Learn to Astronomy: Delve into the mysteries of our infinite universe and uncover the enigma of its boundaries. In this article, we embark on a mind-bending journey to explore where the universe’s edge lies, deciphering the incomprehensible vastness that extends beyond our senses. Prepare to expand your understanding and contemplate the unimaginable limits of the cosmos.
The perplexing question: Does the infinite universe have an endpoint in the vast realm of Astronomy?
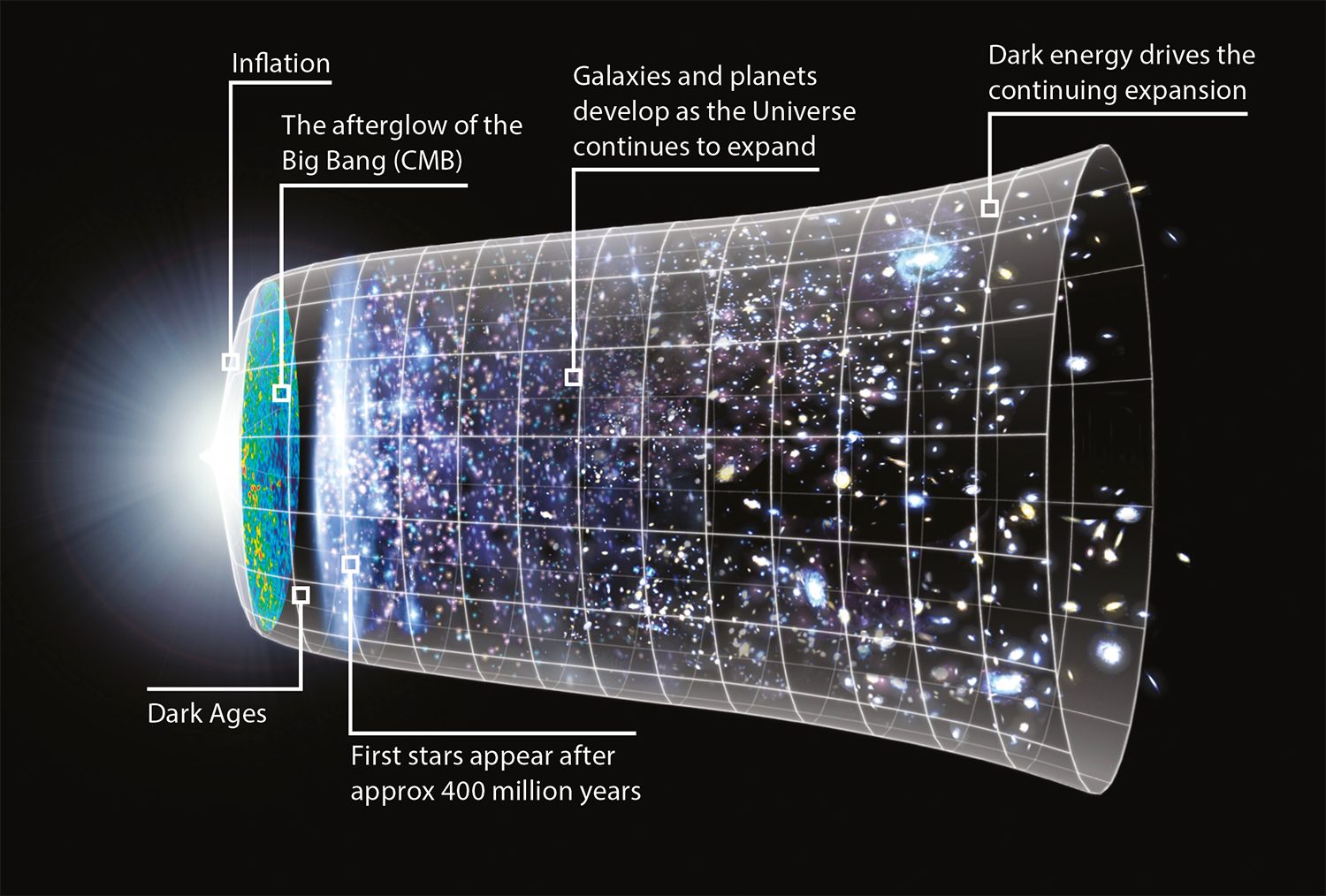
Does the infinite universe have an endpoint in the vast realm of Astronomy? The concept of an infinite universe has puzzled astronomers and scientists for centuries. While space itself is thought to be endless, the observable universe, which is the portion of the universe we can see and study, does have a boundary known as the observable horizon. This boundary is determined by the age of the universe and the speed of light. Anything beyond this horizon is beyond our reach, at least with our current technology.
However, it is important to note that the observable horizon does not necessarily imply an endpoint to the universe. It is merely the limit of what we can currently observe. There may be countless galaxies and celestial objects beyond our reach, stretching out into infinity.
It is a mind-boggling concept to comprehend an infinite universe without an endpoint. Our current understanding of the universe suggests that it is constantly expanding, with galaxies moving away from each other. This expansion raises questions about the nature of the universe’s boundaries. Could there be regions beyond our observable horizon that we will never be able to access or detect? Or does the infinite universe truly have no endpoints?
Scientists are actively researching and exploring various theories to better understand the nature of the universe’s boundaries. One such theory suggests the possibility of a “multiverse” – a collection of countless universes that exist alongside our own. In this scenario, each universe would have its own observable horizon, creating a vast ensemble of parallel realities. Another theory proposes the existence of “wormholes” or shortcuts through space-time, potentially allowing access to other regions of the universe that would otherwise be unreachable.
In conclusion, while the observable universe has a boundary in the form of the observable horizon, the question of whether the infinite universe has an endpoint remains a fascinating ongoing investigation for astronomers and scientists. The search for answers to this perplexing question continues to drive the exploration and understanding of our vast cosmic surroundings.
How Physicists Proved The Universe Isn’t Locally Real – Nobel Prize in Physics 2022 EXPLAINED
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/txlCvCSefYQ”/]
Brian Cox – Alien Life & The Dark Forest Hypothesis
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/o6IQynhsQ1M”/]
Frequent questions
How can we determine the size and shape of the universe if it is infinite?
The size and shape of the universe can still be determined even if it is infinite.
One way to determine the size and shape of the universe is through the study of cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). The CMB is residual radiation from the Big Bang and is spread uniformly throughout space. By analyzing the patterns and fluctuations in the CMB, scientists can gain insights into the geometry of the universe.
Another method involves studying the distribution of galaxies and measuring their distances from us. By observing the redshift of light from distant galaxies, astronomers can determine how fast they are moving away from us. This information, combined with knowledge of the expansion rate of the universe, allows scientists to estimate the distance to these galaxies. By mapping out the positions and distances of numerous galaxies, astronomers can create a three-dimensional map of the universe.
Additionally, studies of gravitational lensing provide clues about the large-scale structure of the universe. Gravitational lensing occurs when the path of light from a distant object is bent by the gravitational pull of a massive object in its path. By observing and analyzing the distortions caused by gravitational lensing, astronomers can infer the distribution of matter in the universe, giving them insight into its overall structure.
While the universe might be infinite, these observational techniques allow astronomers to understand its properties and reveal information about its size and shape at observable scales.
What evidence do we have to support the notion that the universe is infinite and therefore has no end?
There is currently no definitive evidence to support the notion that the universe is infinite and has no end. Our understanding of the universe is limited by our observational capabilities. However, based on several observations and theoretical models, scientists have proposed that the universe could be infinite. Here are a few points that contribute to this idea:
1. Homogeneity and isotropy: Observations show that the distribution of matter and energy in the universe appears to be roughly the same at large scales, suggesting a uniformity and symmetry that could extend infinitely.
2. Flat geometry: Current measurements indicate that the geometry of the universe is flat, which implies that it could potentially extend infinitely without curving back on itself.
3. Inflationary cosmology: The inflationary model of the early universe suggests that the universe underwent a rapid expansion in its very early stages, which could have resulted in an infinite universe.
4. Unbounded expansion: Observations of the cosmic microwave background radiation indicate that the universe is currently undergoing an accelerated expansion. If this expansion continues indefinitely, it could imply that the universe is infinite.
It is important to note that while these points provide some support for an infinite universe, they are not conclusive evidence. The nature of the universe is still a topic of active research and exploration in the field of astronomy and cosmology.
Are there any theories or hypotheses that suggest the possibility of multiple universes coexisting with our own infinite universe?
Yes, there are several theories and hypotheses that propose the existence of multiple universes coexisting with our own. One such theory is the concept of the multiverse, which suggests that our universe is just one of many universes that make up a larger “multiverse.” In this theory, each universe within the multiverse may have different physical laws and properties.
Another hypothesis is the idea of parallel universes or alternate realities. This concept proposes the existence of universes that are similar to ours but with slight variations, such as different outcomes of historical events or different laws of physics. These parallel universes could exist in separate dimensions or in a different space-time continuum.
The inflationary multiverse theory suggests that during the early stages of the universe’s expansion after the Big Bang, different regions underwent rapid inflation, creating separate “bubble” universes. According to this theory, each bubble universe could have different physical properties.
String theory and M-theory propose that there may be multiple dimensions beyond the three spatial dimensions we are familiar with. These extra dimensions could contain other universes, also known as branes, which may interact with our own universe.
It is important to note that these ideas are still speculative, and there is currently no direct observational evidence to confirm the existence of multiple universes. However, they have gained popularity among physicists and cosmologists as possible explanations for certain observed phenomena and as ways to reconcile conflicting theories in physics.
In conclusion, the concept of the universe being infinite presents a mind-boggling question: where does it all end? However, current scientific understanding suggests that the universe, if truly infinite, does not have an end point in a traditional sense.
Our current knowledge of the universe’s expansion indicates that it is continuously stretching and evolving, with no discernible boundary or edge. This idea challenges our intuitive understanding of boundaries and borders, leading us to contemplate the awe-inspiring vastness of the cosmos.
As we continue to delve deeper into the mysteries of the universe, new discoveries and advancements in technology will hopefully shed more light on this intriguing question. Until then, the infinite nature of the universe remains a fascinating subject of exploration for astronomers and philosophers alike, igniting the human curiosity to unravel the secrets of our boundless cosmos.