Have you ever wondered how the sun manages to stay suspended in the vast expanse of space? In this article, we will dive into the fascinating mechanisms that keep our beloved star in place, defying the powerful forces of gravity and ensuring its continual presence in our solar system.
Discover the secrets behind the sun’s remarkable stability and the intricate dance it performs with other celestial bodies. Join us on this journey of cosmic exploration at Learn to Astronomy.
The Mechanics Behind the Sun’s Stability in the Vacuum of Space
The stability of the Sun in the vacuum of space is maintained by a delicate balance between gravitational forces and internal processes. The gravitational force acting on the Sun, caused by its massive size, is constantly pulling matter towards its center. This inward force is counteracted by an outward pressure gradient resulting from the high temperatures and densities in the Sun’s core.
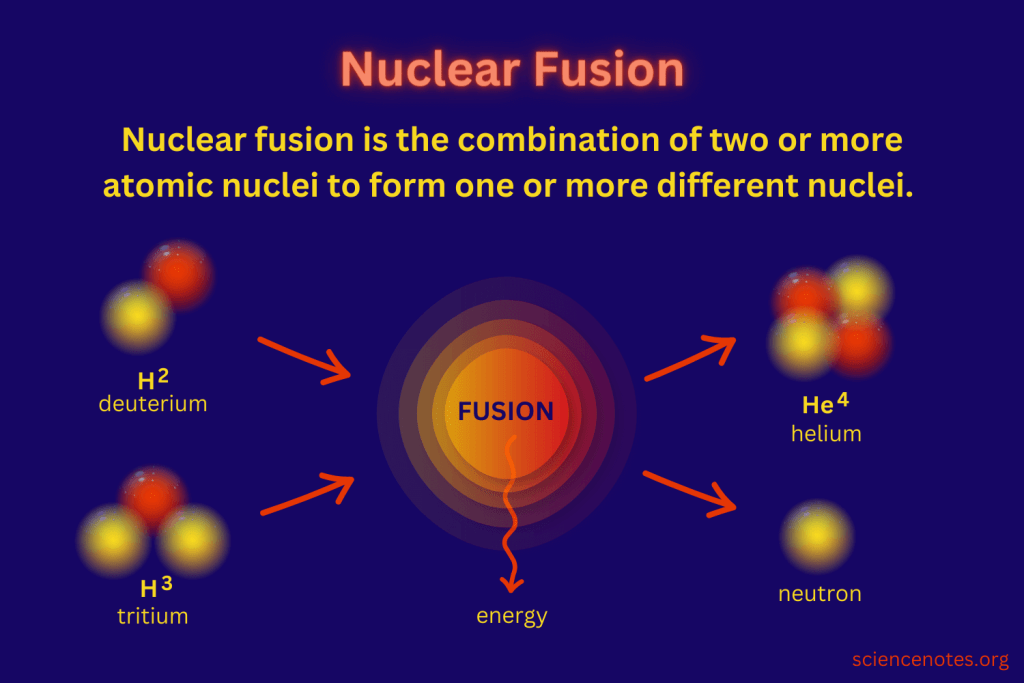
The Sun generates energy through nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms combine to form helium, releasing a tremendous amount of energy in the process. This energy production creates an outward radiation pressure that opposes the gravitational force, helping to maintain the Sun’s stability.
Additionally, the Sun undergoes a continuous process of hydrostatic equilibrium, wherein the weight of the overlying material is balanced by the upward pressure exerted by the lower layers. This equilibrium ensures that the Sun maintains its shape and does not collapse under its own gravity.
Furthermore, the core temperature of the Sun is around 15 million degrees Celsius, which is hot enough to sustain nuclear fusion reactions. This high temperature provides the necessary energy for the Sun to counteract the inward gravitational force.
Overall, the stability of the Sun in the vacuum of space is crucial for the existence of life on Earth. Its ability to maintain a delicate balance between gravitational forces, internal pressure gradients, energy production through nuclear fusion, and hydrostatic equilibrium enables the Sun to shine steadily for billions of years.
How Does The Nucleus Hold Together?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/E8hyodMhbRw”/]
No Human Has Ever Left Earth’s Atmosphere, Here’s Why
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/aPBVGXdsR0I”/]
Frequent questions
How does the sun’s gravitational pull keep it from drifting away in space?
The Sun’s gravitational pull is what keeps it from drifting away in space. Gravity is a force that attracts objects with mass towards each other. In the case of the Sun, its enormous mass creates a strong gravitational field that holds it together. This gravitational force is constantly pulling all the matter within the Sun inward toward its center. The gravitational force is so strong that it overcomes any outward forces trying to push the Sun apart.
The Sun achieves a delicate balance between the inward gravitational force and the outward pressure caused by nuclear fusion in its core. The immense heat and pressure at the Sun’s core cause hydrogen atoms to undergo nuclear fusion, releasing an enormous amount of energy. This energy is what makes the Sun shine. The process of nuclear fusion creates an outward pressure that tends to push the Sun’s material away.
However, the Sun’s gravity counteracts this outward pressure, keeping the mass of the Sun together. The gravitational force pulls everything inward, including the hot plasma created by nuclear fusion. This inward pull maintains the Sun’s shape and prevents it from drifting away into space.
Ultimately, the Sun’s gravitational pull is the primary force that keeps it from drifting away. It’s like a gravitational tug-of-war between the inward pull of gravity and the outward pressure of nuclear fusion. This balance allows the Sun to maintain its stability and continue to shine for billions of years.
What forces counteract the outward push of the sun’s energy and keep it stable in space?
The forces that counteract the outward push of the sun’s energy and keep it stable in space are the inward gravitational force and the pressure from nuclear fusion.
The sun is constantly undergoing nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms combine to form helium, releasing a tremendous amount of energy in the process. This energy creates an outward pressure that tends to push the sun’s material apart. However, the gravity of the sun acts as an inward force, pulling everything towards its center.
The gravitational force of the sun is incredibly strong due to its large mass. It pulls all the material inward, counteracting the outward pressure from the energy generated by nuclear fusion. This balance between the outward push of energy and the inward pull of gravity keeps the sun stable in space.
Therefore, it is the gravitational force and the pressure from nuclear fusion that counteract the outward push of the sun’s energy and maintain its stability in space.
How does the sun maintain its position in space without being pulled towards other celestial bodies?
The sun maintains its position in space without being pulled towards other celestial bodies due to a delicate balance between two forces: gravity and inertia.
Gravity is the force that attracts objects with mass towards each other. In the case of the sun, its immense mass creates a strong gravitational pull that affects all other objects in its vicinity, including planets, asteroids, and comets. However, gravity is not the only force at play.
Inertia, on the other hand, is the property of an object to resist changes in its motion. The sun, being a massive object, has a tremendous amount of inertia. This means that it will continue moving in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. In the case of the sun, the combination of its gravity and inertia causes it to maintain its position in space.
While the sun does exert a gravitational force on surrounding celestial bodies, the strength of its gravity is counteracted by their own inertia as they orbit around the sun. Planets, for example, continually move in elliptical orbits due to the combined influences of the sun’s gravity and their own inertia. This balance of forces allows the sun to remain relatively stable in its position in space.
It is important to note that the sun is not completely stationary. Like all celestial bodies, it is part of the Milky Way galaxy, which is constantly in motion. The sun orbits around the center of the galaxy, along with billions of other stars, influenced by the gravitational forces exerted by other celestial bodies within the galaxy.
In conclusion, the sun maintains its position in space through a delicate balance between the force of gravity and the inertia of both the sun itself and the celestial bodies within its influence. This balance allows the sun to stay relatively stable while also participating in the broader movements of the Milky Way galaxy.
In conclusion, the sun’s ability to stay in space is due to the delicate balance between gravity and nuclear fusion. The immense gravitational force generated by the sun’s mass keeps it together, while the intense heat and pressure at its core enable nuclear fusion to occur. This process releases a tremendous amount of energy, which counterbalances the gravitational pull, preventing the sun from collapsing in on itself.
Understanding the mechanisms that allow the sun to remain stable in space is crucial in comprehending its role in the universe and its impact on Earth. By continuing to study and observe the sun, scientists can gain valuable insights into not only the workings of our star but also the broader field of astronomy. Through ongoing research and exploration, we can further unravel the mysteries of our solar system and beyond.
The sun’s ability to stay in space is a testament to the incredible forces at work in the universe, highlighting the beauty and complexity of the cosmos. As we continue to delve deeper into astronomical phenomena, discoveries about the sun’s stability will undoubtedly contribute to our ever-expanding knowledge of the vast expanse of space.