Learn to Astronomy: Discover the secrets of our universe! In this article, we delve into the intriguing question: Why doesn’t Mars have an atmosphere? Uncover the complex interactions between solar wind, planetary magnetic fields, and geological processes that have led to Mars losing its once-thriving atmosphere. Join us on this journey of scientific exploration.
Unraveling the Mystery: The Absence of an Atmosphere on Mars
Mars, also known as the Red Planet, has long captivated astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. One of the most intriguing features of Mars is its lack of a substantial atmosphere, a characteristic that sets it apart from Earth and other planets in our solar system. But why does Mars have such a thin and virtually non-existent atmosphere?
The absence of an atmosphere on Mars can be attributed to several factors. First and foremost, Mars’s smaller size and lower gravity compared to Earth make it difficult for the planet to retain a significant amount of atmosphere. The weaker gravitational pull allows lighter gases to escape into space more easily.
Additionally, Mars lacks a global magnetic field that would protect its atmosphere from being stripped away by solar wind. Earth’s magnetic field acts as a shield, deflecting charged particles from the sun and preventing them from eroding our atmosphere. Without this protective barrier, Mars is more susceptible to losing its atmosphere over time.
Another contributing factor is the relatively low volcanic activity on Mars. Volcanoes release gases into the atmosphere, replenishing it with new molecules. However, Mars has relatively fewer active volcanoes compared to Earth, which means there is less gas being emitted to sustain its atmosphere.
The absence of a substantial atmosphere on Mars has profound implications for the planet’s habitability. The thin atmosphere cannot retain heat effectively, leading to frigid temperatures on the surface. The lack of atmospheric pressure also makes liquid water unstable, preventing it from existing in a liquid state for long. These conditions make it extremely challenging for life as we know it to survive on the Martian surface.
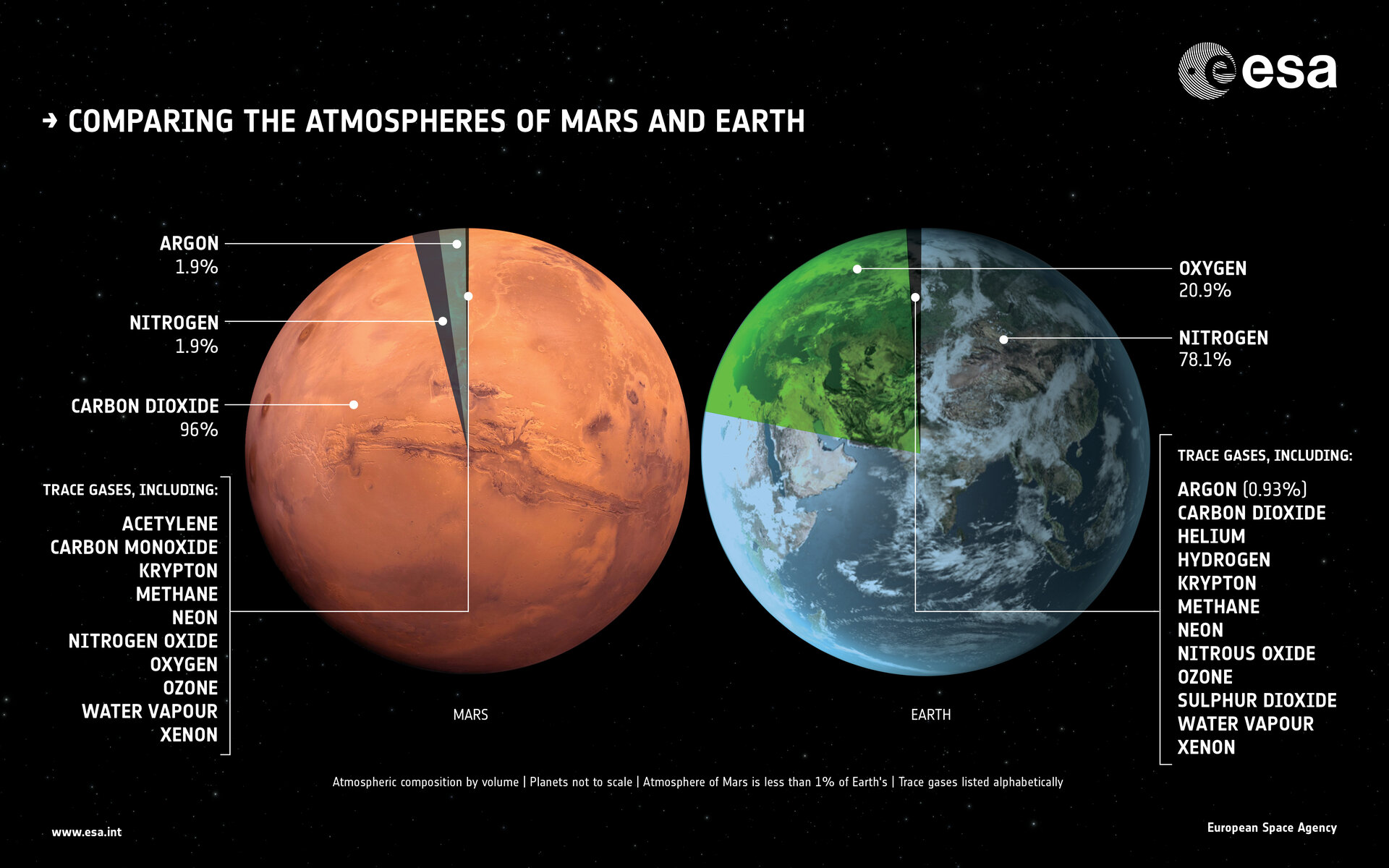
Despite these challenges, the presence of trace amounts of gases, such as carbon dioxide, in the Martian atmosphere suggests that it may have once had a more substantial atmosphere. Scientists believe that ancient Mars could have supported liquid water and potentially even microbial life. Understanding the processes that led to the depletion of Mars’s atmosphere is crucial for unraveling the planet’s past and its potential for hosting life in the future.
In conclusion, the absence of an atmosphere on Mars can be attributed to its smaller size, lower gravity, lack of a global magnetic field, and limited volcanic activity. The implications of this thin atmosphere are far-reaching, affecting the planet’s climate and habitability. Unraveling the mystery behind Mars’s atmospheric loss is not only a fascinating scientific endeavor but also a key to understanding the planet’s past and its potential for harboring life.
You Won’t Believe Your Eyes What NASA Found on Mars
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/yNqTvoc4CJY”/]
NASA Just Announced They Are Monitoring a Huge Escalating Anomaly On The Moon!
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/UzZBuRV4Stc”/]
Frequent questions
What caused Mars to lose its atmosphere over time?
Mars lost its atmosphere over time due to several factors. One of the main reasons is its relatively small size and low gravity compared to Earth. Being less massive, Mars couldn’t hold onto its atmosphere as effectively as our planet.
Another crucial factor is the lack of a global magnetic field on Mars. Earth’s magnetic field acts as a shield, protecting our atmosphere from the solar wind and preventing it from being stripped away. Mars’ weak magnetic field, on the other hand, allowed the solar wind to erode its atmosphere gradually.
Additionally, Mars doesn’t have active tectonic plates like Earth. Plate tectonics play a role in recycling gases from the atmosphere back into the planet’s interior. Without this process, Mars couldn’t replenish its atmosphere efficiently.
Furthermore, Mars lost a significant amount of its atmosphere through erosion. The planet’s thin atmosphere couldn’t provide enough protection against the strong radiation and high-energy particles from the Sun. Over time, these factors caused the loss of volatiles, such as water vapor and carbon dioxide.
Overall, a combination of Mars’ smaller size, weaker gravity, absence of a global magnetic field, lack of tectonic activity, and erosion led to the gradual loss of its atmosphere over time.
How does the lack of a substantial atmosphere on Mars affect its potential for supporting life?
The lack of a substantial atmosphere on Mars significantly affects its potential for supporting life. **Mars has a very thin atmosphere, with an average surface pressure about 100 times lower than Earth’s.** This thin atmosphere means that Mars experiences extreme temperature variations, ranging from extremely cold nights to relatively warm days.
**The thin atmosphere also contributes to Mars’ lack of liquid water.** While there is evidence of vast amounts of ice on Mars, the low atmospheric pressure makes it difficult for water to exist in a liquid state. Water on Mars would either freeze or evaporate quickly due to the low boiling point caused by the thin atmosphere.
Furthermore, **the thin atmosphere provides little protection against harmful radiation from space.** On Earth, our atmosphere acts as a shield, blocking a significant amount of harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from reaching the surface. However, on Mars, the weak atmosphere allows much more UV radiation to penetrate, posing a threat to any potential life forms.
Additionally, the lack of a substantial atmosphere impacts **the greenhouse effect and the ability to retain heat on Mars.** On Earth, the presence of a thick atmosphere and greenhouse gases help trap heat from the Sun, creating a relatively stable and habitable climate. However, the thin atmosphere on Mars cannot effectively retain heat, resulting in extremely cold conditions.
Despite these challenges, scientists continue to search for signs of past or present life on Mars. While the planet’s current conditions are inhospitable to most Earth-like life forms, it is possible that microbial life may have adapted to survive in extreme environments. Future missions, such as NASA’s Mars Sample Return mission, aim to bring back rock and soil samples from Mars to study them for potential signs of life.
Are there any ongoing efforts to study and understand the processes behind Mars’ thin atmosphere?
Yes, there are ongoing efforts to study and understand the processes behind Mars’ thin atmosphere. Mars has a significantly thinner atmosphere compared to Earth, composed mostly of carbon dioxide. Understanding the dynamics and evolution of Mars’ atmosphere is crucial to unraveling the planet’s past climate and potential habitability.
NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission, launched in 2013, is specifically dedicated to studying the Martian atmosphere. MAVEN has provided valuable insights into the processes responsible for the loss of Mars’ atmosphere over time, such as interactions with the solar wind.
In addition to MAVEN, other Mars exploration missions, such as the Mars Rover missions (like Curiosity and Perseverance), gather atmospheric data as part of their scientific objectives. These missions use various instruments to measure the composition, temperature, and dynamics of Mars’ atmosphere to further our understanding of its behavior.
Furthermore, future missions like NASA’s Mars Sample Return (MSR) mission and the European Space Agency’s ExoMars missions aim to collect and return samples from Mars, including samples of its atmosphere. The analysis of these samples will provide even deeper insights into the processes and composition of Mars’ thin atmosphere.
Overall, through spacecraft observations, data analysis, and upcoming missions, scientists continue to advance our understanding of Mars’ atmosphere and the underlying processes at work.
In conclusion, the absence of a significant atmosphere on Mars is due to several factors. One of the main reasons is its low gravity, which allows lighter gases to escape into space more easily. Additionally, Mars lacks a global magnetic field to protect its atmosphere from being stripped away by solar wind.
The loss of its once-thick atmosphere over billions of years has contributed to the planet’s current thin and tenuous atmosphere. While Mars does have some trace gases, such as carbon dioxide, they are not sufficient to create a substantial atmosphere.Understanding the processes that led to the loss of Mars’ atmosphere can provide valuable insights into the evolution of planetary atmospheres and help in our quest to find habitable environments beyond Earth.
As we continue to explore and study Mars, uncovering the mystery behind its lack of atmosphere will be crucial for future human missions and the search for possible signs of life on the red planet.