Learn to Astronomy: In the eternal quest for understanding our origins, a fundamental question arises: who came first, the Earth or the Universe itself? Join us as we delve into this captivating debate, exploring the age-old mysteries that have shaped our cosmos. Journey with us as we unravel the secrets of time and uncover the truths hidden within the vast tapestry of the universe.
The Age of Earth vs. the Universe: Unraveling the Cosmic Chronology
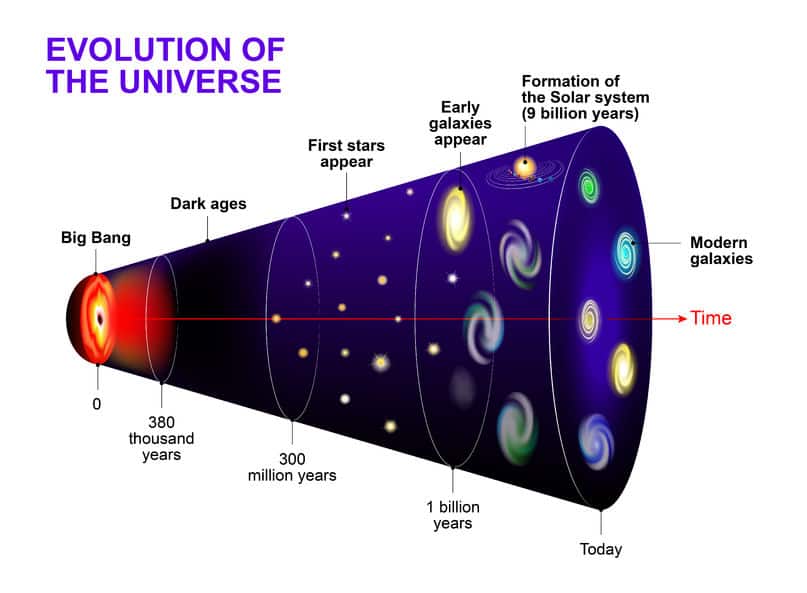
The age of the Earth and the age of the Universe have been subjects of great interest and debate in the field of astronomy. Understanding the cosmic chronology is crucial as it provides insights into the formation and evolution of celestial bodies.
The age of the Earth is estimated to be around 4.5 billion years, determined through various dating methods such as radiometric dating of rocks and minerals. This age corresponds to the time elapsed since the formation of our planet from a primordial nebula.
On the other hand, unraveling the age of the Universe is a more complex task. Astronomers have used different techniques to estimate its age, such as studying the rate of expansion of the Universe and the observed properties of the oldest celestial objects.
One of the key pieces of evidence for determining the age of the Universe is the cosmic microwave background radiation, which is considered to be the afterglow of the Big Bang. By analyzing the properties of this radiation, scientists have estimated the age of the Universe to be approximately 13.8 billion years.
However, it is important to note that our understanding of the cosmic chronology is still evolving and subject to ongoing research and refinement. New observations and improved measurement techniques continue to enhance our knowledge about the age of both the Earth and the Universe.
In summary, unraveling the cosmic chronology is a fascinating area of study in astronomy. The age of the Earth and the age of the Universe provide valuable information about the history and evolution of celestial bodies. By utilizing various dating methods and analyzing different astronomical phenomena, scientists continue to piece together the puzzle of our cosmic timeline.
Michio Kaku: We FINALLY Found What’s Inside A Black Hole!
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/pMdysmpDSsk”/]
Universe Size Comparison 3D
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/i93Z7zljQ7I”/]
Frequent questions
How do scientists determine the age of the Earth and the universe?
Scientists determine the age of the Earth and the universe using various methods and techniques.
For the age of the Earth:
1. Radiometric dating: Scientists use the decay of radioactive isotopes in rocks and minerals to determine their ages. By measuring the ratio of parent isotopes to daughter isotopes, they can calculate the time it took for the parent isotope to decay.
2. Ice cores: By studying the layers in ice cores from polar regions, scientists can estimate the age of the Earth based on the number of layers formed over time.
3. Tree rings: Dendrochronology, the study of tree rings, provides information about past climate conditions and allows scientists to estimate the age of trees and wooden artifacts, which in turn gives insights into the age of the Earth.
For the age of the universe:
1. Big Bang theory: The age of the universe is estimated based on the expansion of space and the cosmic microwave background radiation leftover from the Big Bang. Calculations involving the current rate of expansion allow scientists to determine its age.
2. Hubble’s law: By observing the redshift of galaxies, scientists can determine their velocities and distances. Hubble’s law relates the recessional velocity of galaxies to their distance, which helps estimate the age of the universe.
3. Cosmic microwave background: The measurement of the cosmic microwave background radiation, which is radiation left over from the early stages of the universe, provides valuable information about its age.
It is important to note that these methods are constantly refined and updated as new data becomes available, leading to more accurate estimates of the age of the Earth and the universe.
What evidence do we have to support the idea that the universe is older than the Earth?
There is ample evidence to support the idea that the universe is older than the Earth. One of the key pieces of evidence is the observation of distant galaxies. By analyzing the light emitted by these galaxies, astronomers can determine their distance from us and calculate how long it took for the light to reach Earth. This process, known as measuring cosmological redshift, has revealed galaxies that are billions of light-years away, indicating that the light we see from them has traveled for billions of years. This implies that the universe must be older than our planet.
Another important line of evidence comes from the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). The CMB is a faint glow of radiation left over from the early stages of the universe, about 380,000 years after the Big Bang. Precise measurements of the CMB have allowed scientists to estimate the age of the universe to be about 13.8 billion years. This age determination is independent of any information about Earth’s age and strongly supports the notion that the universe predates our planet.
Moreover, the study of radioactive isotopes and the decay rates of elements in rocks and minerals on Earth provides additional evidence. These methods have been used to estimate the age of the oldest known terrestrial rocks, which date back around 4.4 billion years. Since the Earth had to form after the universe existed, this provides further confirmation that the universe is older than our planet.
Additionally, astronomical observations of white dwarf stars, the remnants of old stars, have provided insights into the age of the universe. By measuring the cooling rate of these stars and comparing it with theoretical models, scientists have estimated an age of around 11-14 billion years for the oldest white dwarfs. This aligns with other age estimates of the universe.
In conclusion, the combination of cosmological observations, knowledge of radioactive decay, and stellar evolution provides compelling evidence that the universe is indeed older than the Earth.
How does the concept of cosmic background radiation help us understand the age of the universe compared to the Earth?
The concept of cosmic background radiation plays a significant role in helping us understand the age of the universe compared to the Earth. Cosmic background radiation refers to the faint radiation that permeates throughout the entire universe, which is believed to be remnants from the early stages of the universe’s formation.
By analyzing the properties of cosmic background radiation, scientists can gain valuable insights into the age of the universe. The radiation is a remnant of the hot, dense state that prevailed shortly after the Big Bang and has been gradually cooling down as the universe expands.
One of the key pieces of evidence for the Big Bang theory is the observation of cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). This radiation was discovered in 1965 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, who were awarded the Nobel Prize for their work. The CMB is the afterglow of the Big Bang and is observed as a nearly uniform glow coming from all directions in the sky, with a temperature of about 2.7 Kelvin (-270.45 degrees Celsius).
Measuring the temperature distribution of CMB allows scientists to determine the age of the universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the universe has been expanding and cooling down since its inception. By studying the patterns and fluctuations in the CMB, scientists can infer the time it took for these patterns to form, giving an estimate of the universe’s age.
Additionally, the composition and properties of cosmic background radiation provide further clues about the age of the universe. The radiation contains information about the matter content, such as the density of ordinary matter, dark matter, and dark energy. Understanding these properties helps scientists estimate the age of the universe and the time it took for structures like galaxies to form.
In contrast, when it comes to the age of the Earth, scientists rely on different methods such as radiometric dating of rocks and minerals. These techniques measure the decay of radioactive isotopes and provide an estimation of the Earth’s age, which is around 4.5 billion years.
In conclusion, the age-old question of whether the Earth or the universe is older remains a fascinating topic of debate in the realm of astronomy. While the Earth is estimated to be approximately 4.5 billion years old, recent scientific advancements have allowed us to gain insights into the age and formation of the universe.
Based on evidence from cosmic microwave background radiation and observations of distant galaxies, the universe is believed to be around 13.8 billion years old. These findings highlight the vast expanse of time that has shaped our existence in the cosmos. However, it is important to note that our understanding of the universe’s age continues to evolve as new technologies and discoveries emerge.
Nonetheless, the awe-inspiring reality remains that both the Earth and the universe have endured unimaginable processes over unfathomable spans of time, reminding us of our place in the grand tapestry of the cosmos. As we delve further into the mysteries of the universe, there is no doubt that our understanding of its age will continue to deepen, unraveling even more profound secrets of our existence.