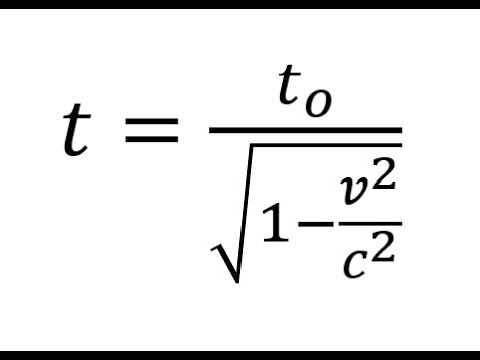Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we explore the concept of time in space and unravel the fascinating question: how many years are 10 years in space? Prepare to be astounded as we delve into the mind-boggling effects of relativity and uncover the secrets of our cosmic clock. Get ready to have your perceptions challenged and your curiosity ignited as we embark on this incredible celestial journey.
Time dilation: Understanding the Equivalence of 10 Earth Years and Space Years in Astronomy
Time dilation is a fascinating concept in astronomy that arises from Einstein’s theory of relativity. It states that time can be influenced by gravity and motion, leading to differences in the passage of time for observers in different reference frames. One concrete example of time dilation in astronomy is the equivalence of 10 Earth years and space years.
When an object is located in a region with a strong gravitational field or is moving at high speeds, time appears to pass slower for that object compared to a stationary observer on Earth. This means that if an astronaut travels close to the speed of light or near a black hole, their perceived time will be significantly slower than that experienced by someone on Earth.
This concept has been verified by numerous experiments and observations, such as the famous Hafele-Keating experiment where atomic clocks were flown around the world.
The equivalence of 10 Earth years and space years stems from the fact that significant time dilation occurs when objects travel at relativistic speeds or are exposed to intense gravitational fields for extended periods of time.
For instance, if an astronaut were to embark on a roundtrip journey that involves traveling at a significant fraction of the speed of light or passing close to a massive object, they might experience a time dilation effect. While the astronaut might perceive that only a few years have passed, upon returning to Earth, they would find that a much longer duration, such as 10 years, has elapsed.
This equivalence highlights the profound nature of time dilation and its impact on our understanding of the universe. It shows that time is not an absolute measure but rather a relative one, dependent on factors like gravity and velocity. This has significant implications for space exploration and our perception of astronomical events. Scientists must take time dilation into account when calculating the ages of distant celestial objects, as their observed time might differ from the time experienced on Earth.
In conclusion, time dilation in astronomy is a captivating concept that reveals the intricate relationship between time, gravity, and motion. The equivalence of 10 Earth years and space years exemplifies this phenomenon, where significant differences in the passage of time can occur due to relativistic speeds or intense gravitational fields. Understanding time dilation is crucial for accurately interpreting astronomical observations and expanding our knowledge of the cosmos.
10 Space Photos That Will Give You Nightmares
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/pb2MkzCgQ-4″/]
This is Why NASA Never Returned to the Moon
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/iFxyNC8sOtI”/]
Frequent questions
How does time dilation affect the perception of 10 years in space?
Time dilation is a phenomenon predicted by Einstein’s theory of relativity, which states that time is not constant and can be experienced differently depending on the relative motion of two observers. In the context of space travel, this means that time can pass at different rates for an astronaut traveling at high speeds compared to someone on Earth.
If an astronaut were to spend 10 years in space traveling at speeds close to the speed of light, time dilation would occur, causing their perception of time to be different from that of people on Earth. Due to the high velocity, the astronaut’s time would appear to pass more slowly compared to someone who remained on Earth.
From the perspective of the astronauts, their 10-year journey may feel much shorter due to time dilation. They would experience time passing at a slower rate, so when they return to Earth, they may find that decades or even centuries have passed for the people they left behind.
This effect has been observed in experiments with atomic clocks on board fast-moving satellites. The clocks aboard these satellites, which are traveling at high speeds relative to the Earth’s surface, tick slightly slower than those on the ground. This small difference in timekeeping demonstrates the reality of time dilation and its impact on our perception of time.
In summary, time dilation can significantly affect the perception of time for astronauts in space. A 10-year journey for them might feel much shorter, while back on Earth, several decades or even centuries may have passed. This fascinating concept showcases the intricate relationship between the laws of physics and our understanding of time.
Does the concept of “space years” differ from Earth years?
The concept of “space years” does not differ from Earth years. In astronomy, a year is typically defined as the time it takes for a celestial body, such as a planet or a moon, to complete one orbit around its parent star. This definition applies universally, regardless of the specific location in space.
However, it is important to note that the duration of a year can vary depending on the orbital characteristics of the celestial body. For example, the length of a year on Earth is approximately 365.25 days, whereas a year on Mercury is only about 88 Earth days due to its closer proximity to the Sun and faster orbital speed.
Therefore, while the concept of a space year remains consistent with Earth years, the actual duration of a year may differ based on the specific celestial body being considered.
Can one’s age be calculated differently after spending 10 years in space due to time dilation effects?
Time dilation effects in space can indeed result in a difference in the perception of time between individuals who have spent time in space and those who have remained on Earth. This is due to the theory of relativity, which states that time can be affected by gravity and speed.
Gravity plays a role in time dilation because it can cause a curvature in space-time. The stronger the gravitational field, the slower time will pass. For example, a clock placed closer to a massive object, such as a black hole, would tick more slowly compared to a clock located further away.
Speed also affects time dilation. According to the theory of relativity, time appears to slow down for an object moving at a high velocity relative to a stationary observer. This effect has been demonstrated and measured using highly accurate atomic clocks on fast-moving objects such as airplanes and satellites.
So, what does this mean for someone spending 10 years in space? Due to the lower gravitational field experienced in space and the potential for high velocities during space travel, an individual in space would experience a slight time dilation compared to someone on Earth.
The exact calculation of the time difference would depend on various factors, including the actual velocity and distance from massive objects. However, it is reasonable to expect that there would be a small difference in age between someone who spent 10 years in space and someone who remained on Earth during that time.
In conclusion, due to the effects of time dilation caused by gravity and speed, an individual’s age could be calculated differently after spending 10 years in space compared to someone on Earth. However, the difference would likely be negligible unless the space travel involved extreme speeds or proximity to massive objects.
In conclusion, the concept of time is drastically altered in the vastness of space. While here on Earth, 10 years may seem like a significant period, it pales in comparison to the immense timescales observed in the cosmos. The distances traveled by celestial bodies over the course of a decade are mind-boggling, as they traverse billions of miles through the vastness of space.
Our understanding of time in relation to astronomical events is not only essential for studying the evolution of stars and galaxies, but also for comprehending the sheer scale of the universe itself. So when we talk about 10 years in space, we must remember that it is merely a fraction of the cosmic timeline, a mere blink of an eye in the grand scope of the universe.
As we continue to explore and unlock the mysteries of the cosmos, we are reminded of our own insignificance in the face of such immense stretches of time and space.