Welcome to Learn to Astronomy! In this article, we will explore the fascinating question of how we know that Jupiter is a gaseous planet. Through careful observation and scientific analysis, we have gathered compelling evidence that Jupiter’s composition primarily consists of hydrogen and helium gases. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of this majestic giant in our solar system.
Understanding the Gaseous Nature of Jupiter: Unveiling the Secrets of the Largest Planet in our Solar System.
Understanding the Gaseous Nature of Jupiter: Unveiling the Secrets of the Largest Planet in our Solar System
Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, has long intrigued scientists and astronomers. Its massive size and unique composition make it a fascinating object of study. By studying Jupiter’s gaseous nature, researchers can unveil the mysteries behind its atmospheric dynamics, weather patterns, and internal structure.
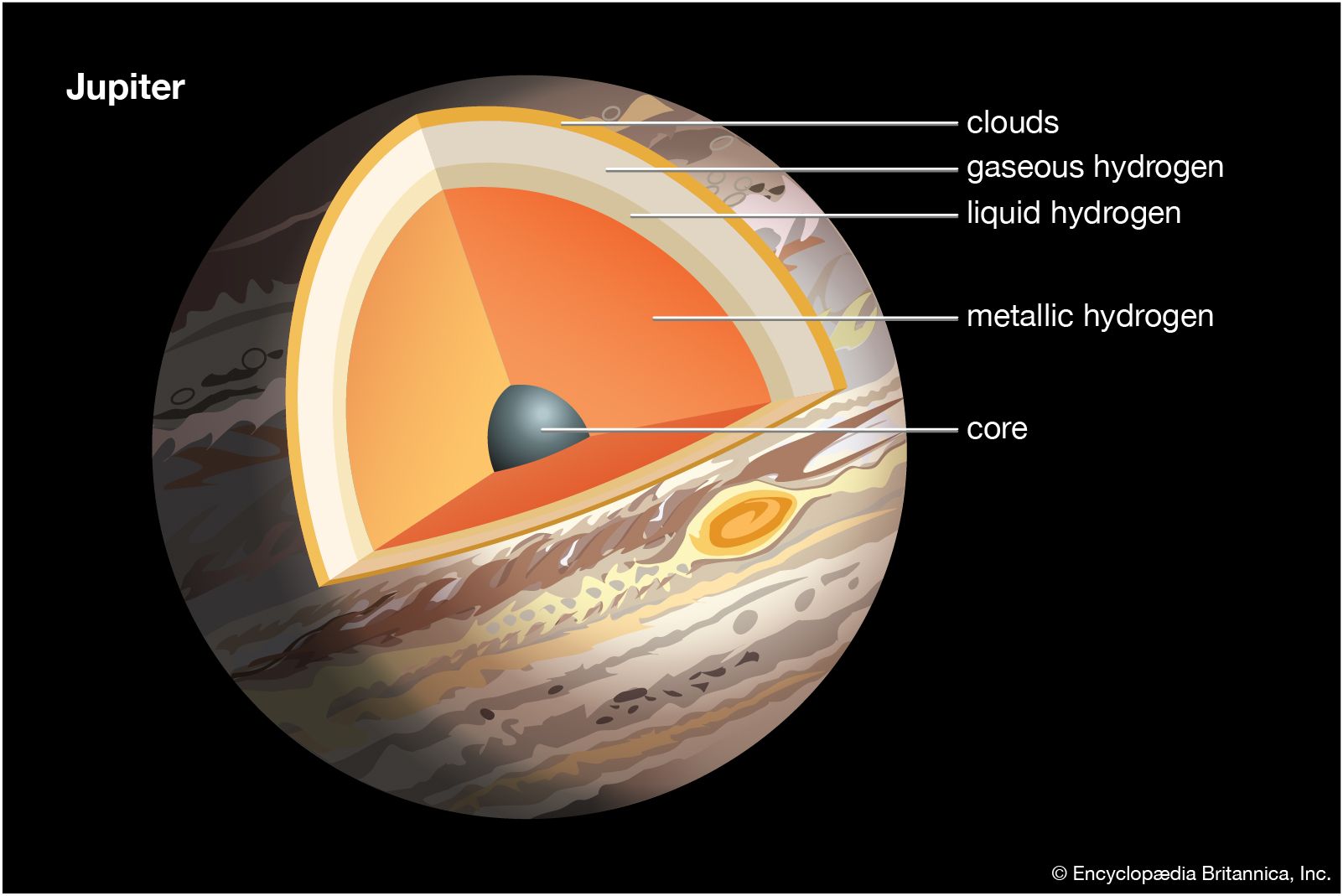
One of the key aspects of Jupiter’s gaseous nature is its thick atmosphere, primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. These gases create the planet’s distinctive bands and swirling storms, such as the famous Great Red Spot. Understanding the intricate dynamics of these gas movements can provide insights into the planet’s weather patterns and atmospheric processes.
Jupiter’s turbulent atmosphere is also responsible for its ever-changing cloud formations. These clouds are composed of various compounds, including ammonia, methane, and water vapor, which create vibrant colors and patterns on the planet’s surface. Studying the composition and behavior of these different cloud layers can help scientists understand the chemical processes occurring within Jupiter’s atmosphere.
Furthermore, investigating the internal structure of Jupiter is crucial to comprehending its gaseous nature. Scientists believe that beneath the colorful clouds lies a dense core made up of heavy elements, possibly surrounded by metallic hydrogen. Exploring the properties and behavior of these materials can provide insights into the planet’s magnetic field, its generation mechanism, and how it affects its gaseous envelope.
In recent years, space missions like Juno have greatly contributed to our understanding of Jupiter’s gaseous nature. By collecting data about its magnetic field, gravity, and atmospheric composition, these missions have shed light on the planet’s complex systems. These discoveries have not only expanded our knowledge of Jupiter but also deepened our understanding of gas giants in general, providing valuable insights into exoplanet research.
In conclusion, studying the gaseous nature of Jupiter is critical to unraveling the secrets of the largest planet in our solar system. By analyzing its atmospheric dynamics, weather patterns, and internal structure, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of not only Jupiter but also other gas giants both within and beyond our solar system.
1 MINUTE AGO: James Webb Telescope Announces A Disturbing Discovery About Betelgeuse!
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/bSdybED7RWk”/]
NASA Just Announced The Moon Shifted And Its Going To Cause Record Flooding On Earth
[arve url=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/Z61oJp6grS4″/]
Frequent questions
What evidence supports the idea that Jupiter is composed predominantly of gas?
There are several pieces of evidence that support the idea that Jupiter is composed predominantly of gas.
Firstly, spectroscopic analysis of Jupiter’s atmosphere has revealed the presence of various gases such as hydrogen and helium. These gases make up the majority of the planet’s composition.
Secondly, observations of Jupiter’s internal structure show that it lacks a solid surface. The planet gradually transitions from its gaseous outer layers to denser regions deeper within. This indicates that the planet does not possess a significant rocky or metallic core, further supporting the notion of a gas-dominated composition.
Additionally, measurements of Jupiter’s mass and density provide further evidence. The low density compared to its mass suggests that Jupiter must consist mainly of light gases rather than dense solids.
Furthermore, studies of Jupiter’s gravitational field and magnetic field offer insights into its composition. The planet’s strong magnetic field is generated by the motion of electrically conducting material within its deep interior. This suggests the presence of a metallic hydrogen layer, formed by the high pressures and temperatures deep inside Jupiter.
Overall, these lines of evidence strongly support the idea that Jupiter is predominantly composed of gas, with hydrogen and helium being the main constituents.
How do scientists determine the composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere?
Scientists determine the composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere through various methods and observations.
One of the key techniques used is spectroscopy. By analyzing the light that Jupiter’s atmosphere absorbs or emits at different wavelengths, scientists can determine the presence and abundance of various gases. Spectroscopic observations of Jupiter have revealed the existence of molecules such as hydrogen, helium, methane, ammonia, water vapor, and trace amounts of other compounds.
Another important method is direct atmospheric entry. Spacecraft, such as NASA’s Galileo probe, have been sent into Jupiter’s atmosphere to collect data on its composition. These probes carry instruments that measure the atmospheric pressure, temperature, and the types of particles present. This direct sampling provides valuable insights into the precise composition and abundances of different gases in Jupiter’s atmosphere.
Additionally, remote sensing instruments are used to study Jupiter’s atmosphere from a distance. Instruments like the Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based observatories capture images and spectra of Jupiter. These observations allow scientists to study the colors and absorption features in the atmosphere, providing crucial information about its composition.
Lastly, computer models and simulations play a significant role in determining the composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere. By inputting known data and physical principles, scientists can simulate the behavior of different gases and deduce their contributions to the overall composition of the atmosphere.
Combining these approaches allows scientists to build a comprehensive understanding of Jupiter’s atmosphere and its chemical makeup. It is worth noting that ongoing observations and advancements in technology continue to refine our knowledge of this fascinating gas giant’s composition.
What is the role of spectroscopy in identifying Jupiter as a gaseous planet?
Spectroscopy plays a crucial role in identifying Jupiter as a gaseous planet. It allows astronomers to analyze the light emitted or absorbed by Jupiter’s atmosphere, helping them determine its composition and physical properties. By separating the incoming light into its different wavelengths, spectroscopy provides valuable information about the elements present in Jupiter’s atmosphere.
Through spectroscopy, scientists have identified the presence of hydrogen and helium as the main components of Jupiter’s atmosphere. They have also discovered trace amounts of other elements such as methane, ammonia, water vapor, and various hydrocarbons. The specific patterns and intensities of light absorption or emission lines provide important clues about the temperatures, pressures, and chemical processes occurring in Jupiter’s gaseous envelope.
Furthermore, spectroscopy enables the study of Jupiter’s atmospheric dynamics, such as its cloud formations and weather patterns. By observing changes in the spectral features over time, scientists can track atmospheric phenomena such as storms, vortices, and global atmospheric circulation. This information helps build a comprehensive understanding of Jupiter’s complex meteorology.
In summary, spectroscopy plays a fundamental role in identifying Jupiter as a gaseous planet by analyzing its atmospheric composition and studying its dynamic behavior.
In conclusion, the evidence overwhelmingly supports the fact that Jupiter is indeed a gaseous planet. Through careful observations and analysis conducted by astronomers over the years, combined with data gathered from space missions such as the Galileo spacecraft, we have gained valuable insights into the composition and structure of Jupiter.
Observations of Jupiter’s atmospheric features, such as its distinct cloud bands and the Great Red Spot, provide strong indications of the planet’s gaseous nature. These features, along with the presence of storms and turbulent weather patterns, are consistent with a planet composed primarily of gas rather than solid matter.
Additionally, measurements of Jupiter’s density coupled with theoretical models have shown that its core, if it even exists, is relatively small compared to the planet’s overall size. This further supports the notion that the vast majority of Jupiter is made up of gaseous materials.
Furthermore, studies of Jupiter’s magnetic field reveal its dynamic nature, which is typical of a planet with a gaseous interior. This magnetic field, generated by the movement of electrically conducting materials deep within the planet, provides further evidence for the gaseous composition of Jupiter.
Overall, the combination of direct observations, density measurements, and magnetic field studies all point to Jupiter being predominately gaseous in nature. It is a fascinating example of a gas giant in our solar system, contributing to our understanding of planetary formation and evolution.