Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of Mars and delve into the composition of its atmosphere. Discover the types of gases that make up the thin blanket surrounding the Red Planet and uncover the secrets hidden within its enigmatic gaseous envelope. Join us on this journey as we unravel the mysteries of Mars’ atmospheric composition.
Exploring the Composition of Mars: Unveiling the Mystery of its Atmospheric Gases
Exploring the Composition of Mars: Unveiling the Mystery of its Atmospheric Gases
Mars, often referred to as the “Red Planet”, has long intrigued astronomers and scientists alike. One of the key aspects of this fascination lies in understanding the composition of its atmosphere. By studying the atmospheric gases present on Mars, scientists can gain crucial insights into the planet’s past, present, and even its potential for supporting life.
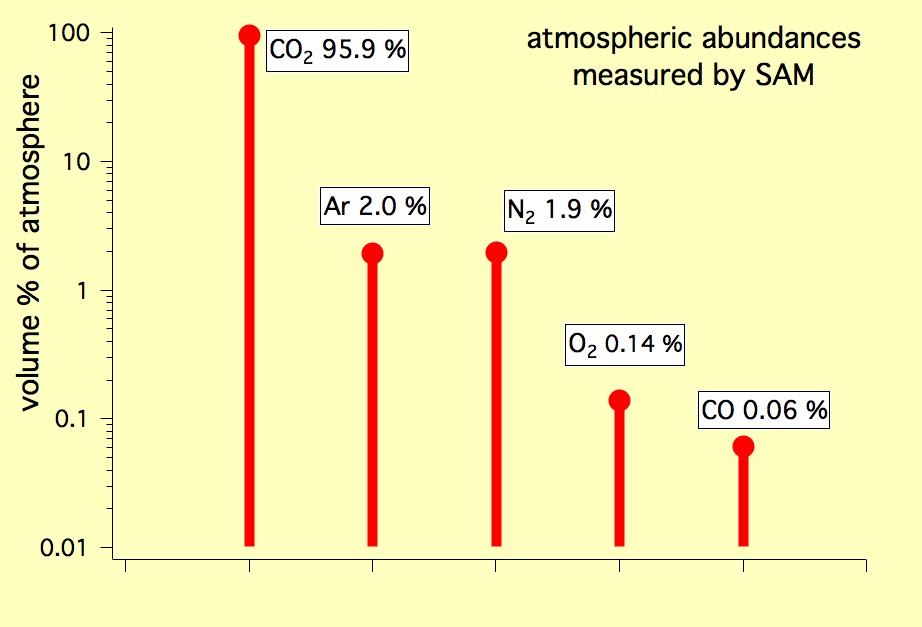
One of the primary components of the Martian atmosphere is carbon dioxide (CO2), accounting for about 95% of the total gas. This high concentration of CO2 creates a thick greenhouse effect, trapping heat and contributing to the planet’s extremely cold conditions. Additionally, small amounts of other gases such as nitrogen, argon, and oxygen are also found in the atmosphere.
However, Mars’ atmosphere is not static. It undergoes seasonal changes, with the polar ice caps expanding and contracting. This behavior suggests that there might be other gases, such as water vapor, that play a role in these variations. Understanding the dynamics of these changes is crucial for unraveling the planet’s past climate and potential habitability.
Furthermore, the presence of methane (CH4) in Mars’ atmosphere has been a subject of intense research and speculation. Methane is an important gas on Earth, often associated with biological activity. While its presence on Mars could be a sign of microbial life, it could also have non-biological origins, such as geological processes or comet impacts. Detecting and analyzing methane levels on Mars continues to be a focus of ongoing missions and research.
The exploration of Mars and the study of its atmospheric composition provide valuable clues about the planet’s geological history, climate evolution, and potential for sustaining life. By utilizing advanced instruments and spacecraft, scientists are gradually uncovering the mysteries surrounding the gases that envelop the Red Planet, bringing us closer to understanding its enigmatic nature.
In conclusion, the composition of Mars’ atmosphere, with its high concentration of carbon dioxide and seasonal variations, provides valuable insights into the planet’s past and potential habitability. The presence of methane adds another layer of complexity and intrigue, raising questions about the possibility of life on Mars. Through ongoing research and missions, scientists are unraveling the mysteries of the Martian gases, shedding light on the enigmatic nature of this fascinating planet.
10 Questionable Things NASA Has Found On Mars
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/bW-U3BSqzFQ”/]
NASA Has Just Found the Most Horrible Planet in the Known Universe
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/bZEEVwa5H78″/]
Frequent questions
What are the main gases present in Mars’ atmosphere?
In Mars’ atmosphere, the main gases present are **carbon dioxide** (CO2), **nitrogen** (N2), and **argon** (Ar). Carbon dioxide makes up the majority of the Martian atmosphere, accounting for about 95.3% of its composition. Nitrogen comprises around 2.7% of the atmosphere, while argon constitutes a small percentage of about 1.6%. Additionally, trace amounts of other gases such as **oxygen**, **carbon monoxide**, **water vapor**, and **methane** have also been detected in the Martian atmosphere.
How do the atmospheric gases on Mars differ from those on Earth?
The atmospheric gases on Mars differ significantly from those on Earth.
Firstly, the composition of the Martian atmosphere is predominantly carbon dioxide (CO2), accounting for about 95% of the total gases present. In contrast, Earth’s atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (N2), oxygen (O2), and trace amounts of other gases, with carbon dioxide comprising less than 0.04%. This vast difference in CO2 levels is one of the reasons why Mars has a much thinner atmosphere compared to Earth.
Another key difference is the absence of significant amounts of oxygen in the Martian atmosphere. Earth’s atmosphere contains approximately 21% oxygen, which is vital for supporting life as we know it. On Mars, the amount of oxygen is less than 0.2%, making it unsuitable for terrestrial organisms that require oxygen for survival.
Apart from carbon dioxide, the Martian atmosphere also contains trace amounts of other gases such as nitrogen, argon, and oxygen. Nitrogen makes up around 2.6% of the Martian atmosphere, while argon accounts for about 1.9%. These percentages are relatively low compared to Earth, where nitrogen constitutes about 78% and argon about 0.93% of the atmosphere.
Furthermore, the absence of an ozone layer is another notable distinction between the atmospheres of Mars and Earth. Earth’s ozone layer plays a crucial role in protecting life on the surface by absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. Without this protective shield, Martian organisms (if they exist) would be exposed to much higher levels of UV radiation.
In summary, the primary differences between the atmospheric gases on Mars and Earth are the predominance of carbon dioxide, the lack of significant oxygen, lower levels of nitrogen and argon, and the absence of an ozone layer. Understanding these differences helps astronomers and researchers gain insights into the unique conditions on Mars and its potential for supporting life.
Is there evidence of any unusual or unexpected gases in Mars’ atmosphere that could indicate past or present microbial life?
Currently, there is no direct evidence of any unusual or unexpected gases in Mars’ atmosphere that definitively indicate past or present microbial life. However, the search for signs of life on Mars is an ongoing mission for various space agencies and scientific organizations.
One of the key goals of NASA’s Mars missions, such as the Mars Science Laboratory (which includes the Curiosity Rover) and the upcoming Mars 2020 mission, is to explore the planet’s habitability and assess its potential for supporting life. These missions include instruments specifically designed to study the chemistry of Mars’ atmosphere and search for potential biomarkers.
While the presence of certain gases like methane has been detected in Mars’ atmosphere, their origin is not yet fully understood. Methane can be produced by both biological and non-biological processes, so its detection alone does not provide conclusive evidence of life. The source of methane on Mars could be geological activity or even remnants of past microbial life, but further investigations are required to establish its origin.
Future missions, such as NASA’s Mars Sample Return mission and the European Space Agency’s ExoMars mission, aim to bring back samples from Mars’ surface for detailed analysis in terrestrial laboratories. These samples could potentially hold valuable clues about Martian microbial life.
In summary, while there is currently no definitive evidence of unusual or unexpected gases indicating past or present microbial life in Mars’ atmosphere, ongoing and future missions continue to investigate this possibility. The search for signs of life on Mars remains a fascinating and active area of research in astronomy.
In conclusion, the study of gases on Mars provides invaluable insights into the planet’s history and potential for sustaining life. The presence of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and traces of oxygen indicates that Mars has an atmosphere, although much thinner than Earth’s. The discovery of methane raises intriguing questions about possible microbial life or geological processes occurring beneath the Martian surface. Furthermore, the detection of water vapor at certain times and regions offers hope for future manned missions and the potential for human colonization. However, much remains to be explored and understood about the complex interplay of gases on Mars, highlighting the need for further research and exploration. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of this fascinating neighbor, we inch closer to unraveling the secrets of our own existence in the vast universe.