Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we will explore the fascinating question: What is the closest point to the sun called? Join us as we dive into the concept of perihelion and discover the incredible phenomenon that occurs when celestial bodies come closest to our blazing star. Prepare to be amazed!
The Perihelion: The Closest Point to the Sun in Astronomy
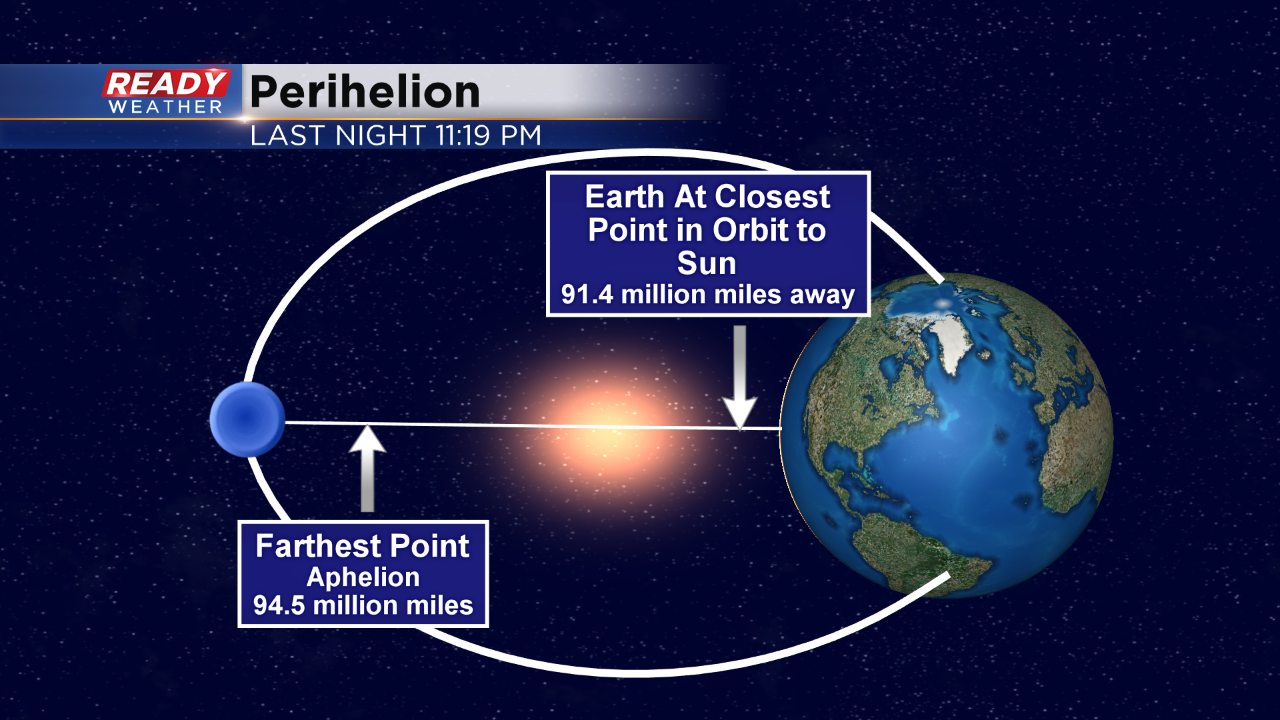
The Perihelion refers to the point in an object’s orbit around the Sun where it is closest to the star. In the context of astronomy, this term is widely used to describe the position of planets, comets, and other celestial bodies within their respective orbits. The distance between the Sun and the perihelion varies depending on the specific object and its orbital characteristics. For example, Earth reaches its perihelion in early January when it is approximately 147 million kilometers (91.4 million miles) away from the Sun. Understanding the perihelion is crucial in studying the dynamics of planetary motion and predicting the behavior of astronomical objects. By observing and calculating the timing and distances of perihelion passages, scientists can gain insights into the nature of celestial bodies and their interactions with the Sun.
What If the Earth and the Sun Switched Places?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/zw9bAq-nMJ0″/]
The Universe Is Not Infinite, There Is a Wall at the Edge!
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/0kWS2L9scBI”/]
Frequent questions
What is the closest point to the sun called in astronomy?
The closest point to the Sun in astronomy is called the **perihelion**.
Can you explain what perihelion means in relation to the sun?
Sure, I’d be happy to explain what perihelion means in relation to the sun.
In astronomy, perihelion refers to the point in a planet’s orbit where it is closest to the sun. It is derived from the Greek words “peri,” meaning near or around, and “helios,” meaning sun.
Perihelion is an important concept because it affects the orbital characteristics of a planet. When a planet is at perihelion, it is traveling at its highest velocity along its orbit, as it is being strongly influenced by the sun’s gravitational pull. This results in a shorter time for the planet to complete its orbit compared to when it is at its farthest point from the sun, known as aphelion.
For example, Earth’s perihelion occurs in early January, while its aphelion occurs in early July. During perihelion, Earth is about 147 million kilometers (91 million miles) away from the sun, compared to approximately 152 million kilometers (94.5 million miles) during aphelion. These variations in distance between the sun and Earth have minor effects on our climate and seasons.
It’s important to note that perihelion and aphelion are not fixed points in a planet’s orbit, but rather they slowly change over time due to various astronomical factors, including gravitational interactions with other celestial bodies.
Overall, understanding perihelion is crucial in studying planetary orbits and determining their positions relative to the sun at different times.
How does Earth’s distance from the sun change throughout its orbit?
Earth’s distance from the sun changes throughout its orbit due to its elliptical shape. The Earth follows an elliptical path around the sun, with the sun located at one of the two foci of the ellipse. This means that the distance between the Earth and the sun is not constant throughout the year.
The closest point in Earth’s orbit to the sun is called perihelion, while the farthest point is called aphelion. Perihelion occurs around January 3rd when Earth is about 147 million kilometers (91.4 million miles) away from the sun. On the other hand, aphelion occurs around July 4th when Earth is about 152 million kilometers (94.5 million miles) away from the sun.
This difference in distance has important implications for Earth’s climate. When the Earth is closer to the sun during perihelion, it receives about 7% more solar radiation compared to aphelion. However, this difference in distance alone is not responsible for the variations in seasons. Other factors like the tilt of Earth’s axis play a more significant role in determining the seasons.
It is important to note that despite the variation in distance during its orbit, the difference in solar radiation received from the sun is relatively small and does not have a drastic impact on Earth’s overall climate system.
In conclusion, the closest point to the sun is known as perihelion. This term refers to the point in an object’s orbit where it is closest to the sun. Understanding the concept of perihelion is crucial in studying celestial bodies and their movements. By observing the changes that occur during this point, scientists can gather valuable information about the characteristics of these objects and their interactions with the sun. So, whether you’re an astronomer or simply curious about our solar system, knowing about perihelion will deepen your understanding of the intricate dance between the sun and its orbiting companions.