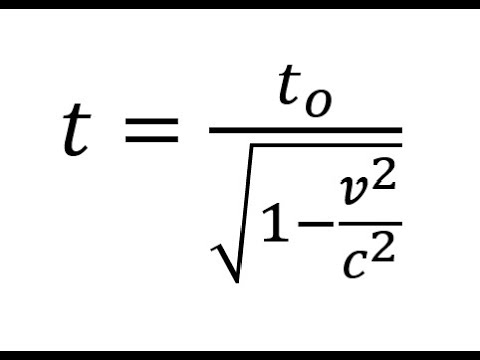Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we delve into the fascinating concept of time in both space and on Earth. 🚀 Explore the perception of time in the vast universe and discover how it varies between different celestial bodies. Join us on this cosmic journey as we unravel the mysteries of time dilation and relativity. Let’s embark on an astronomical adventure together!
Understanding the Perception of Time: Comparing Temporal Differences in Space and on Earth in Astronomy
Understanding the Perception of Time: Comparing Temporal Differences in Space and on Earth in Astronomy
Time perception is a fascinating concept that has intrigued researchers and scientists for centuries. In the field of astronomy, the perception of time takes on a whole new dimension when comparing temporal differences in space and on Earth. Space, with its vast distances and extreme conditions, has a profound impact on how time is experienced.
One of the key factors contributing to temporal differences in space is gravitational time dilation. This phenomenon occurs due to the presence of massive celestial bodies that create gravitational fields capable of warping spacetime. As a result, time passes differently in regions with different gravitational potentials.
Einstein’s theory of general relativity predicts that time moves slower in stronger gravitational fields. For example, near a black hole, where gravity is immensely strong, time would appear to slow down significantly compared to a region further away from the black hole.
Another factor influencing time perception in space is the speed of objects. According to Einstein’s theory of special relativity, as an object approaches the speed of light, time for that object begins to slow down relative to a stationary observer. This phenomenon, known as time dilation, has been observed and measured in experiments with high-speed particles.
On Earth, our perception of time is influenced by various environmental factors and societal constructs. We measure time using clocks and calendars, which provide a standardized reference point for our daily lives. However, it is important to note that our perception of time can also be influenced by psychological and physiological factors.
In space, where there are no external cues or frames of reference, astronauts often experience a distortion of their sense of time. The absence of day-night cycles and the constant floating in microgravity can disrupt the internal body clock, leading to altered perceptions of time passing.
Understanding the temporal differences in space and on Earth is crucial for planning space missions and conducting accurate astronomical observations. Scientists and engineers must account for the effects of time dilation and other temporal phenomena to ensure the success of missions and the correct interpretation of data.
In conclusion, the perception of time in astronomy is a complex and intriguing topic. Space and Earth present distinct temporal differences, influenced by factors such as gravitational time dilation, speed, environmental cues, and societal constructs. Further research and exploration in this area will continue to deepen our understanding of the nature of time and its effects in the universe.
🌎 LIVE: NASA Live Stream of Earth from Space (ISS)
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/4_OT4xFrjmM”/]
Why Is The Universe Perfect?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/lR9r7_MweK8″/]
Frequent questions
How does time dilation affect the passage of time in space compared to on Earth?
Time dilation is a phenomenon predicted by Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity. It states that time can appear to pass at different rates depending on the relative motion between observers and the strength of gravitational fields.
In the context of astronomy, time dilation has significant implications for the passage of time in space compared to on Earth. When an object is in motion or under the influence of a strong gravitational field, time will appear to pass slower for that object compared to a stationary observer.
Special relativity predicts that objects moving at high speeds relative to an observer will experience time dilation. This means that clocks on a fast-moving spacecraft will run slower compared to clocks on Earth. As the velocity of the spacecraft approaches the speed of light, the time dilation effect becomes more pronounced.
General relativity predicts that time also flows differently in strong gravitational fields. In areas of intense gravity, such as near a black hole or a massive star, time appears to pass slower compared to regions with weaker gravity. This is known as gravitational time dilation.
To summarize, time dilation affects the passage of time in space compared to on Earth by making time appear to pass slower for objects in motion or near strong gravitational fields. This effect is a direct consequence of Einstein’s theory of relativity and has been observed and confirmed through various experiments and observations.
What are the factors that contribute to the different rates at which time passes in space and on Earth?
There are several factors that contribute to the different rates at which time passes in space and on Earth:
1. Gravitational Time Dilation: According to Einstein’s theory of general relativity, gravity can affect the flow of time. The stronger the gravitational field, the slower time passes. This means that time moves slower near massive objects like planets, stars, and black holes. In space, where the gravitational field is weaker, time passes at a different rate compared to Earth.
2. Velocity Time Dilation: Another consequence of Einstein’s theory of relativity is that time slows down as an object approaches the speed of light. This effect, known as time dilation, means that time passes slower for objects traveling at high speeds relative to a stationary observer. In space, where spacecraft often travel at significant velocities, time can pass differently compared to Earth.
3. Cosmic Expansion: The universe is constantly expanding, with galaxies moving away from each other. This expansion also affects the passage of time. As the universe expands, the wavelength of light emitted by distant objects increases, causing a redshift. This redshift affects the perceived rate of time in those regions of space.
4. Black Holes: Black holes are extremely massive objects with intense gravitational fields. Near a black hole, the gravitational time dilation is so significant that time effectively stops from the perspective of an outside observer. Time inside a black hole is still a subject of ongoing scientific research and remains a fascinating topic in astronomy.
Overall, these factors contribute to the different rates at which time passes in space and on Earth, highlighting the intricate relationship between gravity, velocity, and the structure of the universe.
How do astronauts’ experiences of time differ while living and working in space compared to being on Earth?
Living and working in space can profoundly alter an astronaut’s perception of time compared to being on Earth. Several factors contribute to this difference.
One significant factor is the lack of natural cues that humans use to track time on Earth, such as the rising and setting of the sun. In space, astronauts experience a phenomenon called “orbital sunset,” where the sun rises and sets every 90 minutes. This rapid transition from daylight to darkness disrupts the regular circadian rhythms that regulate our sleep patterns and perception of time on Earth.
Microgravity also plays a role in distorting an astronaut’s sense of time. In microgravity, there are no gravitational forces acting on the body, causing a reduced sensory input that our brains use to perceive time passing. This lack of physical sensations can make time seem to pass more slowly for astronauts.
Additionally, the busyness of life in space contributes to a different experience of time. Astronauts have tightly scheduled days filled with various tasks and experiments. The constant engagement and focus on fulfilling mission objectives can create a compressed sense of time, making days blend together and feel shorter.
Psychological factors also impact how astronauts experience time in space. Being in a confined environment with a limited number of people and activities can create a sense of monotony and boredom, which can make time seem to drag on. Conversely, moments of excitement and novelty can make time appear to speed up.
Overall, living and working in space fundamentally alters an astronaut’s experience of time compared to being on Earth. The absence of natural cues, microgravity, the busyness of life in space, and psychological factors all contribute to distorting their perception of time.
In conclusion, the concept of time in space and on Earth is a fascinating subject that showcases the vastness and uniqueness of the universe. Through astronomical observations and scientific research, we have come to understand that time experiences vary significantly between these two realms.
In space, time appears to stretch and warp due to the effects of gravity and high velocities. As objects move closer to massive celestial bodies or approach the speed of light, time slows down. This phenomenon, known as time dilation, has been confirmed through various experiments and observations, including the famous Twin Paradox.
On Earth, we experience time in a relatively consistent manner based on our planet’s rotation and orbit around the Sun. Days and nights cycle regularly, and years pass predictably. However, even on Earth, time can be influenced by factors such as altitude and velocity, albeit at much smaller scales compared to space.
Understanding time in space and on Earth is crucial for space exploration missions and satellite operations, where accurate timing is essential. It also plays a vital role in our quest to comprehend the nature of the universe. By studying the intricacies of time, astronomers can unravel the mysteries of cosmic phenomena like black holes, gravitational waves, and the origins of the universe itself.
In conclusion, the study of time in astronomy unveils the extraordinary nature of our reality. As we continue to probe deeper into the cosmos, our understanding of time will evolve, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge and inspiring awe and wonder for generations to come.