Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of Jupiter’s gas. Discover the complexities and mysterious nature of this massive planet as we delve into its composition and the challenges scientists face in understanding its unique atmosphere. Join us on this cosmic journey as we unravel the secrets of Jupiter’s gas giant!
Unlocking the Mysteries: The Elusive Nature of Jupiter’s Gaseous Composition in Astronomical Studies
Jupiter, the giant gas planet of our solar system, has long captured the curiosity of astronomers. Its immense size and unique features have made it a fascinating subject of study. However, despite years of research and observation, there is still much to uncover about its gaseous composition.
Understanding Jupiter’s atmospheric makeup is crucial in deciphering its origin and evolution as well as gaining insight into the formation of gas giants in general. Several missions, such as NASA’s Juno spacecraft, have provided valuable data and images of Jupiter’s clouds and storms, contributing to our knowledge of its weather patterns. Yet, the exact proportions and ratios of gases present in its atmosphere remain a mystery.
One of the main challenges in studying Jupiter’s gaseous composition lies in its vast and turbulent atmosphere. With powerful storms and swirling cloud bands, observing and analyzing the different layers becomes a complex task. Scientists rely on remote sensing techniques, such as spectroscopy, to study the composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere. By analyzing the light reflected or emitted by the planet, they can identify the presence of certain gases and their relative abundance.
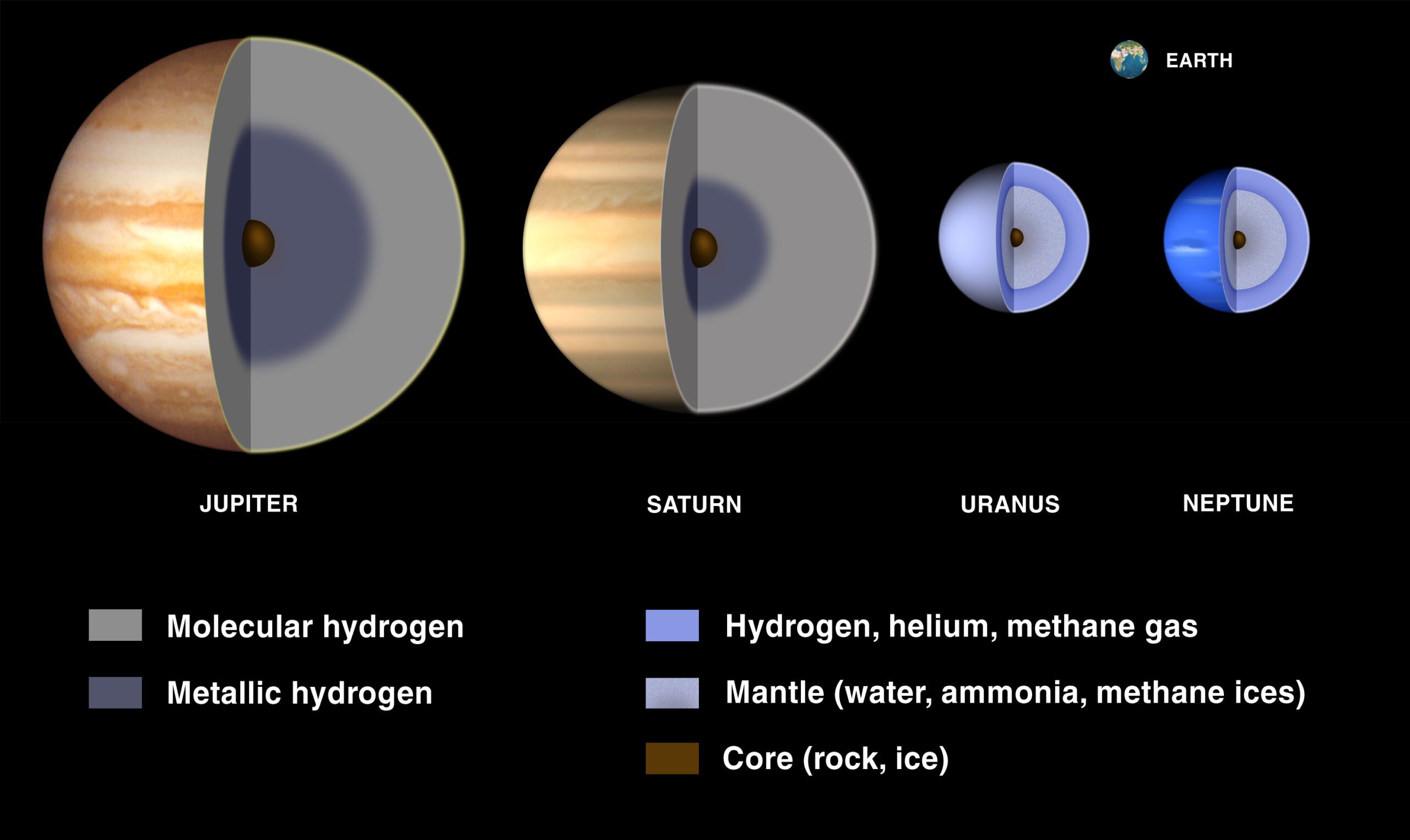
Molecular hydrogen and helium are known to be the dominant components of Jupiter’s atmosphere, but there are also traces of other elements and compounds present. For example, methane, ammonia, and water vapor have been detected, although their exact distributions and concentrations are still not fully understood. Furthermore, there might be additional unidentified compounds that contribute to the complex chemistry of Jupiter’s atmosphere.
Advancements in observational techniques and computational models are essential in unraveling the secrets of Jupiter’s gaseous composition. By improving our understanding of the physical processes occurring within the planet’s atmosphere, scientists can refine their models and predictions. Additionally, future missions like the European Space Agency’s JUICE (JUpiter ICy moons Explorer) will provide further insights into Jupiter’s composition by studying its moons and their interactions with the planet.
In conclusion, unraveling the gaseous composition of Jupiter remains a captivating challenge for astronomers. Understanding the complexities of its atmosphere is not only important for deciphering its own mysteries but also for gaining a deeper understanding of gas giant formation and planetary evolution in the universe. With continued advancements in technology and exploration, we are inching closer to unlocking the secrets hidden within Jupiter’s turbulent clouds.
Michio Kaku: We FINALLY Found What’s Inside A Black Hole!
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/pMdysmpDSsk”/]
Scientists Think There Could Be LIFE on TITAN and It’s Even Weirder Than We Thought!
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/CLPNvdaNgjs”/]
Frequent questions
How dense is Jupiter’s gas compared to Earth’s atmosphere?
Jupiter’s gas is **much denser** compared to Earth’s atmosphere. While Earth’s atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), Jupiter’s atmosphere is predominantly made up of hydrogen (89%) and helium (10%).
The density of Jupiter’s gas is significantly higher than Earth’s due to its immense size and mass. Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system, with a diameter of about 11 times that of Earth. Its gravity is also much stronger than Earth’s, which contributes to the compression and higher density of its atmospheric gases.
Additionally, Jupiter’s atmospheric conditions are quite extreme. The planet experiences powerful storms, such as the famous Great Red Spot, which is a massive storm system that has been raging for centuries. These intense atmospheric disturbances also contribute to the higher density of Jupiter’s gas compared to Earth’s atmosphere.
Is Jupiter’s gas composition uniform throughout its atmosphere?
Yes, Jupiter’s gas composition is not uniform throughout its atmosphere. The gas giants like Jupiter have a layered structure with different compositions as you move deeper into the planet. The outermost layer, called the troposphere, is mainly composed of hydrogen and helium, with trace amounts of methane, water vapor, ammonia, and other compounds.
As you go deeper into the atmosphere, the pressure and temperature increase, causing the gases to undergo changes in their physical properties. Deeper layers of Jupiter’s atmosphere contain metallic hydrogen, which is formed under extreme pressures. So, while the outer layers have a more gaseous composition, the inner layers are dominated by exotic forms of hydrogen. This variation in composition is due to the different conditions present at different depths within Jupiter’s atmosphere.
How does the pressure change with depth in Jupiter’s gas giant?
The pressure in Jupiter’s gas giant increases with depth. As we move deeper into the planet, the weight of the overlying atmosphere and the compressibility of the gas cause the pressure to increase. This is due to the immense gravitational force exerted by the massive planet.
Jupiter’s interior consists of various layers: the outermost layer is the gaseous envelope called the atmosphere, which gradually transitions into the liquid metallic hydrogen layer deeper down. The pressure increases exponentially as we descend into the planet, due to the increasing mass of the overlying gas.
In the upper atmosphere of Jupiter, the pressure is only a few times greater than Earth’s atmosphere. However, as we penetrate deeper into the planet, the pressure becomes incredibly high. At about 1,000 kilometers below the cloud tops, the pressure is estimated to be millions of times greater than Earth’s atmospheric pressure. In the core, pressures reach extreme values due to the huge mass of gas above it.
The precise pressure profile in Jupiter’s interior is still uncertain and can only be estimated through computer models and indirect measurements. The Galileo probe, which descended into Jupiter’s atmosphere in 1995, provided invaluable data about the pressure and temperature profiles, but due to the harsh environment, its measurements were limited to a certain depth.
Study of pressure variations in gas giants like Jupiter gives us insight into their interior structure, dynamics, and formation processes. Understanding the pressure gradients within Jupiter is crucial for comprehending the behavior of its massive storms, such as the Great Red Spot, and the complex interactions between different layers of its atmosphere.
In conclusion, exploring the gas giant Jupiter has provided astronomers with invaluable insights into the fascinating world of planetary physics. The immense pressure and extreme temperatures within Jupiter’s gas atmosphere present numerous challenges that have pushed the boundaries of our understanding. Through a combination of sophisticated space missions and ground-based observations, scientists have been able to unravel some of the mysteries surrounding this mysterious planet.
Despite its name, Jupiter’s atmosphere is no walk in the park. The immense gravitational forces compress the gases and create an environment that is anything but forgiving. The core of Jupiter, shrouded in dense clouds, is subjected to pressures beyond what we can comprehend. With each passing mission, such as the Juno spacecraft currently in orbit around Jupiter, we are piecing together more information about this enigmatic planet.
Understanding the composition and behavior of Jupiter’s gas is crucial for better understanding other gas giants in our solar system and beyond. The data collected from various missions have shown that the gas composition varies with depth, revealing intricate layers within the planet. The presence of metallic hydrogen, a state of hydrogen under extreme pressure, adds another layer of complexity to Jupiter’s gas dynamics.
Studying Jupiter’s gas also provides us with important insights into the formation and evolution of our own solar system. By understanding how gas giants like Jupiter form and interact with their surroundings, we can gain valuable knowledge about the mechanisms that shape planetary systems. This knowledge may even help us in our search for habitable planets beyond our solar system.
In conclusion, the study of Jupiter’s gas presents numerous challenges, but the rewards are equally significant. Our understanding of planetary physics and the dynamic universe is greatly enhanced through the exploration of Jupiter and other gas giants. As we continue to gather data and push the boundaries of scientific knowledge, the mysteries of Jupiter’s gas will undoubtedly continue to captivate and inspire future astronomers.