The Closest Galaxy to Earth: A Fascinating Cosmic Neighbor
Embark on a celestial journey as we unravel the mysteries of the closest galaxy to Earth. Discover the breathtaking beauty and scientific wonders of our cosmic neighbor, with captivating insights into its structure, composition, and dazzling array of stars. Join us as we delve into the intriguing story of our proximity to this extraordinary galactic companion.
The Closest Galaxy to Earth: Exploring the Proximity and Mystery of Andromeda
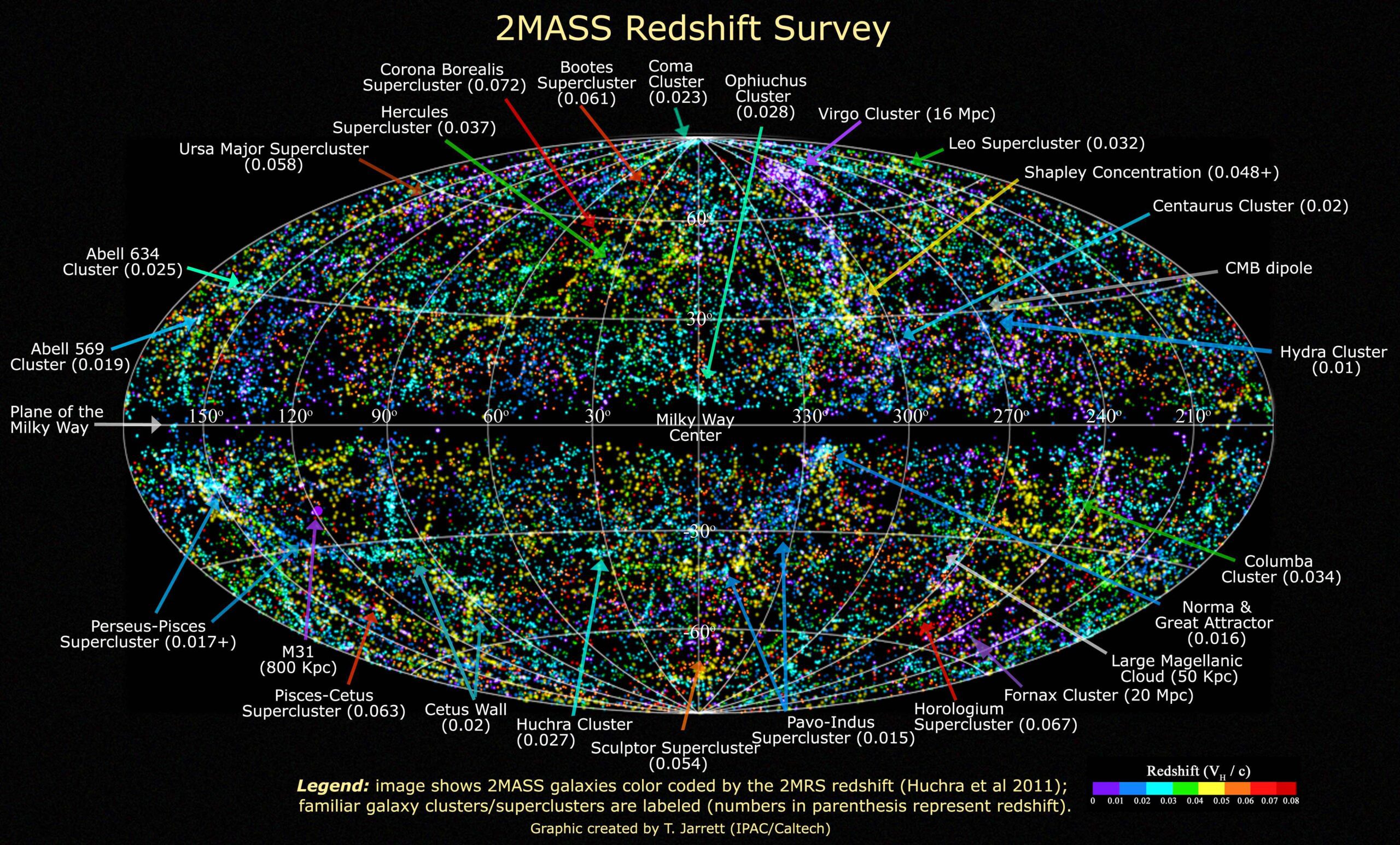
The closest galaxy to Earth is Andromeda, also known as M31. It is located approximately 2.537 million light-years away from our Milky Way galaxy. Andromeda is a spiral galaxy and is visible to the naked eye from Earth, appearing as a faint smudge in the night sky.
One of the most intriguing aspects of Andromeda is its proximity to our galaxy. Scientists believe that in about 4.5 billion years, the Andromeda galaxy will collide with our own Milky Way galaxy, resulting in a new, merged galaxy. This event, known as the Andromeda-Milky Way collision, has sparked great interest among astronomers and astrophysicists.
Studying Andromeda provides valuable insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies. By examining the structure, composition, and dynamics of Andromeda, scientists can glean information about how galaxies, including our own, have developed over time. This understanding contributes to our knowledge of the large-scale structure of the universe.
Furthermore, Andromeda houses a variety of stellar populations, including young, hot-blue stars and older, cooler red stars. These stars offer opportunities for astronomers to study stellar evolution, star formation, and the lifecycle of galaxies. The exploration of Andromeda allows astronomers to compare and contrast it with our Milky Way, providing insight into the diversity of galaxies in the universe.
Despite being the closest large galaxy to our Milky Way, Andromeda still holds many mysteries. For instance, the origin of its peculiar tidal features, such as the diffuse outer halo and accompanying stellar streams, is not fully understood. Exploring these mysteries provides scientists with an opportunity to delve deeper into the intricate workings of galaxies and their evolution.
In conclusion, studying the proximity and mystery of Andromeda is crucial to our understanding of the universe. Its role as the closest galaxy to Earth offers researchers a unique opportunity to explore the dynamics, formation, and evolution of galaxies. By unlocking the secrets held within Andromeda, we can deepen our knowledge of the cosmos and our place within it.
How did they actually take this picture? (Very Long Baseline Interferometry)
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/Q1bSDnuIPbo”/]
What Was Earth Like Before the Dinosaurs?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/GxyjWhz5VT0″/]
Frequent questions
What is the closest galaxy to Earth and how far away is it?
The closest galaxy to Earth is the Andromeda Galaxy, also known as M31. It is approximately 2.537 million light-years away. The Andromeda Galaxy is a spiral galaxy similar in size to the Milky Way and can be seen with the naked eye from Earth. In fact, it is heading towards our galaxy and is expected to eventually collide with the Milky Way in about 4 billion years.
How did astronomers determine that the Andromeda Galaxy is the closest galaxy to Earth?
Astronomers determined that the Andromeda Galaxy is the closest galaxy to Earth through various observational techniques.
One of the key methods used is called parallax, which relies on measuring the apparent shift in the position of a celestial object as seen from different points in Earth’s orbit around the Sun. By comparing the positions of stars in the Andromeda Galaxy relative to more distant background stars, astronomers can calculate its distance.
Another method involves analyzing the brightness of certain types of variable stars called Cepheid variables. These stars have a well-known relationship between their intrinsic brightness and their pulsation period. By measuring the apparent brightness of Cepheids in the Andromeda Galaxy and comparing them to those in nearby galaxies of known distance, astronomers can estimate the distance to Andromeda.
Additionally, astronomers use other distance indicators, such as supernovae and globular clusters, to further refine their measurements. By combining various distance measurements, scientists have concluded that the Andromeda Galaxy is approximately 2.537 million light-years away from Earth, making it the closest spiral galaxy to us.
In conclusion, astronomers determined that the Andromeda Galaxy is the closest galaxy to Earth using techniques like parallax, Cepheid variables, supernovae, and globular clusters to measure its distance.
Can we see the closest galaxy to Earth with the naked eye or do we need a telescope?
We need a telescope to see the closest galaxy to Earth. The closest galaxy to our Milky Way is the Andromeda Galaxy, located about 2.5 million light-years away. While it is the closest spiral galaxy to us, it is not visible to the naked eye due to its distance. However, with a small telescope or even binoculars, you can observe the Andromeda Galaxy as a faint smudge of light in the night sky. It’s a fascinating sight and worth checking out if you have the opportunity.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the closest galaxy to Earth is the Andromeda Galaxy. With its proximity of about 2.537 million light-years away, it is the nearest spiral galaxy to our Milky Way. This intergalactic neighbor has fascinated astronomers and space enthusiasts for centuries, and studying its structure and evolution provides valuable insights into the dynamics of galaxies in general. The Andromeda Galaxy’s close proximity also makes it a potential candidate for future exploration and potential interactions with our own galaxy. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the universe, the Andromeda Galaxy will undoubtedly remain a prominent subject of research and discovery in the field of Astronomy.