Learn to Astronomy: In this article, we explore the fascinating function of a black hole, a celestial object with an immense gravitational pull that can devour anything that comes within its event horizon. Join us on this cosmic journey as we unravel the mysteries of these captivating cosmic phenomena.
Understanding the Role of Black Holes in Astronomy
Understanding the Role of Black Holes in Astronomy is crucial for comprehending the vastness of the universe. These mysterious cosmic objects, formed from the remnants of massive stars, possess an immense gravitational pull that even light cannot escape. Black holes play a vital role in shaping and influencing the structure of galaxies and are believed to be present at the center of most, if not all, galaxies, including our Milky Way.
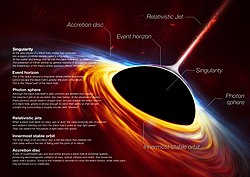
One important role of black holes is their ability to accrete matter. As surrounding gas and dust fall into a black hole, they form an accretion disk that heats up and emits radiation, creating intense bursts of energy. These active black holes, known as quasars, can outshine entire galaxies and provide valuable insights into the early universe.
Furthermore, black holes are responsible for certain stellar phenomena. When a massive star reaches the end of its life cycle, it undergoes a supernova explosion, leaving behind a dense core. If the core’s mass exceeds a specific threshold, it will collapse under its own gravity, forming a black hole. The energy released during this cataclysmic event contributes to the synthesis of heavy elements essential for the formation of new stars and planetary systems.
Additionally, black holes contribute to the formation and evolution of galaxies. Through their gravitational influence, they shape the distribution of stars and influence the dynamics of galactic structures. In some cases, black holes can trigger the formation of new stars by compressing gas clouds and initiating gravitational collapse.
Studying black holes not only expands our knowledge of fundamental physics but also helps us understand the intricate interplay between matter and gravity on cosmic scales. Their existence and behaviors challenge our current understanding of the universe and open avenues for further exploration and discovery.
Neil deGrasse Tyson: “We Just Detected THIS Inside A Black Hole & It’s TERRIFYING!”
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/-h3HdBk-tso”/]
Can a New Law of Physics Explain a Black Hole Paradox?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/yLOHdW7dLug”/]
Frequent questions
What is the primary function of a black hole in the context of astronomy?
The primary function of a black hole in the context of astronomy is to gravitationally capture and consume matter and energy. Black holes are extremely dense objects formed from the remnants of massive stars that have undergone gravitational collapse. Their intense gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from their event horizon.
Black holes play a crucial role in shaping and influencing the evolution of galaxies. As matter falls into a black hole, it forms an accretion disk, where it spirals inward due to gravitational forces. This process releases a tremendous amount of energy in the form of radiation, including X-rays and gamma rays. These energetic emissions can be detected by telescopes and provide valuable information about the physics of black holes and their surroundings.
Black holes also contribute to the growth of galaxies by triggering the formation of new stars. As matter falls into a black hole, it releases powerful jets of high-speed particles that can heat up surrounding gas and trigger star formation. These jets can extend over vast distances and have a significant impact on galactic structures.
Furthermore, the study of black holes helps astronomers understand the fundamental properties of gravity and the nature of spacetime. Black holes are the extreme testing grounds for Einstein’s theory of general relativity and provide insights into the behavior of matter under extreme conditions.
In summary, black holes serve as powerful cosmic engines that shape the dynamics of galaxies, emit energetic radiation, and offer valuable insights into the nature of gravity and spacetime.
How do black holes affect the surrounding space and celestial objects?
Black holes have a profound effect on the surrounding space and celestial objects. One of the most significant influences is their gravitational pull, which is incredibly strong due to their high mass and compact size.
Firstly, black holes can distort the fabric of spacetime, creating what is known as a gravitational singularity. This singularity pulls nearby matter and energy towards it, causing them to spiral into the black hole.
Secondly, as matter falls into a black hole, it forms an accretion disk around it. This disk is composed of superheated gas and dust particles that are caught in the powerful gravitational field. The accretion disk emits enormous amounts of energy, including X-rays and gamma rays, making it visible to telescopes and enabling its detection.
Furthermore, black holes are capable of gravitational lensing. This phenomenon occurs when a black hole’s intense gravity bends and distorts light passing near it. This distortion can magnify or distort the appearance of objects behind the black hole, allowing astronomers to observe distant galaxies or stars that would otherwise be invisible.
Lastly, black holes have the ability to tidally disrupt celestial objects that come too close. The extreme gravitational forces exerted by the black hole can tear apart stars or other massive objects, spaghettifying them as they fall into the black hole.
Overall, black holes have a significant impact on the surrounding space and celestial objects, affecting their trajectories, emitting intense radiation, distorting light, and even tearing apart nearby stars and planets. Their study provides crucial insights into the nature of the universe and the workings of gravity.
What role do black holes play in the formation and evolution of galaxies?
Black holes play a crucial role in the formation and evolution of galaxies. They are extremely dense regions in space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape their gravitational pull.
The formation of black holes is closely linked to the formation of galaxies. According to current theories, galaxies form from the gravitational collapse of massive clouds of gas and dust. As this gas and dust collapse under their own gravity, they form stars. Some of these stars, particularly the most massive ones, eventually run out of fuel and undergo a supernova explosion.
During this explosive event, the core of the star may collapse under its own gravity, forming a black hole. These black holes can then grow over time by accreting matter from their surroundings, such as gas from nearby stars or other black holes. This process is believed to play a significant role in the growth of galaxies.
As black holes grow, they release enormous amounts of energy in the form of radiation and jets of high-energy particles. This energy can have a profound impact on their host galaxies. The intense radiation and jets can heat up and push away surrounding gas, preventing it from collapsing and forming new stars. This process is known as “AGN feedback” (Active Galactic Nucleus feedback), and it helps regulate star formation in galaxies.
Black holes also contribute to the dynamics of galaxies. When two galaxies collide or come close to each other, their central black holes can merge. This merger process releases gravitational waves, which cause the newly formed black hole to recoil and kick back, influencing the movement of stars and matter within the galaxy.
Overall, black holes are essential players in the formation and evolution of galaxies. They influence the growth of galaxies through their accretion of matter, emit powerful energy that regulates star formation, and contribute to the dynamics of galactic interactions. Understanding the role of black holes is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of galaxy formation and evolution.
In conclusion, a black hole is an astronomical entity with the ability to distort space and time with its immense gravitational pull. Its function in the realm of Astronomy is to act as the ultimate cosmic vacuum cleaner, devouring anything that comes within its event horizon. This relentless consumption of matter and energy creates a powerful jet of radiation that can be observed across the electromagnetic spectrum. Despite their enigmatic nature, black holes play a crucial role in shaping the evolution of galaxies by regulating the growth of stars and influencing their surrounding environments. They also provide scientists with invaluable insights into the fundamental laws of physics, challenging our understanding of the universe. Further research and advancements in technology are necessary to unravel the mysteries concealed within these cosmic phenomena and expand our knowledge of the universe we inhabit.