Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we explore the intriguing question: What sets Mars apart from Earth? Discover the unique features of Mars that make it an irresistible destination for future explorations and unveil the mysteries of our neighboring red planet. Join us on this cosmic journey as we delve into the secrets of Mars and unlock its enigmatic allure.
The Mysteries of Mars: Unveiling the Unique Features Absent on Earth
The Mysteries of Mars: Unveiling the Unique Features Absent on Earth in the context of Astronomy.
As humans, we have always been fascinated by the mysteries of the universe. One such enigma that has captured our attention for decades is the planet Mars. Mars is often referred to as the “Red Planet” due to its distinct reddish hue, which is caused by iron oxide (rust) on its surface.
But what makes Mars truly intriguing for astronomers and scientists is the plethora of unique features that are absent on Earth. These features provide valuable insight into the planet’s geological history, potential for harboring life, and possibilities for future human exploration.
One of the most prominent features on Mars is its massive volcanoes. Olympus Mons, for example, is the largest volcano in the solar system, towering at a staggering 13.6 miles (22 kilometers) high. This volcanic giant is roughly three times the height of Mount Everest, making it an awe-inspiring sight.
Another distinctive feature of Mars is its vast canyon system, Valles Marineris. This colossal rift stretches over 2,500 miles (4,000 kilometers) across the planet’s surface and is up to 7 miles (11 kilometers) deep in certain areas. To put it in perspective, Valles Marineris is more than four times longer and eight times deeper than the Grand Canyon on Earth.
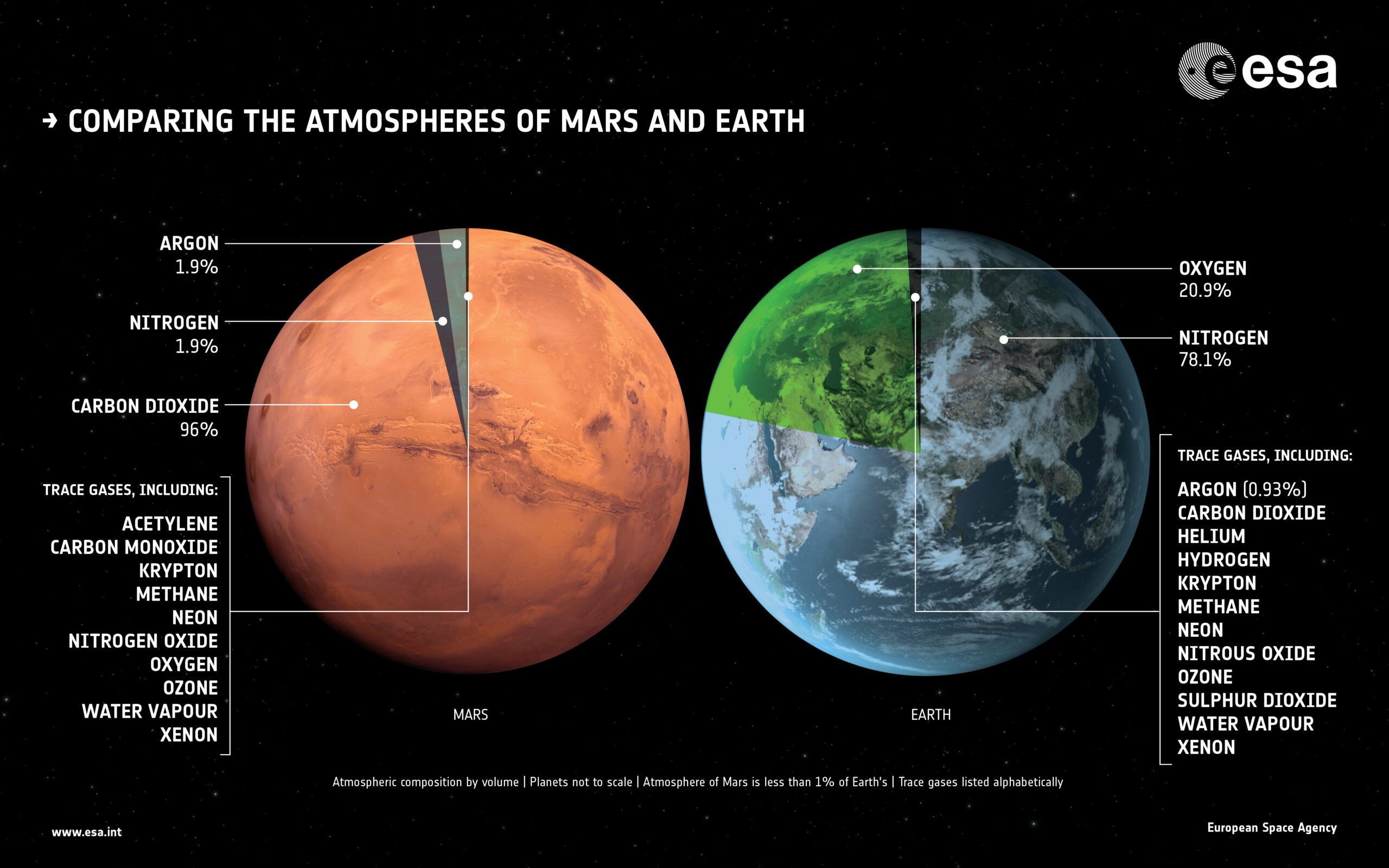
Furthermore, Mars has an incredibly thin atmosphere compared to Earth. Although it is composed mostly of carbon dioxide, its tenuous nature makes it unable to support human life without proper protection. However, this thin atmosphere also means that Mars experiences extreme temperature variations, with temperatures plummeting to -195 degrees Fahrenheit (-125 degrees Celsius) during winter nights.
One of the most tantalizing mysteries surrounding Mars is the possibility of past or present microbial life. Evidence suggests that Mars once had liquid water on its surface, and where there’s water, there’s the potential for life. Scientists have been tirelessly analyzing data from Mars rovers and orbiters in search of clues that could point to past or even current microbial presence.
In addition to these unique features, Mars has polar ice caps, dust storms that can engulf the entire planet, and intricate geological formations that continue to baffle scientists.
Unveiling the mysteries of Mars is an ongoing endeavor that requires meticulous study and exploration. With each new mission to the Red Planet, we inch closer to unraveling its secrets and understanding our place in the universe.
Mars truly holds the key to unlocking answers to some of the most profound questions about our existence and the possibility of life beyond Earth. The more we learn about this intriguing planet, the more we realize how it differs from our home planet and how it might offer valuable insights into the formation and evolution of terrestrial planets in general.
10 Questionable Things NASA Has Found On Mars
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/bW-U3BSqzFQ”/]
Scientists claim! Life on Earth “is not a coincidence” Type-7 Civilization created us with a Purpose
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/BZ7U8iR0z4A”/]
Frequent questions
What unique geological features does Mars possess that Earth lacks?
Mars, often referred to as the “Red Planet,” possesses several unique geological features that are absent on Earth. One of the most prominent features is the presence of massive volcanoes. Mars hosts the largest volcano in the solar system known as Olympus Mons, which stands at an astounding height of 13.6 miles (22 kilometers), making it nearly three times taller than Mount Everest. Additionally, Mars is home to other impressive shield volcanoes such as Ascraeus Mons, Pavonis Mons, and Arsia Mons.
Another distinct feature found on Mars is Valles Marineris, a vast canyon system that stretches across roughly a quarter of the planet’s circumference. This gargantuan chasm is around 2,500 miles (4,000 kilometers) long, up to 125 miles (200 kilometers) wide, and reaches depths of up to 4.35 miles (7 kilometers). For comparison, Earth’s Grand Canyon, while impressive, pales in comparison to the scale of Valles Marineris.
Furthermore, Mars exhibits an abundance of impact craters, which are evidence of its violent past. Impact craters are caused by the collisions of asteroids or comets with the planet’s surface. Due to Mars’ thin atmosphere, more impacts occur on its surface compared to Earth. One of the most well-known Martian craters is the Hellas Planitia, which is a massive impact basin measuring around 1,400 miles (2,300 kilometers) in diameter.
Lastly, Mars is the only known planet to have polar ice caps primarily composed of frozen carbon dioxide, or dry ice. These caps, situated at the planet’s north and south poles, expand and contract with the changing seasons. On Earth, our polar ice caps are primarily made up of water ice.
In conclusion, Mars possesses unique geological features including massive volcanoes, the impressive Valles Marineris canyon system, an abundance of impact craters, and polar ice caps composed of frozen carbon dioxide. These distinctive characteristics provide valuable insights into the geologic history and processes that have shaped the Red Planet.
How does the absence of a magnetic field on Mars impact its atmosphere compared to Earth’s?
The absence of a magnetic field on Mars has a significant impact on its atmosphere compared to Earth’s. Earth’s magnetic field acts as a shield, protecting the planet’s atmosphere from the solar wind. This protective shield prevents the erosion of the atmosphere by trapping charged particles and deflecting them away.
On Mars, however, the lack of a global magnetic field allows the solar wind to directly interact with the Martian atmosphere. The charged particles of the solar wind can penetrate deeper into the atmosphere and cause various effects.
One notable consequence is the accelerated loss of atmospheric gases, including lighter ones like hydrogen and helium. As the solar wind interacts with the upper atmosphere, it can strip away these gases over time. This process, known as sputtering, contributes to the thinning of Mars’ atmosphere.
Additionally, the absence of a magnetic field can also result in the escape of heavier ions from the Martian atmosphere. These heavier ions, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, can be accelerated by the solar wind and escape into space, further depleting the atmosphere.
Furthermore, the lack of a global magnetic field makes Mars more vulnerable to intense solar storms. Solar storms can directly impact the Martian atmosphere and lead to temporary atmospheric disturbances, including enhanced auroras and fluctuations in temperature.
In summary, the absence of a magnetic field on Mars has significant implications for its atmosphere. It contributes to the accelerated loss of gases, including lighter elements, and the escape of heavier ions. It also makes Mars more susceptible to the direct effects of solar storms, which can disrupt the atmosphere.
What specific conditions on Mars make it a potential candidate for supporting past or present microbial life, which Earth does not possess?
Mars, with its unique environmental conditions, harbors several potential factors that make it a candidate for supporting past or present microbial life, which Earth does not possess.
1. Liquid Water: While water is essential for life as we know it, Mars has limited liquid water on its surface due to the low atmospheric pressure and low temperatures. However, there is evidence of water in the form of ice, both at the polar ice caps and beneath the surface. This provides a potential habitat for microbial life adapted to survive in extreme conditions.
2. Perchlorates: Martian soil contains perchlorates, which are powerful oxidizing agents. While they can be harmful to most forms of life on Earth, some microorganisms have evolved the ability to utilize perchlorates as an energy source. This suggests that certain types of microbial life might thrive in the Martian soil.
3. Lack of Ozone Layer: Mars lacks a significant ozone layer, unlike Earth. The ozone layer on Earth protects the surface from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. However, the relatively thin atmosphere of Mars provides only partial shielding against UV radiation, creating niches where UV-tolerant microorganisms may exist.
4. Subsurface Environments: Mars possesses subsurface environments where conditions may be more favorable for microbial life. The icy subsurface, shielded from harsh radiation and extreme temperatures, could potentially provide a stable environment conducive to the existence of microbial organisms.
5. Potential Ancient Habitability: Geological evidence indicates that Mars had a more Earth-like environment in the distant past, with rivers, lakes, and possibly even an ocean. These ancient habitable conditions might have allowed for the emergence and development of microbial life forms that have since gone dormant or adapted to survive under more extreme conditions.
It is important to note that the search for life on Mars is ongoing, and while these conditions hint at the possibility of past or present microbial life, further exploration and analysis are necessary to confirm their existence.
In conclusion, Mars holds a multitude of unique features and characteristics that distinguish it from Earth, making it a captivating celestial body for scientific exploration. From its distinct topography, including the largest volcano and deepest canyon in the solar system, to its dusty and barren landscapes, Mars offers a glimpse into the past and potential future of our own planet.
One of the most striking distinctions is Mars’ lack of a substantial atmosphere, resulting in extreme temperature fluctuations and minimal protection from cosmic radiation. This, combined with the presence of intriguing geological structures, such as polar ice caps and ancient riverbeds, makes Mars an enticing target for further investigation and potential human colonization.
Additionally, the possibility of finding evidence of past or even present life on Mars continues to ignite scientific curiosity and fuel ongoing missions to unlock the red planet’s secrets. While Earth remains our home and supports a vibrant ecosystem, Mars embodies the potential for new discoveries and answers about our place in the universe. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos, the allure of Mars reminds us of the endless wonders yet to be explored.