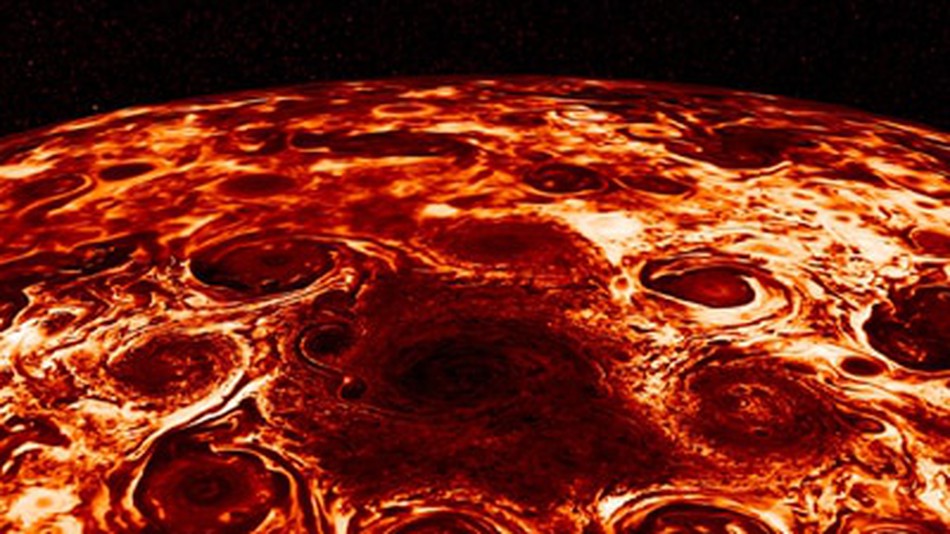
Explore the mysteries of Jupiter’s hidden realm! Beneath its iconic and ever-changing cloud layers lies a world of secrets waiting to be unveiled. In this article, we delve deep into the enigmatic depths of Jupiter, unraveling the mysteries of what lies beneath its mesmerizing facade. Join us on an extraordinary journey through the hidden wonders of the largest planet in our solar system.
Exploring Jupiter’s Hidden Depths: Unveiling the Secrets beneath its Clouds
Exploring Jupiter’s Hidden Depths: Unveiling the Secrets beneath its Clouds
Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, has always been a fascinating subject of study for astronomers. Its massive size and distinctive striped appearance have intrigued scientists for centuries. However, it is the planet’s hidden depths that have recently captured the attention of researchers.
Beneath Jupiter’s iconic cloud bands lies a mysterious world that is shrouded in secrecy. Scientists have long been curious about what lies beneath these clouds and what processes are occurring deep within the planet. Thanks to technological advancements and space missions, we are beginning to unlock those secrets.
One of the key missions exploring Jupiter’s hidden depths is NASA’s Juno spacecraft. Launched in 2011, Juno reached Jupiter in 2016 and has been orbiting the planet ever since. Equipped with an array of scientific instruments, Juno has been collecting crucial data to help us understand the planet’s interior.
The data collected by Juno has challenged some long-held theories about Jupiter. For example, scientists had previously believed that Jupiter’s core was a compact, solid mass. However, Juno’s measurements suggest that the core might actually be a fuzzy, diluted region, potentially made up of heavy elements like rock and metal.
Another intriguing discovery made by Juno is the presence of a powerful magnetic field in Jupiter’s depths. This magnetic field is even stronger than predicted, indicating the presence of a dynamo mechanism that generates the field. Understanding the source and dynamics of this magnetic field is crucial to unraveling the mysteries of Jupiter’s interior.
Additionally, Juno has provided valuable insights into the planet’s atmospheric composition, temperature gradients, and cloud formations. By studying these aspects, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of how Jupiter’s atmosphere interacts with its hidden depths.
The exploration of Jupiter’s hidden depths is not limited to Juno alone. Other spacecraft and telescopes, such as the upcoming European Space Agency’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) mission, are also planned to study the gas giant further. These missions will provide more data and observations that will contribute to our understanding of Jupiter’s complex inner workings.
As we continue to explore Jupiter’s hidden depths, we are not only unraveling the secrets of this magnificent planet but also gaining insights into the formation and evolution of gas giants in general. The knowledge gained from studying Jupiter will undoubtedly help us better understand other massive planets beyond our solar system.
In conclusion, Jupiter’s hidden depths have remained a mystery for centuries. Through space missions like Juno and future explorations, we are gradually unveiling the secrets beneath its clouds. The data collected so far has challenged existing theories and provided valuable insights into Jupiter’s interior, magnetic field, and atmospheric dynamics. As we delve further into the mysterious world of Jupiter’s hidden depths, we can expect more captivating discoveries that will broaden our understanding of this awe-inspiring planet.
NASA Has Just Found the Most Horrible Planet in the Known Universe
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/bZEEVwa5H78″/]
Voyager Just Sent This TERRIFYING New Message Back To Earth!
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/oZ2e1xb56HQ”/]
Frequent questions
What is the composition of Jupiter’s clouds and what lies beneath them?
Jupiter’s clouds are primarily composed of ammonia ice crystals, water vapor, and other trace elements. These clouds form distinct bands that encircle the planet. The light-colored bands are made up of ammonia ice crystals, while the darker bands consist of ammonium hydrosulfide and water vapor.
Beneath Jupiter’s clouds lies a dense layer of hydrogen and helium gases, which make up the majority of the planet’s mass. At deeper levels, the pressure and temperature increase, causing the hydrogen to transition into a metallic state. This metallic hydrogen layer is thought to be responsible for generating Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field.
Even further down, it is believed that Jupiter has a solid core made up of heavy elements such as rock, metals, and ices. However, the exact size and composition of this core remain uncertain. Scientists continue to study and explore Jupiter’s interior using spacecraft missions and advanced observations to unravel the mysteries of this giant gas planet.
How do the different layers beneath Jupiter’s clouds contribute to its unique atmospheric conditions?
Jupiter’s unique atmospheric conditions are strongly influenced by the different layers beneath its clouds.
The outermost layer of Jupiter’s atmosphere is composed of thick, swirling clouds made up of ammonia crystals. These clouds extend tens of kilometers deep and create the characteristic bands and zones that we observe on the planet’s surface. Their formation and dynamics play a crucial role in shaping Jupiter’s weather patterns.
Below the cloud layer, there is a region called the troposphere where most of Jupiter’s weather occurs. This layer is composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, with trace amounts of other compounds. The temperature and pressure decrease with altitude in the troposphere, leading to various atmospheric phenomena such as storms and cyclones. The Great Red Spot, for example, is a massive storm that has been raging for centuries.
Deeper still, beneath the troposphere, lies the stratosphere. This region is characterized by the stratospheric haze, a layer of hydrocarbons and other compounds resulting from the breakdown of methane. The stratosphere is also home to jet streams that flow in alternating directions, contributing to the complex wind patterns observed on Jupiter.
At even greater depths, Jupiter’s atmosphere transitions into a layer known as the transition region or the convective zone. In this region, the pressure and temperature are extremely high, causing hydrogen to behave like a fluid rather than a gas. Convection currents transport heat from the interior of the planet towards the upper layers, influencing the overall energy balance and circulation of the atmosphere.
Finally, scientists believe that below the convective zone, there is a core made up of heavier elements, such as rock and metal. The presence of this core and its interaction with the overlying layers is thought to contribute to Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field.
In summary, Jupiter’s atmospheric conditions are shaped by the interplay between its cloud layers, troposphere, stratosphere, transition region, and core. Each layer influences the temperature, pressure, composition, and dynamics of the atmosphere, resulting in the fascinating and unique features observed on the gas giant.
Are there any geological or hydrological features beneath Jupiter’s clouds, such as oceans or underground structures?
According to current scientific understanding, **Jupiter’s atmosphere consists mostly of hydrogen and helium**, with clouds made up of ammonia and methane. Due to the intense pressures and temperatures that exist deeper within Jupiter, it is believed that no solid surface exists beneath the clouds.
However, recent studies have suggested the possibility of a **deep, “ocean-like” layer** of liquid metallic hydrogen beneath the clouds. This layer would occur in the planet’s interior, where the immense pressures would cause hydrogen to behave like a metal and conduct electricity. Scientists hypothesize that this “ocean” could be quite deep and play a crucial role in generating Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field.
As for underground structures, such as caves or tunnels, there is currently no evidence to support their existence on Jupiter. The planet’s interior is thought to transition gradually from gaseous to metallic hydrogen, without distinct features like solid rock.
In summary, while Jupiter may possess a deep layer of liquid metallic hydrogen beneath its clouds, there are no geological or hydrological features like oceans or underground structures as we typically understand them on Earth. Our understanding of Jupiter’s internal structure is still evolving, and future missions and observations may provide further insights.
In conclusion, the mysterious world that lies beneath the clouds of Jupiter continues to captivate astronomers and researchers alike. Through our exploration missions and telescopic observations, we have gained invaluable insights into the intricate dynamics of this gas giant and its mesmerizing features.
However, there is still much more to uncover. The Juno spacecraft has provided us with unprecedented findings about the planet’s atmospheric composition, magnetic field, and internal structure. These discoveries challenge our existing theories and urge us to delve deeper into the enigmatic depths of Jupiter. By studying the planet’s core, it is possible to unravel the origins of this majestic celestial body and gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms that govern our own solar system.
While the secrets that lie beneath Jupiter’s clouds are yet to be fully revealed, scientists remain determined to unlock its mysteries. With continued advancements in technology and space exploration, we can only hope that one day we will witness firsthand the wonders that reside beneath the veil of clouds on the largest planet in our solar system.