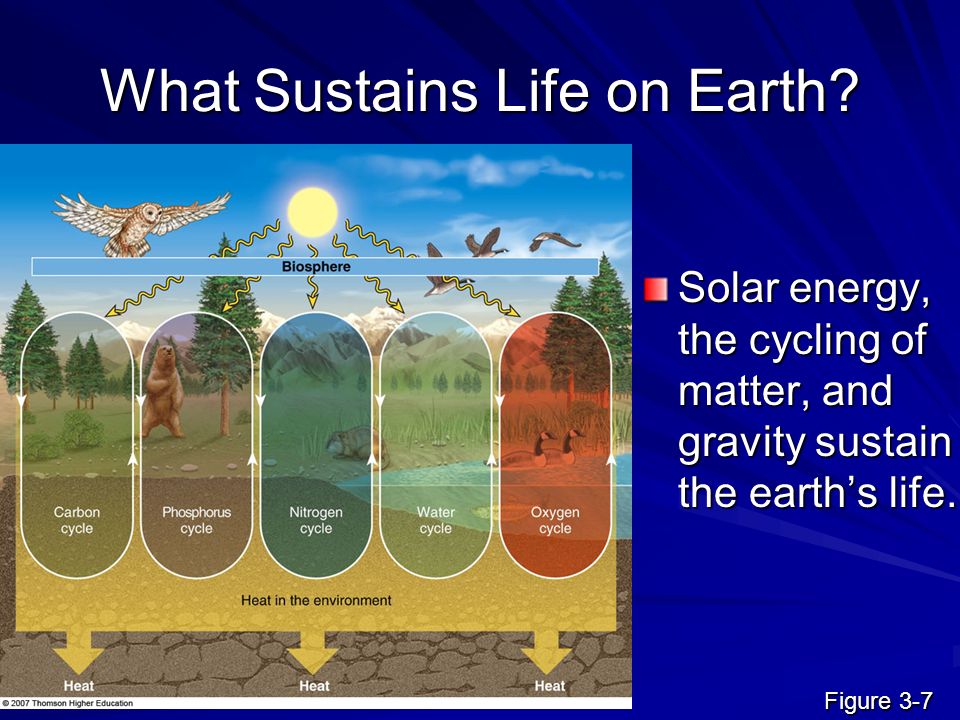
Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we delve into the fascinating question: What is it that sustains our planet Earth? Explore the intricate balance of natural phenomena and processes that make life possible on our beautiful blue planet. Join us as we unlock the secrets behind Earth’s sustainability and understand the interconnections between various factors that contribute to its habitability.
The Cosmic Balance: Unveiling the Forces that Sustain Planet Earth
From the vast expanse of the cosmos to the intricate workings of our own planet, the forces of nature play a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth. Understanding these forces is key to unraveling the mysteries of the universe and appreciating the delicate balance that keeps our planet thriving.
One of the most powerful forces at play is gravity, the invisible hand that holds everything together. It shapes the formation of galaxies, controls the motion of celestial bodies, and keeps our feet firmly planted on the ground. Without gravity, planets would drift aimlessly through space, deprived of the conditions necessary for life to emerge.
Another force essential to our existence is electromagnetism, the dynamic interplay between electricity and magnetism. It governs the behavior of charged particles, creates luminous displays like the auroras, and powers the countless technologies we rely on. From the formation of stars and galaxies to the everyday operations of our electronic devices, electromagnetism permeates every aspect of our astronomical understanding.
In the quest to sustain life, the role of radiation cannot be overlooked. Both visible and invisible, radiation permeates the cosmos and plays a vital part in maintaining Earth’s habitability. The sun, our nearest star, provides the radiant energy needed for photosynthesis, allowing plants to convert sunlight into the oxygen we breathe and the food we eat. Radiation also shapes the climate, drives weather patterns, and enables vital chemical reactions.
Additionally, the strong and weak nuclear forces, which govern interactions at the atomic level, are responsible for the processes that power stars and unleash tremendous amounts of energy in nuclear reactions. These forces are intricately linked to the creation of heavy elements, the fuel for life as we know it.
Finally, the cosmic balance is maintained by the mysterious dark matter and dark energy, the enigmatic forces that shape the structure and expansion of the universe. While their exact nature remains elusive, scientists believe that dark matter provides the gravitational glue that holds galaxies together, while dark energy propels the accelerated expansion of the universe.
In conclusion, the forces at play in the vast cosmic arena are intricately connected, working together to sustain the delicate balance essential for life on our planet. From gravity to electromagnetism, radiation to nuclear forces, and even the mysterious dark matter and dark energy, each force contributes to the grand tapestry of existence. Only by understanding and appreciating these forces can we navigate the cosmos and truly comprehend the beauty and wonder of our astronomical home.
What the Earth is really standing on | The REAL TRUTH beyond SCIENCE
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/RoyFXQnOnfc”/]
Religions Are Promoting The Kalaum Reptilian God
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/z9iRztMczuI”/]
Frequent questions
What role does the sun play in sustaining the Earth?
The sun plays a crucial role in sustaining the Earth. It is the primary source of energy for the planet. Through the process of nuclear fusion, the sun converts hydrogen into helium, releasing an immense amount of energy in the form of light and heat. This energy reaches the Earth in the form of sunlight.
Sunlight provides heat and regulates the temperature on our planet. It warms the Earth’s surface, creating weather patterns and driving atmospheric circulation. This, in turn, influences global climates and helps create diverse ecosystems.
Moreover, **sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen. This process not only allows plants to grow and produce food but also produces oxygen, which is vital for sustaining life on Earth.
The sun’s gravitational pull also plays a significant role in maintaining the orbits of the planets in the solar system, including Earth. The gravitational interaction between the sun and the Earth keeps our planet in a stable orbit, ensuring the right distance and conditions for life to thrive.
In addition to its direct effects, the sun influences Earth’s climate through its sunspot activity and solar cycles. These cycles can affect the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth, leading to variations in climate patterns over long periods.
Overall, the sun is crucial for sustaining life on Earth. Its energy, heat, and light provide the necessary conditions for the existence of diverse ecosystems, regulate temperatures, drive weather patterns, and support the process of photosynthesis, all of which make our planet habitable.
How do the Earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field contribute to its ability to sustain life?
The Earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field play crucial roles in sustaining life on our planet.
The atmosphere acts as a protective blanket that shields the Earth from harmful solar radiation, such as ultraviolet (UV) rays. Presence of an ozone layer within the atmosphere absorbs most of the Sun’s UV radiation, preventing it from reaching the surface. This protection is essential for the survival of life as high levels of UV radiation can cause DNA damage and harm living organisms.
Additionally, the atmosphere regulates the temperature on Earth. It helps distribute heat by trapping some of the Sun’s energy and preventing it from escaping back into space. This phenomenon, known as the greenhouse effect, maintains a suitable average temperature for life to thrive. Without this natural insulation, the Earth would be much colder, making it challenging for living organisms to survive.
Moreover, the Earth’s atmosphere is composed of a mixture of gases that are essential for life. Oxygen, for instance, is necessary for respiration and metabolism in most organisms, including humans. Nitrogen, although inert, is crucial for the synthesis of amino acids and proteins, which are building blocks of life. Carbon dioxide, despite having a negative reputation due to climate change, plays a vital role in photosynthesis, the process through which plants convert sunlight into energy.
In addition to the atmosphere, the Earth’s magnetic field contributes to the sustainability of life. The magnetic field is generated by the movement of molten iron in the Earth’s core. It creates a protective shield around the planet that deflects charged particles emanating from the Sun, forming what is called the magnetosphere.
This magnetosphere prevents the solar wind, a stream of charged particles, from directly hitting the Earth’s surface. These particles can strip away the atmosphere over time and expose life to harmful radiation. The magnetic field also traps charged particles from the Sun, creating beautiful auroras near the poles but keeping them away from where most life resides.
In summary, the Earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field work together to protect life on our planet. The atmosphere blocks harmful solar radiation, regulates temperature, and provides essential gases for living organisms. The magnetic field shields the planet from the Solar wind, preventing the erosion of the atmosphere and reducing exposure to harmful particles. Understanding these protective mechanisms is crucial in our quest to explore other celestial bodies and determine their potential habitability.
What are the key factors that contribute to the Earth’s stable climate and habitability?
The key factors that contribute to Earth’s stable climate and habitability are numerous and interconnected, providing a suitable environment for life as we know it.
Firstly, the presence of liquid water is crucial for sustaining life on Earth. Water acts as a solvent, facilitating chemical reactions necessary for life processes. The abundance of water on our planet, due to its position in the habitable zone of the solar system and the presence of an atmosphere that retains this vital resource, allows for the existence of oceans, lakes, and rivers.
Secondly, the atmosphere plays a significant role in maintaining a stable climate and habitable conditions. Earth’s atmosphere consists primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with trace amounts of other gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. This composition is crucial for regulating temperature, redistributing heat, and protecting against harmful solar radiation. The greenhouse effect caused by certain gases, particularly carbon dioxide, helps maintain a relatively stable climate by trapping heat in the atmosphere.
The magnetosphere is another key factor in Earth’s habitability. Our planet has a strong magnetic field generated by the movement of molten iron in its core. This magnetic shield effectively protects the surface from the solar wind and cosmic rays, which can be detrimental to life. It also helps retain the atmosphere by preventing its escape into space.
Furthermore, plate tectonics have played a vital role in Earth’s climate stability and habitability over geological timescales. The movement and collision of continental plates result in the formation of mountain ranges, diverse ecosystems, and the recycling of atmospheric carbon dioxide through weathering. These processes regulate the carbon cycle and prevent runaway greenhouse or icehouse effects.
The presence of a stable star like the Sun is fundamental to Earth’s habitability. The Sun provides the necessary energy for life through photosynthesis, which supports the primary productivity of ecosystems and drives climate dynamics.
Lastly, the long-term stability of Earth’s orbit has contributed to the maintenance of steady climate conditions over millions of years. Variations in Earth’s orbital parameters, such as eccentricity, axial tilt, and precession, result in cyclical climate changes on timescales of tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of years. However, the overall stability of our orbit has allowed for the evolution and persistence of complex life forms.
In conclusion, a combination of factors including the presence of liquid water, a protective atmosphere, a strong magnetosphere, plate tectonics, a stable star like the Sun, and a stable orbit are essential for Earth’s stable climate and habitability. These factors work in concert to create an environment suitable for the existence and flourishing of life as we know it.
In conclusion, it is fascinating to explore the factors that sustain our planet Earth in the vast realm of astronomy. From the strong gravitational pull that keeps us anchored to the Sun’s warmth and light, to the delicate balance of our atmosphere that shields us from harmful cosmic rays, each component plays a crucial role in the sustenance of life on Earth. Our ability to adapt and evolve in harmony with these celestial elements underscores the remarkable resilience of our planet.
However, as stewards of this fragile blue dot in the universe, it is imperative that we continue to nurture and protect the Earth’s resources for future generations. By understanding the intricacies of our celestial surroundings, we can ensure a sustainable future for our planet and all its inhabitants. So let us marvel at the wonders of astronomy and be inspired to live in harmony with the forces that sustain our beautiful home.