Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of Mars and explore how it compares to our home planet, Earth, in terms of environmental characteristics. Join us as we uncover the similarities and differences between these two captivating celestial bodies.
Mars vs Earth: A Comparative Analysis of Environmental Characteristics in Astronomy
Mars vs Earth: A Comparative Analysis of Environmental Characteristics in Astronomy
Introduction:
In the field of Astronomy, the comparison between Mars and Earth is of significant interest. Both planets have unique environmental characteristics that make them intriguing subjects for study. This article aims to provide a comparative analysis of key environmental factors on Mars and Earth, shedding light on their similarities and differences.
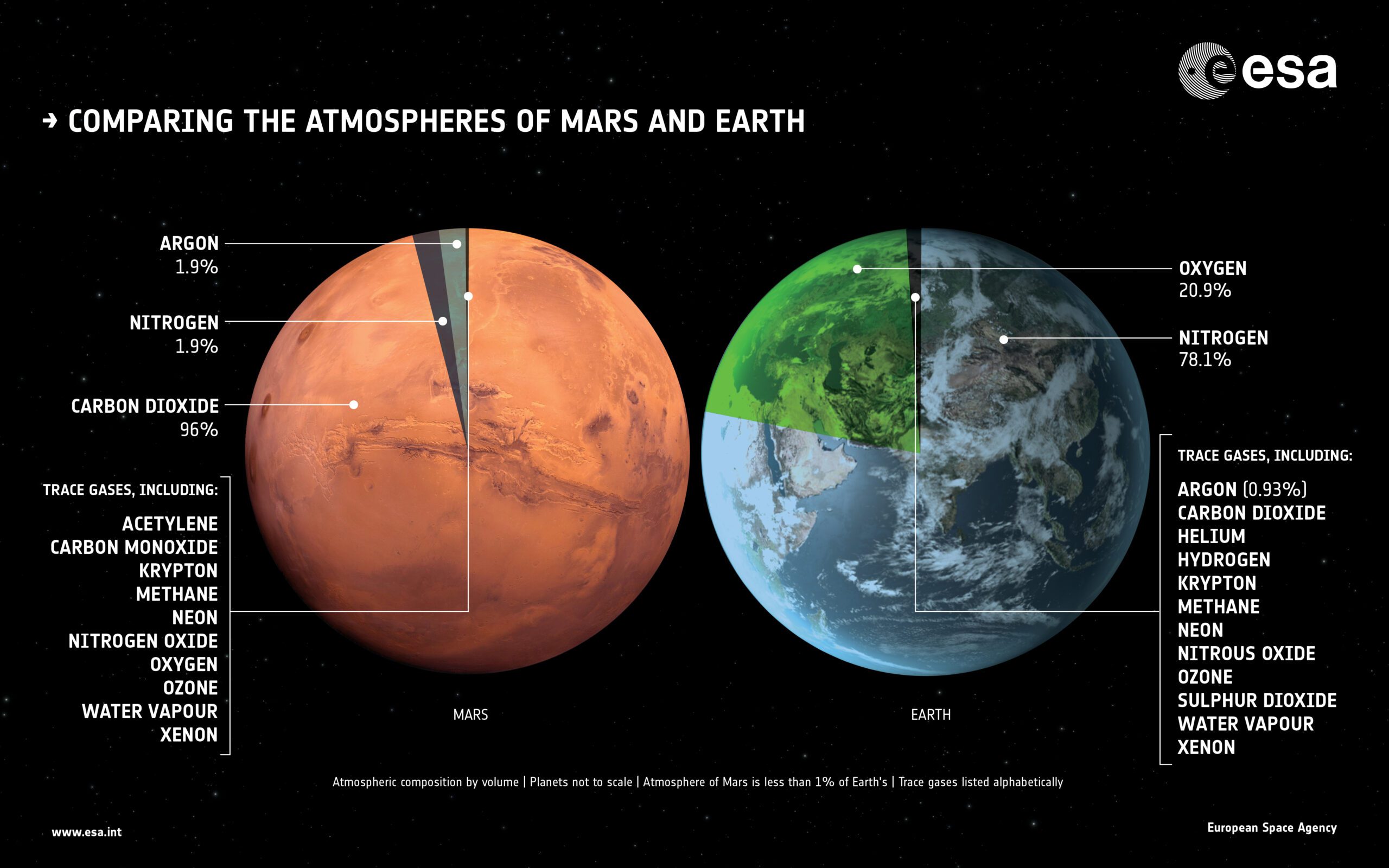
Atmosphere:
Both Mars and Earth have atmospheres, but they differ vastly in composition and density. Earth’s atmosphere primarily consists of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), along with trace amounts of other gases. On the other hand, Mars has a very thin atmosphere composed mainly of carbon dioxide (95%), with traces of nitrogen and argon. The difference in atmospheric composition leads to variations in air pressure and temperature, making Mars significantly colder than Earth.
Climate:
Mars has a harsh and extreme climate compared to Earth. Its thin atmosphere offers minimal insulation, resulting in large temperature fluctuations. The average temperature on Mars is around -80 degrees Fahrenheit (-62 degrees Celsius), whereas Earth’s average temperature hovers around 60 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius). Additionally, Mars experiences dust storms that can last for months, covering the entire planet in a reddish haze. Earth, on the other hand, has a more stable climate with regular weather patterns.
Surface Features:
The surface features of Mars and Earth also show significant differences. Mars is known for its red-colored barren landscapes, dominated by impact craters, volcanoes, and vast deserts. Earth, in contrast, has a diverse range of landforms, including mountains, valleys, plains, and oceans. Mars also boasts the largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons, which is three times higher than Mount Everest. Earth, however, has a more varied topography, including the world’s highest mountain peaks.
Liquid Water:
One of the most critical distinctions between Mars and Earth is the presence of liquid water. While Earth has abundant water in the form of oceans, lakes, and rivers, Mars only has small amounts of water vapor in its atmosphere. There is evidence suggesting that Mars once had flowing rivers and lakes, but they have long dried up. Recent discoveries have indicated the presence of subsurface ice on Mars, raising the possibility of future exploration for potential water sources.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the comparison between Mars and Earth in terms of environmental characteristics is fascinating. Both planets offer unique insights into the possibilities and limitations of planetary environments. While Earth has a more habitable climate with abundant liquid water, Mars presents challenging conditions that make it an intriguing target for future research and exploration. Through continued scientific exploration, we can further understand the fundamental processes that shape these two celestial bodies and potentially uncover clues about the existence of life beyond our planet.
Voyager Just Sent This TERRIFYING New Message Back To Earth!
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/oZ2e1xb56HQ”/]
Why Don’t We Explore Venus If It’s Much Closer To Earth Than Mars?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/MJ4NrCa7tn0″/]
Frequent questions
How does the atmosphere on Mars compare to that of Earth in terms of composition and pressure?
The atmosphere on Mars differs significantly from that of Earth in terms of composition and pressure.
Composition: The Martian atmosphere is primarily composed of carbon dioxide (95.32%). In contrast, Earth’s atmosphere is predominantly made up of nitrogen (78%) with oxygen making up about 21% of the atmosphere.
Pressure: The atmospheric pressure on Mars is much lower compared to Earth. The average surface pressure on Mars is about 6.36 millibars (0.00636 times Earth’s atmospheric pressure at sea level). In comparison, Earth has an average atmospheric pressure of around 1013 millibars at sea level.
Other Differences: Due to its thin atmosphere, Mars experiences extreme temperature differences between day and night. The lack of a significant greenhouse effect on Mars also means that it cannot retain heat as efficiently as Earth does. Additionally, the Martian atmosphere lacks the protective ozone layer present in Earth’s atmosphere, which shields our planet from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
Overall, the composition and pressure of the Martian atmosphere make it inhospitable for humans without protective equipment. However, it plays a crucial role in understanding the planet’s climate, weather patterns, and the potential for supporting microbial life in extreme environments
What are the main differences in temperature and weather patterns between Mars and Earth?
Mars and Earth have significant differences in temperature and weather patterns due to their varying atmospheres and distances from the Sun.
The average temperature on Mars is much colder than on Earth. While Earth has an average temperature of about 15°C (59°F), the average temperature on Mars is around -63°C (-81°F). This extreme cold is primarily due to Mars’ thin atmosphere, which is about 100 times thinner than Earth’s atmosphere. The lack of a substantial greenhouse effect and the farther distance from the Sun also contribute to the low temperatures on Mars.
Weather patterns on Mars are characterized by frequent dust storms, which can cover the entire planet for weeks or even months. These dust storms can create dramatic changes in temperature and atmospheric conditions. On Earth, we experience a variety of weather patterns, including hurricanes, tornadoes, and thunderstorms, which are driven by interactions between air masses, humidity, and the rotation of the planet.
Another significant difference between Mars and Earth is the absence of liquid water on Mars’ surface. While Earth has abundant water bodies, such as oceans, lakes, and rivers, Mars only has traces of water vapor in its atmosphere and frozen water at its poles. This lack of liquid water greatly affects the potential for weather patterns and the possibility of sustaining life on Mars.
In conclusion, compared to Earth, Mars has much lower average temperatures, frequent dust storms, and the absence of liquid water. These differences in temperature and weather patterns are mainly attributed to Mars’ thin atmosphere, greater distance from the Sun, and lack of liquid water on its surface.
How do the geological features on Mars, such as mountains and valleys, differ from those found on Earth?
On Mars, the geological features such as mountains and valleys differ from those found on Earth in several ways.
1. Size: Martian mountains and valleys can be much larger compared to their counterparts on Earth. For example, Olympus Mons, the largest volcano in the solar system, has a height of 13.6 miles (22 kilometers) and a diameter of about 370 miles (600 kilometers), dwarfing even the tallest peaks on Earth.
2. Formation: Mars lacks plate tectonics, so most of its geological features are believed to have formed through volcanic activity rather than the movement of crustal plates. This means that Martian mountains and valleys are predominantly volcanic in origin.
3. Erosion: Mars has a thin atmosphere that does not provide the same level of protection against erosion as Earth’s thicker atmosphere. As a result, Martian mountains and valleys can be more preserved and less eroded than their Earth counterparts. This is particularly evident in the presence of sharp, rugged mountain ranges on Mars.
4. Lack of water: Water is one of the key shaping forces on Earth, but Mars is currently dry and has very little liquid water on its surface. This absence of water limits erosion processes such as rivers carving valleys or glaciers shaping mountains, which are common on Earth.
5. Impact craters: Mars has a higher density of impact craters compared to Earth due to its thinner atmosphere and lack of weathering and tectonic activity. These impact craters can sometimes disrupt or modify the original geological features, creating unique landscapes on Mars.
In summary, the geological features on Mars, including mountains and valleys, differ from Earth’s due to their larger size, volcanic origins, less erosion, absence of significant water, and higher prevalence of impact craters.
In conclusion, when comparing the environmental characteristics of Mars and Earth, it becomes evident that Mars is an inhospitable planet for human life. Its thin atmosphere, lack of liquid water, extreme cold temperatures, and high radiation levels make it an extremely challenging environment to sustain life as we know it. On the other hand, our home planet, Earth, with its rich atmosphere, abundant water resources, moderate temperatures, and protective magnetic field, provides the perfect conditions to support a diverse range of life forms.
Nevertheless, exploring Mars and understanding its unique environmental characteristics play a crucial role in expanding our knowledge of planetary evolution and potential habitability beyond Earth. These studies not only help us gain further insights into the origin and evolution of our own planet but also pave the way for future human missions to Mars.
Despite the differences between Mars and Earth, one thing is clear: the study of these two planets continues to captivate scientists and astronomers alike, pushing the boundaries of our understanding of the universe. As we unravel the mysteries of Mars and deepen our understanding of its environmental characteristics, we may be one step closer to answering the age-old question: are we alone in the cosmos?