Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we explore the fascinating question: What is the planet most similar to Earth? Join us as we delve into the depths of space to uncover the celestial body that closely resembles our own precious planet. Let’s embark on an astronomical journey together!
The Search for Earth’s Twin: Discovering the Most Earth-like Planet
The Search for Earth’s Twin: Discovering the Most Earth-like Planet in the context of Astronomy.
Astronomy is the scientific study of celestial objects, such as stars, planets, comets, and galaxies. It involves observing, analyzing, and understanding the vastness of the universe. One of the most intriguing questions in astronomy is whether there are other Earth-like planets in the universe.
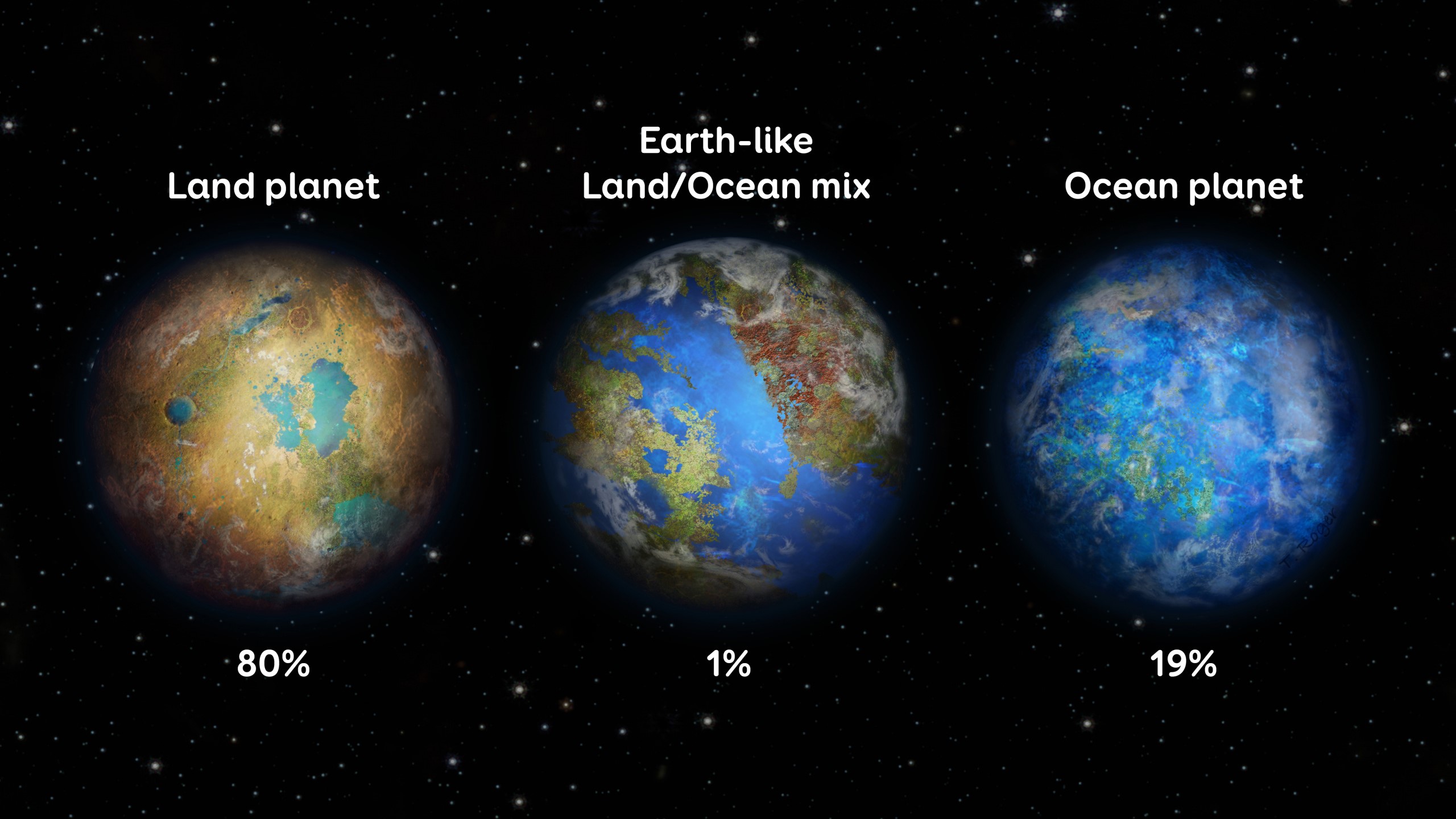
Earth, our home planet, is uniquely suited to support life as we know it. It has the right distance from its star, a stable climate, and an abundance of liquid water. Scientists believe that the discovery of an Earth-like planet could have significant implications for the existence of extraterrestrial life.
In the quest for finding Earth’s twin, astronomers have made tremendous advancements in the past few decades. The development of new technologies, such as powerful telescopes and space probes, has allowed scientists to detect and analyze exoplanets—planets orbiting stars outside our solar system.
The Kepler Space Telescope, launched by NASA in 2009, revolutionized exoplanet research by surveying a portion of the Milky Way galaxy. It discovered thousands of exoplanets, many of which are considered to be Earth-like. These planets are located within their star’s habitable zone, where conditions may be suitable for liquid water to exist.
Astronomers use various methods to identify Earth-like planets. One common technique is the transit method, where astronomers look for slight dips in a star’s brightness caused by a planet passing in front of it. Another method is the radial velocity method, which detects small wobbles in a star’s motion caused by the gravitational tug of an orbiting planet.
Tess, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, launched in 2018, aims to continue the search for Earth’s twin. It will observe nearly the entire sky over two years, studying thousands of stars and searching for new exoplanets.
Finding an Earth-like planet is challenging because it requires a combination of factors to create a habitable environment. However, as technology advances, astronomers are getting closer to discovering our cosmic neighbor.
The search for Earth’s twin is not only about understanding the origins of life but also about expanding our perspective on our place in the universe. The discovery of an Earth-like planet would provide valuable insights into the possibilities of life existing beyond our own solar system, making us ponder the question: Are we alone in the universe?
In conclusion, the search for Earth’s twin is an ongoing endeavor in the field of astronomy, driven by curiosity and the desire to explore the vastness of space. Discovering an Earth-like planet would have profound implications for our understanding of life’s existence beyond Earth.
10 Space Photos That Will Give You Nightmares
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/pb2MkzCgQ-4″/]
Things You Were Lied to About Space
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/UKTHKQobJRg”/]
Frequent questions
Which exoplanet is considered the closest match to Earth in terms of size, composition, and potential habitability?
The exoplanet that is considered the closest match to Earth in terms of size, composition, and potential habitability is **Kepler-452b**. It was discovered by NASA’s Kepler spacecraft and is located about 1,400 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Cygnus. Kepler-452b is roughly 1.6 times the size of Earth and has a similar composition, implying a rocky surface.
It orbits its star at a distance that places it within the habitable zone, also known as the “Goldilocks zone,” where liquid water could exist on its surface. This suggests the potential for the presence of life as we know it. However, further studies are required to determine the exact conditions and atmospheric composition of Kepler-452b. Nonetheless, its similarities to Earth make it one of the most intriguing candidates for further exploration and study in the search for life beyond our solar system.
What factors determine if a planet can be classified as the most Earth-like among the known exoplanets?
The most Earth-like exoplanets can be determined by several factors:
1. Size and Mass: A planet that is similar in size and mass to Earth is more likely to have a similar composition and gravity, creating conditions conducive to supporting life as we know it.
2. Orbit and Distance from its Star: An Earth-like exoplanet should orbit within the habitable zone, also known as the Goldilocks zone, where liquid water can exist on its surface. This zone is neither too close nor too far from the star, allowing for potentially habitable conditions.
3. Atmosphere: The presence of an Earth-like atmosphere, including suitable levels of oxygen and other gases, is crucial for supporting life. Observing the composition and stability of an exoplanet’s atmosphere can give insights into its potential habitability.
4. Temperature: The temperature range on an exoplanet should allow for liquid water to exist. A temperature range similar to Earth’s, where water can be in its liquid state, increases the chances of supporting life.
5. Star Type: The type of star that the exoplanet orbits can influence its potential habitability. Stars similar to our Sun, known as G-type main-sequence stars, are generally considered good candidates for hosting Earth-like planets.
6. Surface Conditions: Factors such as the presence of a solid surface, stable geology, and the absence of extreme conditions like intense radiation or constant volcanic activity are important for an Earth-like environment.
It is important to note that while these factors can help classify exoplanets as Earth-like, further studies and observations are necessary to determine their actual habitability and the presence of life.
How do scientists measure the similarity between Earth and other planets to determine their potential habitability?
Scientists measure the similarity between Earth and other planets to determine their potential habitability using several metrics and observations. One crucial factor is the planet’s distance from its host star, as it affects the planet’s temperature range and the ability to sustain liquid water. The presence of liquid water is considered a vital ingredient for life as we know it.
Scientists also analyze the planet’s atmosphere to assess its suitability for habitability. They look for the presence of gases such as carbon dioxide, oxygen, and water vapor, which are crucial for supporting life. The composition of the atmosphere can provide valuable insights into whether a planet has the necessary conditions for sustaining life.
Another important factor is the presence of a magnetic field. Earth’s magnetic field protects us from harmful solar radiation and cosmic rays. Therefore, scientists look for signs of a magnetosphere when determining a planet’s potential habitability. This can be inferred through observations of the planet’s interaction with its host star and the presence of auroras.
Geological activity is also an essential aspect to consider. Plate tectonics and volcanic activity play significant roles in regulating the planet’s climate, recycling nutrients, and providing energy sources for organisms. Scientists study planetary surfaces to determine if similar geological processes exist, indicating a higher likelihood of habitability.
Comparing a planet’s size and mass to that of Earth can also provide valuable information. These properties influence the planet’s gravity, atmospheric pressure, and geological activity, which all contribute to habitability.
Overall, scientists use a combination of data and observations from telescopes, spacecraft missions, and theoretical models to evaluate the similarity between Earth and other planets. While no two planets are identical, these comparative analyses help scientists pinpoint the potential habitability of exoplanets and expand our understanding of life in the universe.
In conclusion, while there are several exoplanets that share similarities with Earth, one stands out as the most similar: Kepler-452b. This distant planet, located in the habitable zone of its star, has a similar size to Earth and orbits its star at a comparable distance. Furthermore, Kepler-452b has the potential for liquid water on its surface, which is a key ingredient for life as we know it. While there is still much to learn about this intriguing exoplanet, its similarities with Earth make it a fascinating target for future research and exploration. Understanding Kepler-452b could provide valuable insights into the possibility of finding habitable environments and even extraterrestrial life beyond our own solar system.