regions can incorporate it into their molecular clouds. These clouds collapse under gravity, forming protostars that ignite into new stars.
The cycle of stellar birth and death continues as matter is recycled over billions of years, enriching the universe with heavier elements through each generation of stars. This ongoing process has led to the diverse array of elements and compounds we observe today.
In conclusion, astrophysics provides a framework for understanding how matter is formed from energy through processes such as nucleosynthesis in the early universe and stellar fusion reactions. The study of these phenomena helps us comprehend the origins and composition of the matter that surrounds us.
In conclusion, the question of where all matter comes from is a fundamental one in the field of astronomy. Through extensive research and observations, scientists have established that the universe originated from a singularity, a point of infinite density and temperature, through a phenomenon known as the Big Bang. This event marked the beginning of everything we know today.
However, the origin of matter itself is still not fully understood. While the Big Bang theory explains how the universe expanded and evolved, it does not provide a complete explanation for the creation of matter.
One possible explanation is through particle physics. According to this theory, matter could have emerged from the interactions of fundamental particles during the early stages of the universe. These particles, such as quarks and leptons, combined to form atoms, which eventually led to the creation of stars, galaxies, and everything we see around us.
Another hypothesis suggests that matter could have been produced during cosmic inflation. This theory posits that the rapid expansion of the universe shortly after the Big Bang generated energy that transformed into matter. The precise mechanisms behind this process are still being studied by physicists and astronomers.
Furthermore, ongoing experiments at particle accelerators, such as the Large Hadron Collider, aim to recreate conditions similar to those present during the early universe. These experiments could potentially shed light on the origin of matter and help scientists understand how particles interact and form the building blocks of the universe.
In summary, the question of where all matter comes from remains a fascinating and complex puzzle in the field of astronomy. While significant progress has been made in understanding the origins of the universe through the Big Bang theory, the exact processes that led to the creation of matter are still open for investigation.
Continued research and experiments will be crucial in unraveling this mystery and expanding our knowledge of the cosmos.