Learn to Astronomy: Discover the ideal time to soak up the sun for maximum vitamin D absorption. In our latest article, we delve into the science behind the best time to sunbathe, ensuring you get the most out of those rays while staying safe. Come join us on this enlightening journey!
The Astronomical Perspective: Finding the Optimal Time for Sunbathing to Boost Vitamin D Levels
The Astronomical Perspective: Finding the Optimal Time for Sunbathing to Boost Vitamin D Levels
Sunbathing is a popular activity for many people who enjoy soaking up the sun’s rays and getting a tan. However, there is another important benefit to sunbathing that often goes overlooked – the production of vitamin D in the body.
Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining good health, as it helps to regulate calcium and phosphorus levels in the body. It also aids in the absorption of calcium, which is essential for strong bones and teeth. Furthermore, vitamin D plays a role in supporting a healthy immune system and promoting overall well-being.
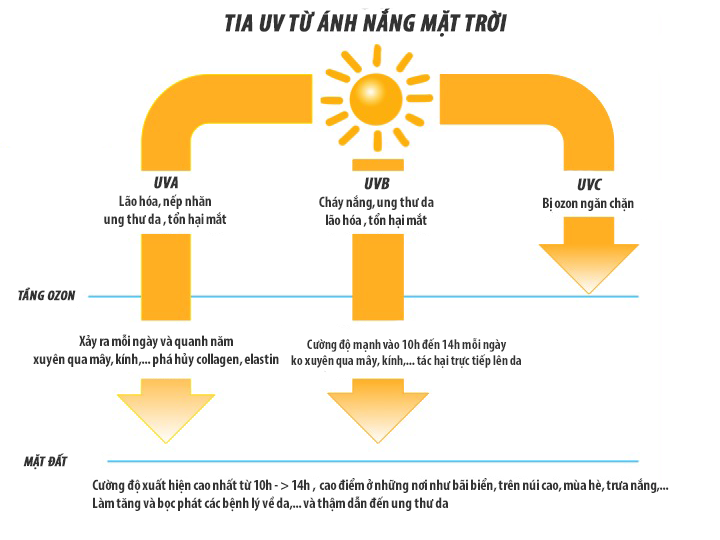
The primary source of vitamin D comes from exposure to sunlight. When our skin is exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation from the sun, it triggers a chemical reaction that converts a form of cholesterol in our skin into vitamin D3. This inactive form is then transformed into an active form of vitamin D by our liver and kidneys.
However, not all sunlight exposure is equal when it comes to vitamin D production.
The angle at which the sun’s rays hit the Earth is an important factor to consider. The sun’s angle changes throughout the day and varies depending on the time of year and your location on the globe. The strongest UVB radiation occurs when the sun is high in the sky, which is typically around midday.
Therefore, to maximize vitamin D production, sunbathing during midday hours is key.
Another factor to consider is the latitude at which you are located. People who live closer to the equator receive more intense sunlight throughout the year compared to those living at higher latitudes. This means that individuals living in northern or southern regions may need to spend more time in the sun to achieve adequate vitamin D levels.
It is also important to note that sunscreen, while crucial for protecting the skin from harmful UV radiation that can cause skin cancer, can inhibit vitamin D production. Sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF) reduces the amount of UVB radiation absorbed by the skin and, subsequently, the amount of vitamin D produced.
Therefore, it is important to find a balance between protecting your skin and getting enough sun exposure for vitamin D synthesis.
In conclusion, understanding the astronomical perspective can help us determine the optimal time for sunbathing to boost vitamin D levels. Sunbathing during midday hours when the sun is high in the sky and taking into account your location on the globe can maximize vitamin D production. Additionally, finding the right balance between sunscreen use and sun exposure is crucial for maintaining healthy vitamin D levels.
The keto mistake I wish I could undo
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/GoYWOwnKJ3A”/]
23 Signs Your Body Needs More Nutrients: How to Address the Deficiencies
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/UqLuyop6Xtc”/]
Frequent questions
What is the optimal time of day to sunbathe in order to maximize vitamin D production, considering the Earth’s rotation and the position of the Sun in relation to the observer?
The optimal time of day to sunbathe for maximizing vitamin D production depends on various factors, including the Earth’s rotation and the position of the Sun in relation to the observer.
Vitamin D synthesis primarily occurs when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation from the Sun. UVB radiation is responsible for triggering the conversion of a precursor molecule in the skin into vitamin D.
To maximize vitamin D production, it is recommended to expose your skin to sunlight when the Sun is at a higher angle in the sky, typically between 10 am and 3 pm. During this time, the Sun’s rays have to travel a shorter distance through the atmosphere, which reduces the absorption and scattering of UVB radiation. Consequently, more UVB radiation reaches the Earth’s surface, increasing the potential for vitamin D synthesis.
It is important to note that the Sun’s position in the sky changes throughout the year due to the tilt of the Earth’s axis and its orbit around the Sun. Therefore, the optimal time for sunbathing may vary depending on the season and geographical location. For example, during summer months and closer to the equator, the Sun is generally higher in the sky, providing more opportunities for vitamin D production compared to winter months or higher latitudes.
However, it is crucial to balance the benefits of vitamin D synthesis with the potential harm caused by excessive UV exposure. Prolonged exposure to intense sunlight without protection can increase the risk of skin damage and skin cancer. Therefore, it is recommended to practice sun safety measures, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and sunglasses, while also considering individual factors such as skin type and sensitivity to sunlight.
In summary, the optimal time of day for sunbathing to maximize vitamin D production is typically between 10 am and 3 pm when the Sun is at a higher angle in the sky. However, it is essential to consider individual circumstances and practice sun safety measures to protect the skin from harmful UV radiation.
How does the Earth’s tilt affect the availability of sunlight and the best time to sunbathe for synthesizing vitamin D?
The Earth’s tilt affects the availability of sunlight and influences the best time to sunbathe for synthesizing vitamin D.
The Earth is tilted on its axis at about 23.5 degrees relative to its orbit around the Sun. This tilt causes the changing seasons and variations in the amount of sunlight reaching different parts of the planet throughout the year.
During summer in the hemisphere tilted towards the Sun, that particular region receives more direct sunlight and experiences longer days. This means there are more daylight hours available for sunbathing and synthesizing vitamin D. In contrast, during winter in the same hemisphere, the tilt causes the Sun to be lower in the sky, resulting in shorter days and less direct sunlight. Thus, the availability of sunlight for vitamin D synthesis decreases during winter.
In the hemisphere tilted away from the Sun, the opposite effect occurs. Summer brings longer days and more direct sunlight, while winter brings shorter days and less direct sunlight. The availability of sunlight for vitamin D synthesis follows this pattern as well.
The best time to sunbathe for synthesizing vitamin D varies depending on the latitude and time of year. Generally, it is recommended to expose your skin to sunlight when the Sun is highest in the sky, typically between 10 a.m. and 3 p.m. during the summer months. This is when the UVB rays, responsible for triggering vitamin D synthesis in our skin, are more intense. However, it is crucial to balance sun exposure to avoid harmful effects such as sunburn or skin damage.
It’s important to note that individual factors such as skin tone, age, and geographic location also play a role in determining the optimal time and duration of sun exposure for vitamin D production. Consulting a healthcare professional or dermatologist is always recommended to ensure safe sunbathing practices and adequate vitamin D synthesis.
Can studying the path of the Sun across the sky throughout the year help determine the best times and seasons for sunbathing to ensure sufficient vitamin D synthesis with minimal exposure to harmful UV radiation?
Studying the path of the Sun across the sky throughout the year can indeed help determine the best times and seasons for sunbathing while ensuring sufficient vitamin D synthesis with minimal exposure to harmful UV radiation.
The Sun’s path across the sky changes throughout the year due to the tilt of the Earth’s axis. This phenomenon causes the angle at which sunlight reaches different latitudes on Earth to vary. By understanding this motion, we can make informed choices about when and for how long it is safe to expose our skin to the Sun.
Determining the best times for sunbathing involves considering factors such as the altitude of the Sun above the horizon, the length of shadows cast by objects, and the intensity of UV radiation. These factors depend on the time of day, the season, and the geographical location.
During the summer months, when the Sun is higher in the sky, more direct sunlight reaches the Earth’s surface, leading to the highest levels of UV radiation and vitamin D synthesis. However, prolonged exposure during midday can also increase the risk of sunburn and skin damage. It is generally advisable to limit sun exposure between 10 am and 4 pm when the Sun is at its highest point.
In contrast, during the winter months, especially at higher latitudes, the Sun’s angle is much lower, resulting in less intense UV radiation reaching the surface. Consequently, it may be necessary to spend more time outdoors during midday to achieve sufficient vitamin D synthesis.
By monitoring the Sun’s path over time, individuals can optimize their sunbathing habits by determining the best times and seasons for exposure. It is important to strike a balance between obtaining enough vitamin D and minimizing the risks associated with excessive UV radiation. Remember to always take into account personal factors like skin type and sensitivity.
In summary, studying the path of the Sun across the sky throughout the year can provide valuable insights into the best times and seasons for sunbathing to ensure sufficient vitamin D synthesis with minimal exposure to harmful UV radiation.
In conclusion, timing is crucial when it comes to sunbathing for vitamin D in the context of Astronomy. While the sun is at its highest point in the sky during midday, it is important to note that this is also when the UV rays are the strongest, increasing the risk of sunburn and skin damage. Therefore, it is recommended to aim for shorter exposure times during this period and instead opt for early morning or late afternoon sunbathing sessions. During these times, the UVB rays necessary for vitamin D synthesis are still present but with reduced intensity, minimizing the risk of harmful effects. Remember to always practice safe sun habits, such as wearing sunscreen and protective clothing, and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the optimal sunbathing duration and frequency based on individual needs and skin type. By being mindful of the best time to soak up the sun’s rays, we can maximize our vitamin D intake while staying aware of the impact of UV radiation on our bodies.