Welcome to Learn to Astronomy, where we dive into the wonders of the universe! In this article, we will explore the fascinating topic of Martian seasons. Discover how the Red Planet experiences its own unique cycle of climate changes and uncover the secrets behind these mesmerizing phenomena. Join us on this journey of celestial exploration!
Mars: Unveiling the Enigmatic Seasons of the Red Planet
Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun in our solar system, has long fascinated scientists and astronomers alike. With its distinctive reddish appearance, Mars has earned the nickname “The Red Planet.” One of the most intriguing aspects of Mars is its enigmatic seasons, which have puzzled researchers for centuries.
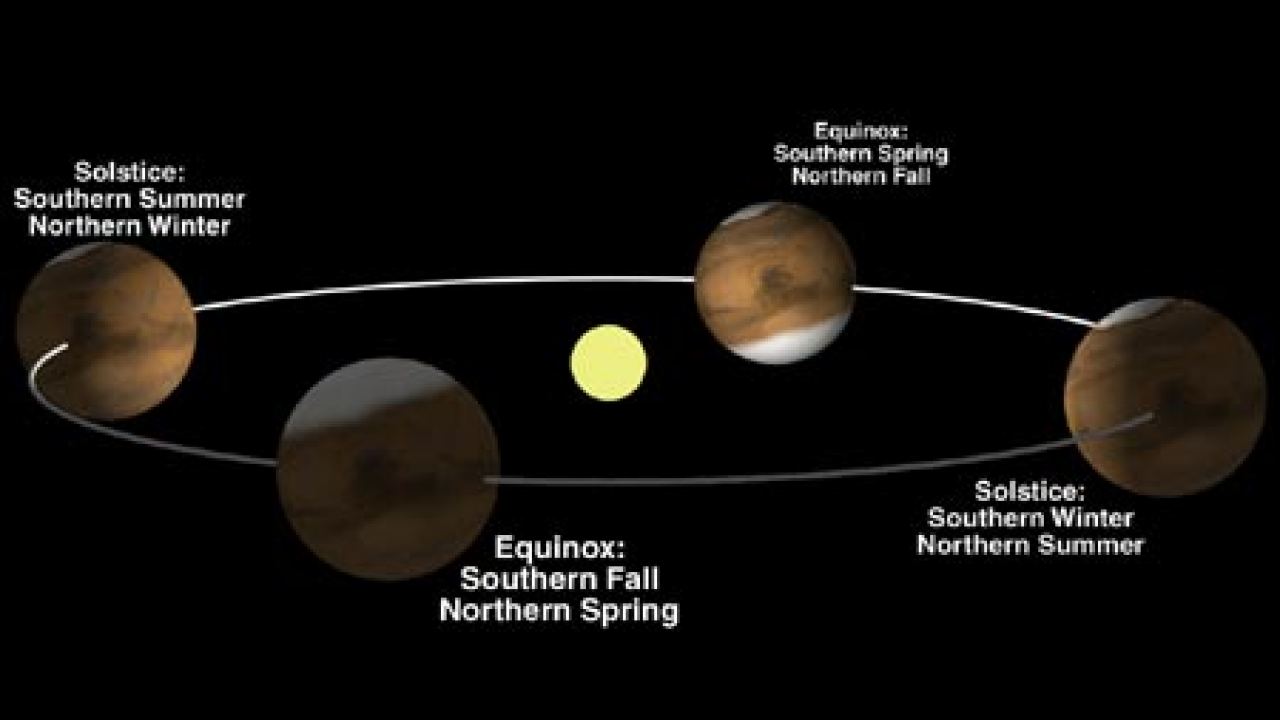
Seasonal variations on Mars are primarily the result of its tilted axis and elliptical orbit around the Sun. Similar to Earth, Mars experiences four seasons – spring, summer, autumn, and winter. However, the duration and intensity of these seasons differ significantly from those on our home planet.
The tilt of Mars’ axis is similar to Earth’s, but slightly more pronounced, leading to more extreme seasonal changes. The tilt causes variations in the amount of sunlight different regions of Mars receive throughout the year. This variation influences atmospheric processes and temperature patterns, resulting in distinct seasonal characteristics.
During the Martian spring and summer, the planet’s polar ice caps begin to shrink as the temperature rises, causing the release of carbon dioxide gas into the atmosphere. This process leads to the formation of additional clouds and dust storms, creating a hazy environment. These phenomena contribute to the reddish hue that gives Mars its iconic appearance.
Autumn on Mars is marked by a decrease in temperature, causing the remaining atmospheric carbon dioxide to condense and freeze. The polar ice caps expand once again as the frozen carbon dioxide accumulates, creating stunning polar landscapes.
Winter on Mars is the most severe season, with temperatures plummeting and the polar ice caps reaching their maximum size. The atmosphere becomes extremely cold and thin, making it difficult for spacecraft to operate efficiently. Winter storms can also generate powerful winds, generating massive dust storms that can envelop the entire planet.
Studying the seasons of Mars not only satisfies our curiosity about another world but also provides valuable insight into planetary climate systems. By analyzing the data gathered from various missions and probes, scientists can gain a better understanding of Earth’s climate and potentially make advancements in predicting and mitigating climate change.
In conclusion, the enigmatic seasons of Mars offer an intriguing glimpse into the complex dynamics of this neighboring planet. As we continue to explore and study Mars, we will undoubtedly uncover more mysteries and fascinating details about its unique seasonal variations.
Scariest Space Images That NASA Can’t Explain
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/Xtmm_4ftyTQ”/]
Mars New 4K: Craziest Findings by NASA Perseverance Rover
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/CSkqqECd9mo”/]
Frequent questions
What are the distinctive seasons on Mars and how do they differ from Earth’s seasons?
Mars experiences distinct seasons, similar to Earth. However, due to Mars’ longer orbit and its axial tilt of 25.2 degrees (compared to Earth’s 23.5 degrees), the Martian seasons are significantly different from those on Earth.
Spring: Spring on Mars occurs in the northern hemisphere when Mars is approaching the Sun, resulting in increased sunlight and warming temperatures. As the snow and ice from winter begin to melt, liquid water may temporarily flow on the surface.
Summer: The Martian summer begins when Mars is closest to the Sun in its elliptical orbit. Summers on Mars are relatively short but can still reach temperatures above freezing in some regions. Dust storms are more common during this season, due to the increased intensity of solar radiation causing atmospheric heating.
Fall/Autumn: In the fall, Mars moves away from the Sun, leading to decreasing sunlight and dropping temperatures. Dust storms can persist into the autumn season, affecting visibility and climate conditions.
Winter: Winters on Mars are harsh, with temperatures dropping well below freezing. Polar ice caps grow larger as carbon dioxide freezes from the atmosphere, forming a layer of seasonal frost. These caps expand and contract with the changing seasons.
It is important to note that the Martian year is about 687 Earth days long, resulting in longer seasons compared to Earth’s approximately 365-day year. The differences in Mars’ atmosphere composition and low atmospheric pressure also contribute to variations in how Mars’ seasons manifest compared to Earth.
How does Mars’ axial tilt contribute to the variations in seasons on the planet?
Mars’ axial tilt, which is similar to Earth’s, plays a crucial role in the variations of seasons on the planet. The axial tilt of Mars refers to the angle at which its axis is tilted in relation to its orbit around the Sun.
Just like Earth, Mars experiences different seasons due to this axial tilt. However, unlike Earth’s tilt of approximately 23.5 degrees, Mars has a tilt of about 25 degrees. This slightly greater tilt leads to more pronounced seasonal variations on Mars.
As Mars orbits the Sun, different regions receive different amounts of sunlight throughout the year. During its northern hemisphere’s summer solstice, the northern hemisphere of Mars tilts toward the Sun, exposing it to more direct sunlight. This leads to warmer temperatures and longer days in the northern hemisphere, resulting in its summer season.
Conversely, during its northern hemisphere’s winter solstice, the region tilts away from the Sun. This causes less sunlight to reach the northern hemisphere, leading to colder temperatures and shorter daylight hours – the winter season.
The opposite occurs in the southern hemisphere. When it is summer in the northern hemisphere, it is winter in the southern hemisphere, and vice versa.
The axial tilt also affects Mars’ polar ice caps. During the hemisphere’s winter season, the polar ice caps expand as atmospheric water vapor freezes. As the seasons change and it becomes summer in a hemisphere, part of the polar ice cap may melt, releasing carbon dioxide and creating seasonal variations in the planet’s atmosphere.
In summary, Mars’ axial tilt determines the amount of sunlight different regions receive throughout the year, resulting in distinct seasons on the planet.
Are there any observable changes in weather patterns during different seasons on Mars?
Yes, there are observable changes in weather patterns during different seasons on Mars.
Mars experiences four distinct seasons similar to Earth, but due to its longer year, each season lasts approximately twice as long. The Martian seasons are caused by the planet’s axial tilt, similar to Earth. However, there are significant differences in the weather patterns between the two planets.
During spring and summer on Mars, the polar ice caps shrink due to sublimation, where solid ice turns directly into vapor. This process releases water vapor into the atmosphere, leading to the formation of clouds near the poles. These clouds are mostly composed of water ice crystals.
In the fall and winter seasons, the poles experience condensation as temperatures drop. This leads to the formation of carbon dioxide (dry ice) clouds, which produce a significant change in the weather patterns. These dry ice clouds can cover large areas and cause events such as dust storms, which are more frequent during these seasons.
One of the most remarkable weather phenomena observed on Mars is the occurrence of massive dust storms that can engulf the entire planet. These dust storms usually happen during the spring and summer seasons and are known as “global dust storms.” These storms can last for weeks or even months, significantly impacting the atmospheric conditions and surface temperature.
Overall, while the atmosphere of Mars is much thinner than Earth’s, there are still noticeable changes in weather patterns during different seasons, including cloud formation, dust storms, and variation in temperature.
In conclusion, the study of Mars’ seasons unveils a fascinating pattern that mirrors our own planet’s but with intriguing variations. As MAVEN continues to provide us with valuable insights into the Martian atmosphere, we are gradually piecing together the puzzle of what drives these distinct seasonal changes.
From the dust storms of summer to the frozen polar caps of winter, Mars showcases a dynamic and ever-evolving climate system. Understanding these seasonal shifts is crucial for future manned missions and potential colonization efforts. By unraveling the mysteries of Mars’ seasons, we uncover important clues about the past, present, and future of this enigmatic planet and its potential to harbor life. As we eagerly await further missions and discoveries, Mars remains a captivating destination for astronomers and space enthusiasts alike.