Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we delve into the fascinating topic of how life begins on Earth. We examine the crucial ingredients and processes that contribute to the formation of life as we know it, shedding light on our extraordinary planet’s origins. Join us on this captivating journey through the cosmic wonders that shape our existence.
The Origin of Life on Earth: Insights from an Astronomical Perspective
The Origin of Life on Earth: Insights from an Astronomical Perspective
The search for the origin of life on Earth has long fascinated scientists and researchers alike. While many theories exist, one perspective that continues to shed light on this complex question is the study of astronomy.
Astronomy, the study of celestial objects and phenomena, plays a critical role in understanding the conditions necessary for life to arise. By observing distant planets, stars, and galaxies, astronomers have been able to gather valuable data that provide insights into the early stages of our own planet’s development.
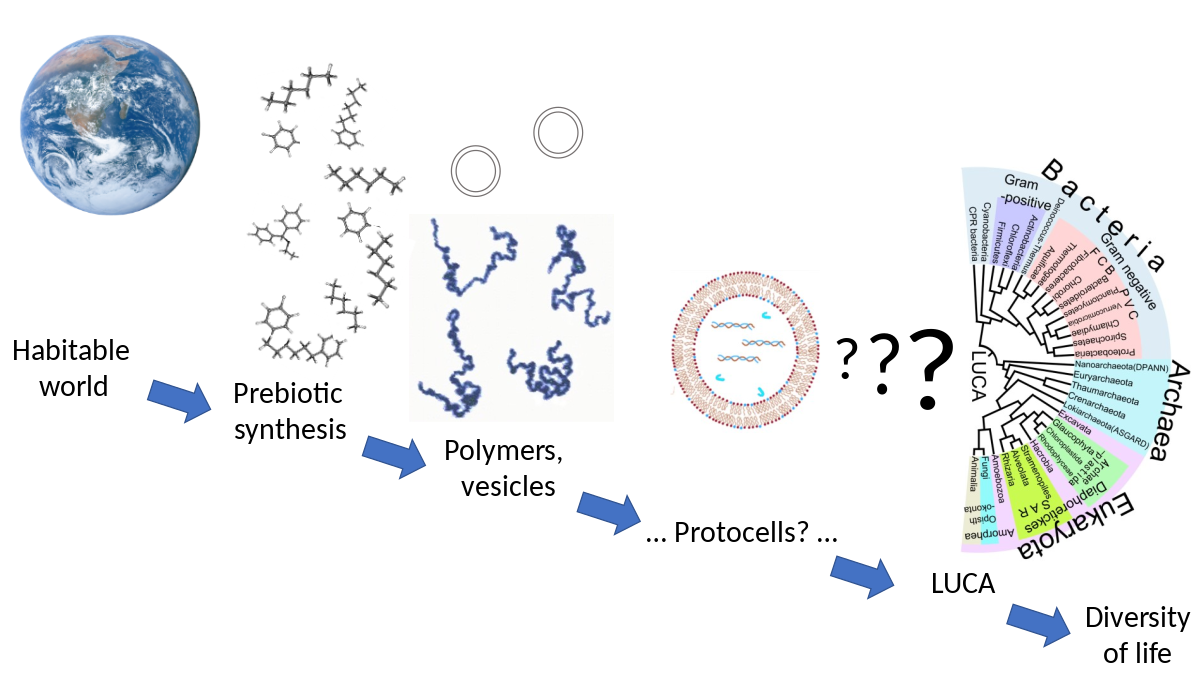
One key aspect explored by astronomers is the presence of organic molecules in space. These complex carbon-based compounds are the building blocks of life as we know it. Through spectroscopy, scientists have detected the presence of organic molecules in interstellar clouds, protoplanetary disks, and even meteorites that have fallen to Earth. This evidence suggests that the ingredients necessary for life may have been present throughout the universe long before the formation of our own planet.
Furthermore, the study of exoplanets – planets orbiting stars outside our solar system – has revealed an astounding diversity in planetary systems. The discovery of potentially habitable exoplanets, known as “Goldilocks planets,” has fueled the speculation that life may exist beyond Earth. Astronomical observations help us identify the conditions required for a planet to sustain liquid water, a crucial element for the emergence of life as we know it.
Additionally, astrobiology, a multidisciplinary approach that combines aspects of astronomy, biology, and chemistry, seeks to uncover the connections between life on Earth and the cosmic environment. By studying extremophiles, organisms capable of surviving in extreme conditions on Earth, scientists hope to understand the potential for life in other hostile environments, such as Mars or moons of Jupiter and Saturn.
In conclusion, the field of astronomy provides valuable insights into the origin of life on Earth. Through the study of organic molecules in space, the exploration of exoplanetary systems, and the interdisciplinary approach of astrobiology, astronomers continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding the emergence of life in our universe.
If the Universe Formed from Nothing, Who Created the Nothing?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/KPEmBzlSU2I”/]
What Was The Earth Like 1 Billion Years Ago?
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/nTT8Z6fI7_8″/]
Frequent questions
What role did celestial events, such as meteorite impacts or the formation of the Moon, play in the origin of life on Earth?
Celestial events, such as meteorite impacts and the formation of the Moon, played a crucial role in the origin of life on Earth.
Meteorite impacts, especially during the early stages of our planet’s history, delivered valuable organic molecules and water to Earth. These organic molecules are the building blocks of life, and their delivery through meteorites greatly enriched the primordial soup on our planet. Additionally, these impacts provided the energy required for complex chemical reactions to occur, increasing the likelihood of the formation of more complex molecules.
The formation of the Moon also had a significant impact on the development of life on Earth. The Moon’s gravitational pull created tides, which played a crucial role in the evolution of early life forms. Tidal pools provided a stable environment where complex chemical reactions could occur, leading to the formation of early self-replicating molecules and eventually, the emergence of life.
Furthermore, the Moon’s presence helped stabilize Earth’s axial tilt, resulting in a more stable climate. This stability allowed for the development of ecosystems and the evolution of complex life forms over long periods of time.
In summary, celestial events such as meteorite impacts and the formation of the Moon not only delivered essential ingredients for life but also provided the necessary conditions for life to emerge and thrive on Earth.
Could life have originated elsewhere in the universe and been transported to Earth through panspermia?
Panspermia is a theory that suggests life could have originated elsewhere in the universe and been transported to Earth through various mechanisms. It proposes that microorganisms, such as bacteria or spores, could have hitched a ride on comets, asteroids, or even interstellar dust particles, allowing them to survive the harsh conditions of space and eventually reach our planet.
There is ongoing debate within the scientific community about the plausibility of panspermia as a means of life’s origin on Earth. While it remains a possibility, it currently lacks strong empirical evidence to support it.
However, recent scientific discoveries have provided some intriguing insights. For example, researchers have found the presence of organic molecules, including amino acids and nucleobases, in meteorites that have fallen to Earth. These molecules are essential building blocks of life as we know it. Additionally, extremophiles—microorganisms capable of surviving in extreme conditions—have been discovered thriving in environments previously thought to be uninhabitable. This suggests that life may be more resilient and adaptable than previously believed.
The discovery of potential habitable environments beyond Earth, such as liquid water on Mars or the subsurface oceans on moons like Enceladus and Europa, further fuels the discussions surrounding panspermia. It raises the question of whether life could have independently originated in these environments or if it was introduced through panspermia.
In conclusion, while the concept of panspermia is intriguing and scientifically plausible, more research and evidence are needed to support its validity. The ongoing investigation into extraterrestrial life and the exploration of habitable environments within our own solar system provide exciting prospects for further understanding the origins of life on Earth and the potential for life elsewhere in the universe.
How did the early Earth’s environment, including its atmosphere and oceans, contribute to the development of the first forms of life?
These questions explore various aspects of the origins of life on Earth and how astronomical events and conditions may have played a crucial role in the emergence of life on our planet.
The early Earth’s environment, including its atmosphere and oceans, played a significant role in the development of the first forms of life.
The atmosphere of the early Earth was primarily composed of gases like nitrogen, carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and ammonia. It lacked significant amounts of free oxygen, unlike the present-day atmosphere. This composition was conducive to the formation of organic molecules, which are essential for life.
It is believed that the early Earth’s oceans played a crucial role in the development of life. The oceans provided a stable and protected environment where complex chemical reactions could occur. This allowed the synthesis of various organic compounds, including amino acids, sugars, and nucleotides, which are the building blocks of life.
Additionally, the early Earth experienced intense volcanic activity and frequent meteorite impacts. These events released energy and introduced various elements and minerals into the environment. The energy from volcanic activity and meteorite impacts could have provided the necessary conditions for the formation of more complex organic molecules.
Astronomical events also played a part in the development of life on Earth. For instance, comets and asteroids are thought to have delivered organic molecules and water to our planet. These events brought new materials to the early Earth, enriching its environment and providing the raw materials necessary for life.
Furthermore, the early Earth was subjected to intense ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun, as its protective ozone layer had not formed yet. While high levels of UV radiation can be harmful to life, it is believed that this radiation also played a role in the formation of organic molecules and the evolution of early life forms.
In summary, the early Earth’s environment, including its atmosphere, oceans, volcanic activity, and astronomical events, contributed to the development of the first forms of life. These conditions provided a fertile ground for the synthesis of organic molecules and the evolution of life on our planet.
In conclusion, the study of Astronomy provides valuable insights into how life begins on Earth. Through observations and research, scientists have been able to unravel the intricate processes that played a vital role in the formation of our planet and the subsequent emergence of life.
From the primordial soup to the complex interplay of environmental conditions, every step of the journey towards life on Earth is a captivating tale of cosmic happenings. The chemical reactions, energy sources, and celestial events that shaped our world created the ideal conditions for life to take hold and thrive.
Furthermore, the discovery of exoplanets and the potential for habitable environments beyond our solar system open up even more possibilities for the existence of extraterrestrial life. The search for signs of life in the vastness of space continues to fuel our curiosity and push the boundaries of our understanding.
As we gaze upon the stars and contemplate our place in the universe, it becomes clear that the origin of life on Earth is deeply intertwined with the dynamics of the cosmos. Astronomy serves as a reminder of the immense beauty and complexity of the universe that gave rise to life, and it urges us to protect and cherish our planet.
In the grand tapestry of the cosmos, we are just one small speck of life, connected to the greater cosmic story of creation and evolution. Studying Astronomy not only expands our knowledge but also humbles us, reminding us of the remarkable journey that started billions of years ago and continues to unfold around us.
Let us embrace the wonders of Astronomy and cherish the incredible gift of life that has been bestowed upon us. As we explore the unknown, may we always marvel at the mysteries of the universe and seek to unravel the secrets of how life begins, not just on Earth, but perhaps on other worlds too.