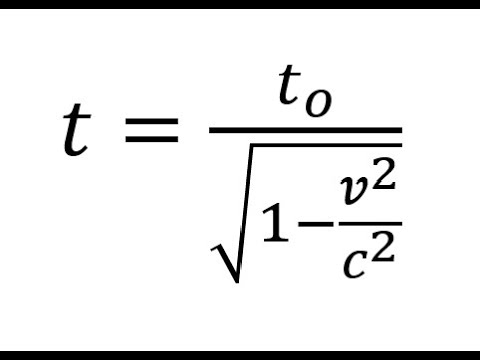Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we explore the fascinating concept of how time is perceived in space. Join us as we delve into the question: “How many are 1 year in space?” Discover the mind-boggling effects of extended space missions and the impact it has on our understanding of time. Get ready for an astronomical journey like no other!
How Many Earth Years Equivalent is One Year in Space? Exploring the Astronomical Time Scales
One year in space is not equivalent to a specific number of Earth years. This is because different celestial bodies have varying orbital periods around their respective central objects. For example, one year on Mars is approximately 1.88 Earth years while one year on Jupiter is about 11.86 Earth years.
When exploring astronomical time scales, it is important to consider the concept of a sidereal year. A sidereal year is the time it takes for a planet or moon to complete one orbit around its central object with respect to the stars. For Earth, a sidereal year is about 365.25 days.
However, when we talk about a calendar year or a tropical year which is based on the seasons, it is approximately 365.24 days. This slight difference is due to the precession of Earth’s axis.
It is worth noting that the concept of a year becomes more complex when we consider exoplanets (planets outside our solar system). Their orbital periods can vary significantly, ranging from just a few days to several Earth years.
In summary, the length of a year in space varies depending on the celestial body in question and should be taken into account when exploring astronomical time scales.
This is Why NASA Never Returned to the Moon
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/iFxyNC8sOtI”/]
Scientists Reveal That Our Universe Is 27 Billion Years Old, Not 13.8 Billion! Here’s How
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/hx2uXS4IEoo”/]
Frequent questions
How does time dilation affect the perception of one year in space compared to on Earth?
Time dilation refers to the phenomenon where time appears to run at different rates depending on the relative motion or gravitational field between two observers. In the context of space travel, this concept becomes particularly relevant.
According to special relativity, as proposed by Albert Einstein, time dilation occurs when an object is moving at velocities close to the speed of light. As an astronaut travels through space at high speeds, time for them will pass slower compared to someone on Earth.
This means that if an astronaut spends a year in space, their perception of time would be diluted, and they would experience less elapsed time compared to someone on Earth. This effect is known as time dilation in special relativity. Precisely how much time dilation occurs depends on the speed of the spacecraft relative to Earth.
However, it’s important to note that the effects of time dilation become more significant as one approaches the speed of light, which is currently beyond our technological capabilities. Therefore, for most space travel missions we have conducted so far, the differences in perceived time would be negligible.
General relativity, on the other hand, explains time dilation in the presence of strong gravitational fields. In this case, the closer an observer is to a massive object like a planet or a black hole, the more time appears to slow down for them compared to someone in a weaker gravitational field.
Thus, if an astronaut were to spend a year orbiting a black hole, for example, time dilation due to the intense gravitational field would cause them to experience less elapsed time compared to an observer on Earth.
In summary, both special relativity and general relativity predict time dilation effects that would impact the perception of one year in space compared to on Earth. The specific magnitude of this dilation depends on the speed of the spacecraft or the strength of the gravitational field experienced by the observer.
What are the specific factors that contribute to determining the length of one year in space?
The length of one year in space is determined by several factors, including the orbit and the gravitational pull of the celestial body being orbited.
In the case of Earth, a year is defined as the time it takes for our planet to complete one orbit around the Sun. This orbital period is approximately 365.25 days, which is why we have leap years every four years to account for the extra quarter day.
However, in space, the length of a year can vary depending on the celestial body being orbited. For example, the length of a year on Mars is roughly 1.88 Earth years, as Mars takes longer to complete its orbit around the Sun.
Additionally, other factors such as the eccentricity of the orbit and the presence of other gravitational influences can also affect the length of a year in space. For instance, planets with highly elliptical orbits will experience variations in their orbital speed, which can result in longer or shorter years.
It’s worth noting that astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) experience slightly shorter years compared to those on Earth due to the station’s orbital velocity. The ISS orbits Earth at an average altitude of about 408 kilometers (253 miles) and completes about 15.5 orbits per day, resulting in approximately 16 sunrises and sunsets every 24 hours.
In summary, the specific factors that contribute to determining the length of one year in space include the orbital period, the gravitational pull of the celestial body being orbited, eccentricity of the orbit, and other gravitational influences.
Can the concept of a year be accurately defined in space, considering its lack of reference to Earth’s orbit around the Sun?
In space, the concept of a year can still be accurately defined, even without reference to Earth’s orbit around the Sun. A year is typically defined as the time it takes for a planet to complete one orbit around its star. This definition can be applied to any celestial body in space, whether it’s a planet orbiting a star or a moon orbiting a planet.
For example, on Mars, a year is defined as the time it takes for the planet to orbit the Sun once. On Saturn, a year is defined as the time it takes for the planet to complete one orbit around the Sun.
In this way, the concept of a year remains meaningful and applicable to celestial bodies beyond Earth, as it represents the completion of an orbital cycle. However, it’s important to note that the duration of a year may vary depending on the specific celestial body and its orbit around its star.
In conclusion, the concept of time becomes increasingly fascinating when we consider the duration of one year in space. Being deprived of the natural cycles and rhythms we experience on Earth, astronauts must adapt to a completely different understanding of time. With the absence of day-night cycles and changing seasons, they rely on man-made systems to measure time and maintain their daily routines. However, the significance of marking a year in space goes beyond mere practicality. It symbolizes the extraordinary achievements of humans venturing beyond our home planet and the remarkable advancements in technology and understanding of the universe. As we continue to explore and push the boundaries of space travel, our perception of time is sure to evolve, revealing even more wonders waiting to be uncovered. So, as we ponder the complexities of time and its manifestations within the realm of astronomy, let us marvel at the resilience and adaptability of human ingenuity that allows us to measure and comprehend the passage of time even in the most extraordinary circumstances.