Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of meteor speeds. Discover how these celestial objects hurtle through space at incredible velocities and learn about the factors that influence their dynamics. Join us on this celestial journey to uncover the awe-inspiring speeds of meteors in our vast universe.
Understanding the Velocity of Meteors in Astronomy
The velocity of meteors is crucial in the field of astronomy. Meteors, also known as shooting stars, are small particles that enter Earth’s atmosphere and burn up, creating a luminous trail. The velocity of meteors refers to their speed as they travel through space before entering the atmosphere.
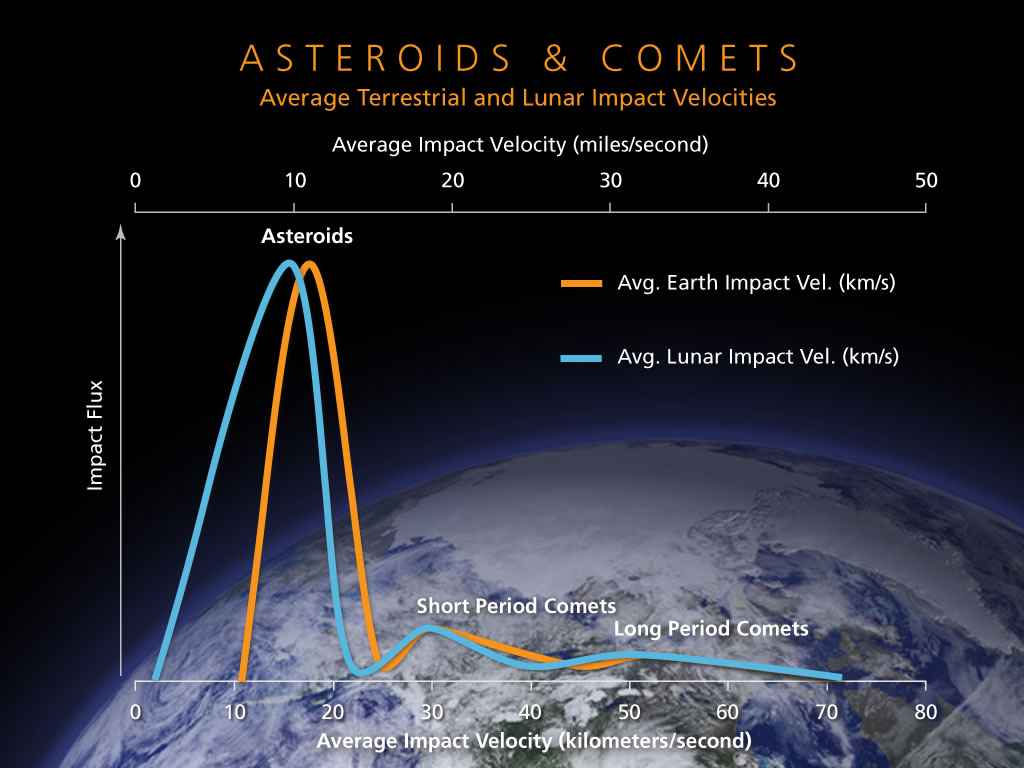
The velocity of meteors can vary significantly depending on various factors such as the size and composition of the meteoroid, its angle of entry, and the gravitational forces acting upon it. Average velocity of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere is around 40 kilometers per second (25 miles per second).
This incredible speed is due to their initial velocities in space combined with the acceleration caused by Earth’s gravity.
Measuring the velocity of meteors is challenging but essential for understanding the nature of these celestial objects. Scientists use various techniques to estimate velocity, including radar systems that track meteor echoes and video recordings that capture the meteor’s trajectory. By analyzing the data obtained from these methods, researchers can calculate the initial velocity and potentially unravel the meteoroid’s origin.
The velocity of meteors plays a significant role in determining their fate once they enter Earth’s atmosphere. Most meteors, due to their high velocities, disintegrate completely before reaching the surface. However, larger meteors with slower velocities may survive the atmospheric entry and reach the ground, becoming meteorites.
Studying these meteorites provides valuable insights into the composition and history of our solar system.
In conclusion, understanding the velocity of meteors is essential in the field of astronomy. It helps scientists determine the behavior, origin, and fate of these fascinating objects that grace our night skies.
Why Going Faster Than Light Leads to Time Paradoxes?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/_9mpdMj10D0″/]
If Humans Lived 400 Years, You’d Still Be a Teen at 80
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/HT6iWaHygzI”/]
Preguntas Frecuentes
What is the average speed of a meteor entering the Earth’s atmosphere?
The average speed of a meteor entering the Earth’s atmosphere is around 40 kilometers per second (25 miles per second). This speed can vary depending on the size and composition of the meteor, as well as its angle of entry and location in the atmosphere.
Meteors are typically traveling at high velocities when they enter the Earth’s atmosphere, often reaching speeds exceeding 70 kilometers per second (43 miles per second). As they collide with particles in the atmosphere, the friction generated causes them to heat up and create the streak of light known as a shooting star, or meteor.
Can meteors travel faster than the speed of light?
No, meteors cannot travel faster than the speed of light. According to Einstein’s theory of relativity, the speed of light is an absolute limit in our universe. Nothing can travel faster than light. Meteors are small rocky or metallic objects that enter Earth’s atmosphere and burn up due to friction.
They typically travel at speeds between 11 to 72 kilometers per second, which is incredibly fast but still much slower than the speed of light, which is about 299,792 kilometers per second. Meteors obey the laws of physics and cannot exceed the speed of light.
How does the speed of a meteor affect its visibility and brightness?
The speed of a meteor can have a significant impact on its visibility and brightness.
When a meteor enters the Earth’s atmosphere, it undergoes intense heating due to air compression. This process causes the meteor to vaporize and create a glowing trail of ionized gas, known as a meteor train. The brightness of a meteor depends on the amount of light it produces, which is determined by various factors, including its size, composition, and velocity.
Higher-speed meteors tend to be brighter and more easily visible compared to slower ones. This is because a faster-moving meteor experiences greater air resistance, leading to more intense heat and brighter light emission. The increased energy generated by a high-speed meteor can result in a more luminous and easily observable event.
However, extremely high-speed meteors can also create a phenomenon known as a bolide. A bolide is an exceptionally bright meteor that explodes with a sudden burst of light and often produces a sonic boom.
These events are caused by the intense atmospheric pressure encountered by the meteor, usually due to its high entry speed. Bolides can be incredibly striking and visible even during daylight hours.
In summary, the speed of a meteor affects its visibility and brightness, with higher-speed meteors generally being more luminous and easily observed. The intense heat generated by faster-moving meteors increases the likelihood of creating a bright meteor train or a spectacular bolide event.
In conclusion, the speed of a meteor plays a significant role in understanding its impact and behavior in our atmosphere. As it hurtles through space, a meteor can reach speeds of several tens of thousands of kilometers per hour, creating a stunning display of light and heat upon entry into our atmosphere.
Understanding the immense velocity at which meteors travel helps astronomers calculate their trajectories and predict potential hazards they may pose to Earth. Furthermore, studying the speed of meteors provides valuable insights into the origin and composition of these celestial objects.
By analyzing their velocity, scientists can determine if they originate from the asteroid belt or the distant reaches of our solar system. Ultimately, the speed of a meteor is not only an awe-inspiring aspect of astronomy but also a crucial factor in unraveling the mysteries of our universe.