Learn to Astronomy: Explore the enigma of Mars’ arid landscape in our latest article: “Why is there no water on Mars?” Uncover the captivating reasons behind this perplexing phenomenon as we delve into the geological, atmospheric, and historical factors that contribute to the absence of liquid water on the Red Planet. Journey with us to unravel the mysteries of Mars’ dry surface and uncover its potential for extraterrestrial life.
Unveiling the Mystery: Exploring the Absence of Water on Mars in Astronomy
Unveiling the Mystery: Exploring the Absence of Water on Mars
The absence of water on Mars has been a perplexing question for astronomers and researchers for decades. Since the early observations of Mars through telescopes, scientists have observed hints of a once-wet planet. However, the search for liquid water on Mars has proven to be a complex and challenging endeavor.
One of the primary reasons for the absence of water on Mars is its thin atmosphere. Unlike Earth, Mars has a much thinner atmosphere, which cannot support liquid water in a stable state. The extremely low atmospheric pressure on Mars causes any water present to either freeze or evaporate rapidly, making it impossible for liquid water bodies to exist on the surface.
Another factor contributing to the absence of visible water on Mars is the planet’s low temperature. Mars is significantly colder than Earth, with average temperatures dropping well below freezing. These frigid conditions further inhibit the presence of liquid water, as it would instantly freeze upon contact with the planet’s surface.
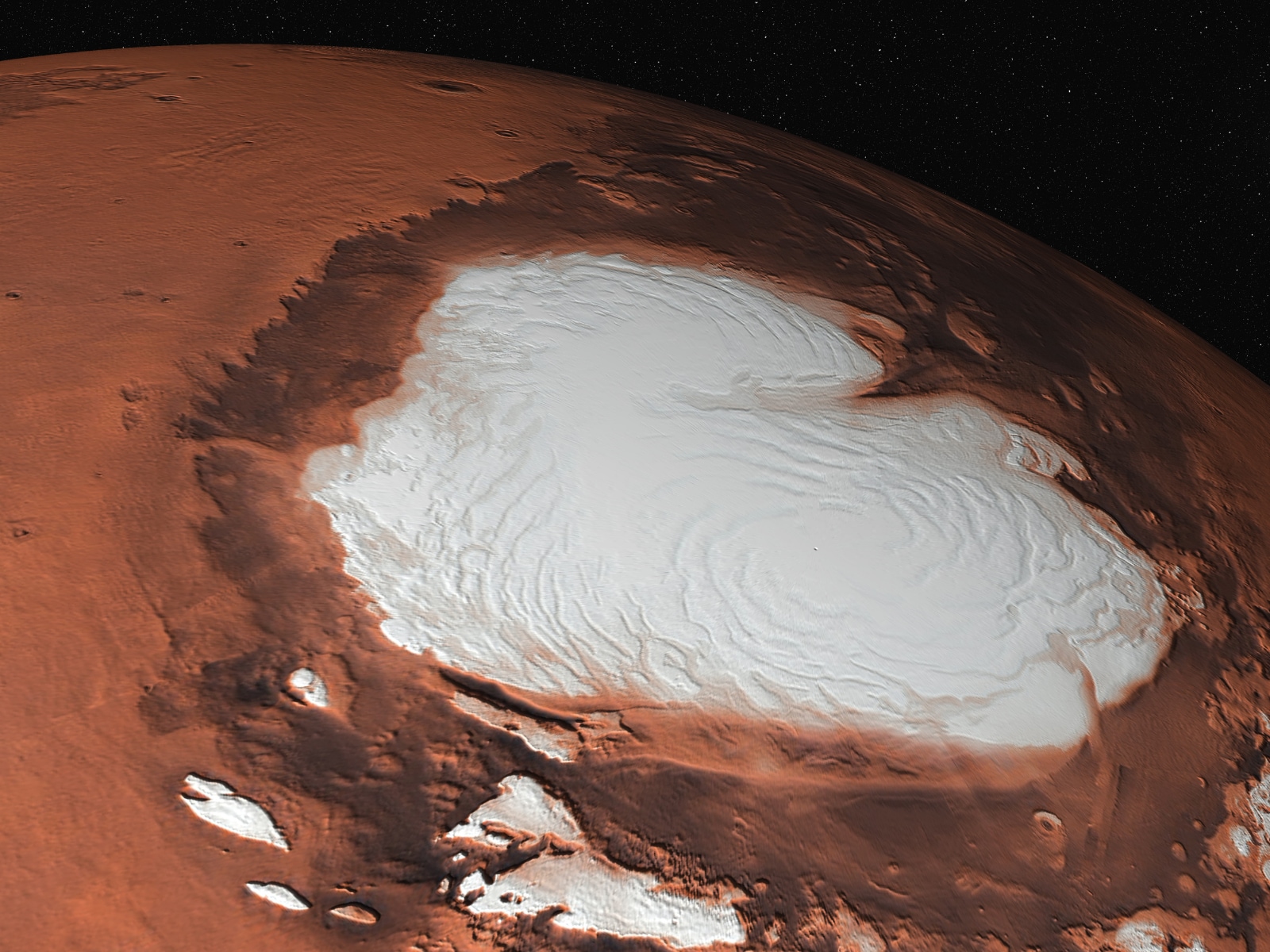
However, while visible liquid water might not be present on Mars, recent discoveries have indicated the existence of frozen water in the form of ice caps and subsurface reservoirs. These findings suggest that water may still be present on the planet in a solid or frozen state.
Scientists have also explored the possibility of briny water on Mars. The presence of salts and minerals in the Martian soil could potentially lower the freezing point of water, allowing it to remain in a liquid state despite the harsh conditions. This hypothesis has gained traction in recent years, with evidence of hydrated salts detected on the planet’s surface.
In conclusion, although the absence of visible liquid water on Mars remains a mystery, scientific advancements have shed light on the presence of frozen water and the potential for briny water on the planet. Further exploration and research are necessary to unravel the complexities surrounding water on Mars and unlock the secrets of the Red Planet.
Place HTML tags in the most important sentences of the text:
The absence of water on Mars has been a perplexing question for astronomers and researchers for decades. One of the primary reasons for the absence of water on Mars is its thin atmosphere. The extremely low atmospheric pressure on Mars causes any water present to either freeze or evaporate rapidly, making it impossible for liquid water bodies to exist on the surface. Another factor contributing to the absence of visible water on Mars is the planet’s low temperature. Recent discoveries have indicated the existence of frozen water in the form of ice caps and subsurface reservoirs. These findings suggest that water may still be present on the planet in a solid or frozen state. The presence of salts and minerals in the Martian soil could potentially lower the freezing point of water, allowing it to remain in a liquid state despite the harsh conditions.
10 Questionable Things NASA Has Found On Mars
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/bW-U3BSqzFQ”/]
Perseverance Rover Sent Latest SHOCKING Images of Martian Life
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/a18HmVeRbYc”/]
Frequent questions
What factors contribute to the scarcity of water on Mars?
There are several factors that contribute to the scarcity of water on Mars:
1. Thin Atmosphere: Mars has a very thin atmosphere compared to Earth, which makes it difficult for water to exist in its liquid form. The low atmospheric pressure causes water to either freeze or evaporate, leading to its scarcity.
2. Low Temperatures: Mars has extremely cold temperatures, especially at the poles where water ice is more likely to be found. These low temperatures make it challenging for liquid water to exist on the planet’s surface, further contributing to its scarcity.
3. Lack of Erosion: Mars lacks the same level of erosion processes such as rainfall and flowing water as Earth. Without significant erosion, water is unable to accumulate in large quantities and is quickly lost due to evaporation or sublimation into the atmosphere.
4. Escape to Space: Mars has a weaker gravity compared to Earth, which means that its atmosphere is more easily lost to space. Over time, this loss of atmosphere has resulted in the loss of water as well, further contributing to its scarcity.
5. Geological Processes: Mars has undergone extensive geological processes that have altered its surface and potentially trapped water in underground reservoirs or ice caps. The challenge lies in accessing and utilizing these water resources effectively.
In conclusion, the combination of Mars’ thin atmosphere, low temperatures, lack of erosion, escape of water and atmosphere to space, and geological processes contribute to the scarcity of water on the planet. These factors make finding and harnessing water resources a significant challenge for future human exploration and colonization of Mars.
How does the lack of a substantial atmosphere on Mars affect the presence of water?
The lack of a substantial atmosphere on Mars has a significant impact on the presence of water. Unlike Earth, Mars has a very thin atmosphere that does not provide sufficient pressure for liquid water to exist on the surface. The atmospheric pressure on Mars is about 0.6% that of Earth’s, making it impossible for liquid water to be stable.
However, despite the low atmospheric pressure, water can still exist on Mars in the form of ice. The polar ice caps on Mars consist mainly of frozen water, similar to Earth’s polar ice caps. Additionally, there is evidence of water ice in the subsurface of Martian soil and within certain craters.
The thin atmosphere also affects the behavior of liquid water on Mars. If water were to exist in liquid form under the current conditions, it would rapidly evaporate due to the low atmospheric pressure. The low temperatures on Mars also make it difficult for liquid water to be stable on the surface.
Overall, the lack of a substantial atmosphere on Mars limits the presence of liquid water on its surface, but it does not completely eliminate the existence of water. The discovery of water ice in various forms suggests that Mars may have had a more significant amount of water in the past, which could have supported the possibility of life. Further exploration and studies are necessary to better understand the history and potential for water on Mars.
What implications does the absence of liquid water on Mars have for potential human colonization efforts?
The absence of liquid water on Mars has significant implications for potential human colonization efforts. Water is essential for life as we know it, and its absence makes it much more challenging for humans to survive and establish a sustainable colony.
Without liquid water, the primary challenge would be providing enough water for drinking, growing crops, and maintaining essential systems. Water is heavy and costly to transport from Earth, so finding local sources of water on Mars would be crucial. While there is evidence of subsurface ice on Mars, accessing and extracting this water would be technologically complex and energy-intensive.
Furthermore, without liquid water, the Martian environment becomes extremely hostile to life. Water is not only a source of hydration, but it is also necessary for basic biological functions, such as cellular metabolism. The absence of liquid water severely limits the potential for sustaining plant and animal life, which in turn affects the availability of food and oxygen.
In addition, liquid water is a critical resource for fuel production. Hydrogen and oxygen obtained from water can be turned into rocket propellant through processes like electrolysis. This could enable future interplanetary travel and facilitate the return of astronauts to Earth. Without accessible water, the refueling and resupplying of spacecraft on Mars would be highly complicated and prohibitively expensive.
However, it’s important to note that even with the absence of liquid water, human colonization efforts on Mars are still technically feasible. Advances in technology and innovation may allow us to overcome these challenges. For example, future missions could focus on developing efficient water extraction techniques or harnessing other resources like Martian subsurface reserves of water ice.
In conclusion, while the absence of liquid water presents numerous challenges, it does not completely negate the possibility of human colonization on Mars. Future missions will need to prioritize finding and utilizing water resources effectively to ensure the long-term sustainability of a Martian colony.
In conclusion, the absence of water on Mars remains a puzzling aspect of the planet. While there is evidence that liquid water may have once existed on its surface, numerous factors have contributed to its disappearance over time. The thin atmosphere and low atmospheric pressure play a significant role in the inability to sustain liquid water, as it quickly evaporates and escapes into space. Additionally, the lack of a global magnetic field on Mars allows the solar wind to strip away water molecules from its upper atmosphere. However, recent discoveries of subsurface ice and briny water flows provide hope for the potential presence of water in some form on the planet. Future missions and research will shed further light on this enduring mystery, and further exploration is needed to understand the true extent of water’s role on Mars.