Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we explore the fascinating phenomenon of objects that are “attracted to the sun”. Through captivating visuals and intriguing explanations, we unveil the secrets behind celestial bodies orbiting our radiant star. Join us on this enlightening journey as we delve into the gravitational dance between the sun and its captivating companions.
Unlocking the Secrets of Solar Attraction: The Sun’s Magnetic Pull Explored in Astronomy
The Sun’s magnetic pull is a fascinating phenomenon that astronomers have been studying for years. It plays a crucial role in many aspects of our solar system, from the formation of planets to the generation of solar flares and space weather.
Understanding the Sun’s magnetic field is key to unraveling its mysteries. Scientists have observed that the Sun’s magnetic field is generated by the movement of charged particles within its interior. This movement creates loops and twists in the field lines, resulting in the formation of sunspots and other magnetic structures on the surface.
One of the most intriguing aspects of the Sun’s magnetic field is its ability to attract and influence celestial bodies. Planets, comets, and even asteroids can be influenced by the Sun’s magnetic pull, leading to changes in their orbits and trajectories. This phenomenon, known as magnetic interaction, has been observed in various objects within our solar system.
Solar flares, powerful eruptions of energy from the Sun’s surface, are closely linked to its magnetic field. These flares occur when the magnetic field lines become highly twisted and release a tremendous amount of energy. Studying solar flares can provide valuable insights into the behavior of the Sun’s magnetic field and its impact on space weather.
In recent years, space missions and telescopes have allowed astronomers to observe the Sun’s magnetic field in unprecedented detail. NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and the European Space Agency’s Solar Orbiter are among the missions dedicated to studying the Sun and its magnetic properties.
By understanding the Sun’s magnetic pull, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of how our solar system formed and evolved. It also helps in predicting and mitigating the potential impacts of solar flares and other space weather events on Earth and our technological infrastructure.
In conclusion, the Sun’s magnetic pull is a captivating subject in astronomy, with implications that extend beyond our own planet. By studying and deciphering its secrets, astronomers continue to shed light on the complex interplay between magnetic fields, celestial bodies, and space weather in our solar system.
🌟CLIENTS ✨ This music to attract customers and money in 1 day
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/bp1PJJR-xC0″/]
Understanding Universal law of Gravitation!
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/Af9lRX4xsr0″/]
Frequent questions
What celestial objects or phenomena have the highest gravitational pull, attracting the Sun?
The Sun is primarily attracted to celestial objects with a higher mass and therefore a stronger gravitational pull. The most significant object attracting the Sun is the center of our own Milky Way galaxy, known as Sagittarius A*. It is a supermassive black hole that has a mass approximately 4 million times that of our Sun. However, since the distance between the Sun and Sagittarius A* is immense, the gravitational influence is relatively small compared to other closer objects.
Other important objects attracting the Sun include massive galaxies and galaxy clusters in the cosmic web. As the largest structures in the universe, they exert a gravitational force on the Sun and other nearby galaxies. The gravitational pull from these massive objects can impact the motion and orbit of the Sun to some extent.
Furthermore, individual massive stars within our galaxy and nearby galaxies can have a gravitational effect on the Sun’s motion. These include stars like Betelgeuse and Rigel in the Orion constellation, which are significantly more massive than the Sun. However, their influence is relatively small due to the vast distances between stars.
It’s worth noting that the Sun’s gravitational pull is not solely influenced by one celestial object but rather by the collective mass distribution of all surrounding objects in the universe.
How does the Sun’s gravitational attraction affect the motion of planets and other objects in the solar system?
The Sun’s gravitational attraction plays a crucial role in determining the motion of planets and other objects in the solar system.
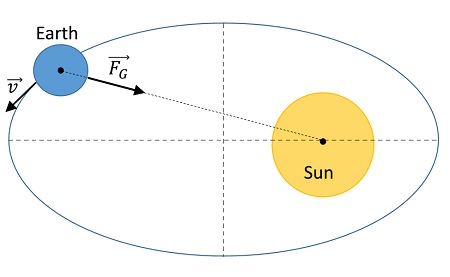
According to Newton’s law of universal gravitation, every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force that is directly proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Therefore, the massive Sun exerts a significant gravitational pull on all the objects in its vicinity, including planets, moons, asteroids, and comets.
This gravitational force exerted by the Sun causes two key effects on the motion of these objects:
1. Orbital Motion: The gravitational force from the Sun pulls the planets and other objects towards it, causing them to move in elliptical orbits around the Sun. This force acts as a centripetal force that keeps the objects in their respective paths. The shape and size of the orbits depend on the mass of the object and its distance from the Sun. The closer an object is to the Sun, the stronger the gravitational force, resulting in higher orbital speeds.
2. Stability: The Sun’s gravitational pull also provides stability to the solar system. By keeping the planets in their orbits, it prevents them from wandering off into space or colliding with each other. The balance between the Sun’s attractive force and the inertia of the planets governs their stable motion.
Furthermore, the Sun’s gravitational influence extends beyond its immediate surroundings:
1. Tidal Forces: The Sun’s gravity also causes tidal forces on objects within the solar system. These tidal forces result in phenomena such as tidal locking (where one side of an object always faces the Sun) and tidal heating (causing internal heat generation in some moons).
2. Interactions with other celestial bodies: The gravitational attraction between the Sun and other massive objects in the galaxy can also influence the motion of the solar system. For example, the gravitational pull of nearby stars or passing comets can cause slight perturbations in the orbits of planets, leading to long-term changes in their paths.
In summary, the Sun’s gravitational attraction is responsible for determining the orbital motion and stability of planets and other objects in the solar system, ensuring their orderly motion and preventing them from straying off into space.
Can you explain how the Sun’s gravitational force attracts comets and asteroids towards it?
In the realm of astronomy, the Sun’s gravitational force plays a crucial role in attracting comets and asteroids towards it. The strength of this force depends on both the mass of the Sun and the distance between the Sun and the object being affected.
Comets and asteroids are small celestial bodies that orbit the Sun. They are primarily composed of ice, rock, and various volatile compounds. When their elliptical orbits bring them close to the Sun, the gravitational force exerted by our star becomes significant.
The Sun’s immense mass creates a gravitational field that extends throughout the solar system. As comets and asteroids approach the Sun, they experience the pull of this gravitational force, causing them to deviate from their original paths.
As a result of the Sun’s gravitational attraction, comets and asteroids are drawn towards it with increasing velocity. Their trajectories bend inward due to the gravitational force, leading them to move closer to the Sun. This process is often referred to as “falling towards the Sun” or “being captured by the Sun’s gravity.”
Once comets and asteroids get too close to the Sun, they are subjected to intense heat and radiation. The heat causes the volatile substances on their surface to vaporize, forming a glowing coma (a cloud of gas and dust) around the nucleus. This results in the characteristic bright tails seen when comets graze the Sun.
In some cases, particularly for comets, the gravitational force of the Sun can cause their orbits to change significantly. They may be ejected from the solar system entirely or sent on new paths that bring them back for repeated encounters with the Sun.
To summarize, the Sun’s gravitational force attracts comets and asteroids towards it due to its massive size. This force alters their trajectories, pulling them closer and causing them to undergo various transformations as they interact with the intense heat and radiation near the Sun.
In conclusion, the phenomenon that attracts the sun plays a fundamental role in the field of Astronomy. Understanding the gravitational pull and its effects on celestial bodies has allowed scientists to unravel mysteries of the universe and predict astronomical events with great precision.
By studying the interactions between the sun and other objects, such as planets and moons, astronomers have gained valuable insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system and beyond. The powerful force of gravity exerted by the sun influences the motion, composition, and even the shape of celestial bodies, shaping the intricate tapestry of our cosmic neighborhood.
It is through the tireless efforts of astronomers that we continue to deepen our understanding of how the sun’s gravitational pull sustains the delicate balance that allows life to flourish on Earth. As we venture further into space exploration, unraveling the mysteries of the sun’s attraction will undoubtedly remain a key focus in expanding our knowledge of the universe and our place within it.